
Assuming an independent assortment of alleles, the expected phenotypic ratio from a dihybrid cross is
A. 1:1:1:1
B. 4:0:4:0
C. 9:3:3:1
D. 9:3:4
E. 4:2:8:2
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: The independent assortment law of Mendel states that the alleles of two or more separate genes are sorted independently of one another into gametes. In other words, for one gene, the allele a gamete receives from one gene does not influence the allele that it receives from another gene.
Complete answer:
Mendel experimented with almost 30,000 pea plants over the next several years to find out how characteristics are inherited. Mendel chose common, garden-variety pea plants for his experiments because pea plants are fast-growing and easy to raise. They also have several different visible characteristics including seed form and color, flower color, pod form and color, placement of pods and flowers on stems, and stem length. Each of these characteristics has two common traits therefore they are called dihybrid.
A Dihybrid cross is a cross involving two pairs of different characters in the same species. Plants with only yellow round seeds are generation ${F_1}$ where a cross is made between yellow-round and wrinkled green seeds (both pure line homozygous), but four forms of combinations are found in generation ${F_2}$.
Two of these variations are identical to the mixture of parents and two other new combinations, round green and wrinkled yellow, respectively.
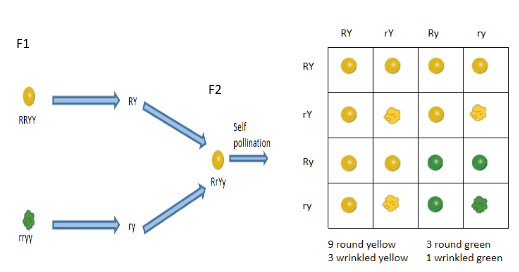
The ratio of four different combinations in the F2 progeny was:
9 (round yellow) : 3 (round green) : 3 (wrinkled yellow) : 1 (wrinkled green)
This is called phenotypic dihybrid ratio.
So, the correct answer is C i.e, '9: 3: 3: 1'.
Note: Pea plants generally do self-pollination, but Mendel was interested in heterozygous offspring in ${F_2}$ progeny for a dihybrid cross. Therefore, Mendel removed anthers of some parent i.e, ${F_1}$ plants, and pollinated them by hand with pollens of other parent plants of his choice.
Complete answer:
Mendel experimented with almost 30,000 pea plants over the next several years to find out how characteristics are inherited. Mendel chose common, garden-variety pea plants for his experiments because pea plants are fast-growing and easy to raise. They also have several different visible characteristics including seed form and color, flower color, pod form and color, placement of pods and flowers on stems, and stem length. Each of these characteristics has two common traits therefore they are called dihybrid.
A Dihybrid cross is a cross involving two pairs of different characters in the same species. Plants with only yellow round seeds are generation ${F_1}$ where a cross is made between yellow-round and wrinkled green seeds (both pure line homozygous), but four forms of combinations are found in generation ${F_2}$.
Two of these variations are identical to the mixture of parents and two other new combinations, round green and wrinkled yellow, respectively.

The ratio of four different combinations in the F2 progeny was:
9 (round yellow) : 3 (round green) : 3 (wrinkled yellow) : 1 (wrinkled green)
This is called phenotypic dihybrid ratio.
So, the correct answer is C i.e, '9: 3: 3: 1'.
Note: Pea plants generally do self-pollination, but Mendel was interested in heterozygous offspring in ${F_2}$ progeny for a dihybrid cross. Therefore, Mendel removed anthers of some parent i.e, ${F_1}$ plants, and pollinated them by hand with pollens of other parent plants of his choice.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




