
Assume that there are 6 types of nitrogen bases available and 40 types of an amino acid are available for protein synthesis, then in genetic code, each codon made up by minimum how many nitrogen codons?
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 2
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins.
The genes that encode proteins are composed of tri-nucleotide units better known as codons.
Complete answer: We have 4 types of nitrogenous bases namely, purines (Guanine and Adenine) and pyrimidines (Cytosine and Thymine) in DNA; (Cytosine and Uracil) in RNA. The genetic code is made up of 64 codons and it is a triplet and each codon codes for one amino acid in the body.
The main underlying reason for this is the fact that the anticodon loop of the tRNA molecule has sites for three codons only.
So, considering the hypothetical situation in the given question i.e. if there are 6 nitrogenous bases, even then codons have to triplet.
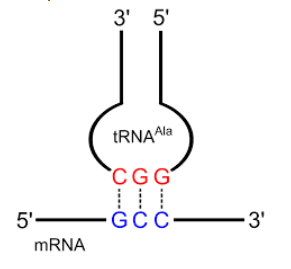
So, the correct answer is option A. 3.
Note: The genetic code is widely shared by a diverse range of organisms and it is extremely significant for the fact that it proves the common origin of modern-day organisms on Earth. It was decided by the scientist Marshall W. Nirenberg in the 1960s.
The genes that encode proteins are composed of tri-nucleotide units better known as codons.
Complete answer: We have 4 types of nitrogenous bases namely, purines (Guanine and Adenine) and pyrimidines (Cytosine and Thymine) in DNA; (Cytosine and Uracil) in RNA. The genetic code is made up of 64 codons and it is a triplet and each codon codes for one amino acid in the body.
The main underlying reason for this is the fact that the anticodon loop of the tRNA molecule has sites for three codons only.
So, considering the hypothetical situation in the given question i.e. if there are 6 nitrogenous bases, even then codons have to triplet.

So, the correct answer is option A. 3.
Note: The genetic code is widely shared by a diverse range of organisms and it is extremely significant for the fact that it proves the common origin of modern-day organisms on Earth. It was decided by the scientist Marshall W. Nirenberg in the 1960s.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




