
Assertion:
The IUPAC name of citric acid is \[2 - hydroxy - propane - 1,2,3 - tricarboxylic acid\].
Reason:
When an unbranched C atom is directly linked to more than two like-functional groups, then it is named as a derivative of the parent alkane which does not include the C atoms of the functional groups.
a.) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
b.) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
c.) Assertion is correct but the Reason is incorrect.
d.) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: I To answer this question, we will have to first recall the rules of IUPAC nomenclature for organic compounds. We must also first draw the structure of citric acid for better understanding.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of citric acid is:
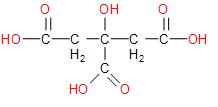
Let us now look at the rules involved in the nomenclature of carboxylic acids.
We should remember that carboxylic acid is given the highest priority order among all functional groups. Hence, they are almost always the main suffix. Systematic names of carboxylic acids are always written using the suffix ‘oic acid’ or ‘carboxylic acid’ or the prefix ‘carboxy’.
Further if an unbranched chain is linked to two or more carboxyl groups, all carboxyl groups are named from the parent hydride by substituting the use of the suffix ‘carboxylic acid’, preceded by the appropriate numerical prefix ‘tri’, ‘tetra’ etc. and appropriate locants.
Therefore the naming of Citric acid as \[2 - hydroxy - propane - 1,2,3 - tricarboxylic acid\] is correct and in accordance with the rule mentioned above. This also corresponds with the reasoning when an unbranched C atom is directly linked to more than two like-functional groups, then it is named as a derivative of the parent alkane which does not include the C atoms of the functional groups.
Hence, the correct answer is Option (A) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
Note:
We can be assured that since the IUPAC nomenclature of Citric acid is a bit cumbersome, the informal name ‘Citric acid’ is also accepted in scientific documents and is retained for IUPAC as general nomenclature.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of citric acid is:

Let us now look at the rules involved in the nomenclature of carboxylic acids.
We should remember that carboxylic acid is given the highest priority order among all functional groups. Hence, they are almost always the main suffix. Systematic names of carboxylic acids are always written using the suffix ‘oic acid’ or ‘carboxylic acid’ or the prefix ‘carboxy’.
Further if an unbranched chain is linked to two or more carboxyl groups, all carboxyl groups are named from the parent hydride by substituting the use of the suffix ‘carboxylic acid’, preceded by the appropriate numerical prefix ‘tri’, ‘tetra’ etc. and appropriate locants.
Therefore the naming of Citric acid as \[2 - hydroxy - propane - 1,2,3 - tricarboxylic acid\] is correct and in accordance with the rule mentioned above. This also corresponds with the reasoning when an unbranched C atom is directly linked to more than two like-functional groups, then it is named as a derivative of the parent alkane which does not include the C atoms of the functional groups.
Hence, the correct answer is Option (A) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
Note:
We can be assured that since the IUPAC nomenclature of Citric acid is a bit cumbersome, the informal name ‘Citric acid’ is also accepted in scientific documents and is retained for IUPAC as general nomenclature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




