
Assertion: Presence of a nitro group at ortho or para position increases the reactivity of haloarenes towards nucleophilic substitution.
Reason: Nitro group, being an electron withdrawing group decreases the electron density over the benzene ring.
A) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
B) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
C) Assertion is wrong but reason is the correct statement.
D) Assertion is correct but reason is wrong statement.
Answer
529.5k+ views
Hint:This can be explained by the Mesomeric effect. Mesomeric effect is a property of substituents or functional groups attached to an organic compound that either withdraw or donate electrons into the main chain or in this case benzene ring.
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to the Mesomeric effect, substituents or functional groups that donate electrons into the benzene ring are known as $ + M$ effect groups and the substituents that withdraw electrons from the benzene ring are called $ - M$ effect groups.
It is usually favored that $ + M$ effect groups are attached at the ortho and para positions of the benzene ring and $ - M$ effect groups at the meta position for the stability of the compound.
When a $ - M$ group is attached at ortho or para positions of the benzene ring, its reactivity increases.
Let us write down the given compound as follows:
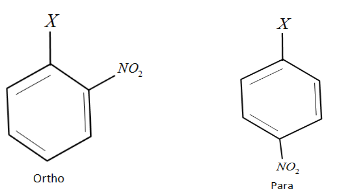
Here X is a halogen.
When a $ - M$ effect group such as $N{O_2}$ is attached at the ortho or para positions of the benzene ring, they reduce the electron density at the reactive center of the benzene ring i.e. the halogen position. This accounts for the high reactivity of haloarenes when the nitro group is attached to its ortho or para positions.
Therefore, the right answer is option A.
Note: The substituent given to us is $N{O_2}$ which is a strong $ - M$ effect group or withdrawing group. This group takes up electrons from the benzene ring to stabilize its Nitrogen and Oxygen atoms. This inturn reduces the electron density inside the benzene ring making it more reactive.
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to the Mesomeric effect, substituents or functional groups that donate electrons into the benzene ring are known as $ + M$ effect groups and the substituents that withdraw electrons from the benzene ring are called $ - M$ effect groups.
It is usually favored that $ + M$ effect groups are attached at the ortho and para positions of the benzene ring and $ - M$ effect groups at the meta position for the stability of the compound.
When a $ - M$ group is attached at ortho or para positions of the benzene ring, its reactivity increases.
Let us write down the given compound as follows:

Here X is a halogen.
When a $ - M$ effect group such as $N{O_2}$ is attached at the ortho or para positions of the benzene ring, they reduce the electron density at the reactive center of the benzene ring i.e. the halogen position. This accounts for the high reactivity of haloarenes when the nitro group is attached to its ortho or para positions.
Therefore, the right answer is option A.
Note: The substituent given to us is $N{O_2}$ which is a strong $ - M$ effect group or withdrawing group. This group takes up electrons from the benzene ring to stabilize its Nitrogen and Oxygen atoms. This inturn reduces the electron density inside the benzene ring making it more reactive.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




