
Assertion: Pili are tubular structures present in bacteria that help in conjugation.
Reason: Formation of pili is controlled by F+ or fertility factor.
A) Both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
B) Both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
C) Assertion is true but the reason is false
D) Both assertion and reason are false
Answer
507.6k+ views
Hint: Pili are thread-like structures present in many bacteria and Archaebacteria. It is made up of the protein pilin. The pili help in the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another and also in surface attachment.
Complete answer:
Conjugation is the process of the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another. The process of conjugation takes place through direct contact. One bacterium serves as a donor and the other as the recipient. This is the type of sexual reproduction. This does not take place for all bacterium and can also take place between the bacterium of different species. The donor bacterium carries a sequence of DNA which is known as the F factor.
During conjugation, both the bacterium comes close to each other. This triggers the formation of a mating bridge. The DNA transfers from one bacterium to another through this bridge. This DNA contains the genes which help in making and transfer pili. The pili elongate and form the conjugation tube and also attaches to the recipient as shown in the diagram below.
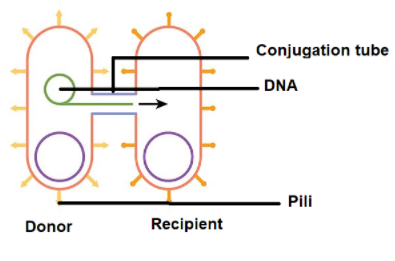
The fertility factor F+ is a plasmid that is transferred from the donor to the recipient. The one that contains F=factor is considered as a donor. They also signal for the proteins which help in the attachment of the pili to the recipient.
Thus the correct answer is option ‘A’.
Note: The pili are antigens. They are fragile and are changed continuously. At times they get altered with the different composition which all together changes the antigenicity of the pili.
Complete answer:
Conjugation is the process of the transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another. The process of conjugation takes place through direct contact. One bacterium serves as a donor and the other as the recipient. This is the type of sexual reproduction. This does not take place for all bacterium and can also take place between the bacterium of different species. The donor bacterium carries a sequence of DNA which is known as the F factor.
During conjugation, both the bacterium comes close to each other. This triggers the formation of a mating bridge. The DNA transfers from one bacterium to another through this bridge. This DNA contains the genes which help in making and transfer pili. The pili elongate and form the conjugation tube and also attaches to the recipient as shown in the diagram below.

The fertility factor F+ is a plasmid that is transferred from the donor to the recipient. The one that contains F=factor is considered as a donor. They also signal for the proteins which help in the attachment of the pili to the recipient.
Thus the correct answer is option ‘A’.
Note: The pili are antigens. They are fragile and are changed continuously. At times they get altered with the different composition which all together changes the antigenicity of the pili.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




