
Assertion: Phase is negative for a purely capacitive circuit.
Reason: In the capacitive circuit, the current leads the voltage.
A. Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
B. Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion
C. Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
D. Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: We know that an AC circuit has input voltage and current, in the sinusoidal form. Thus there are 3 possible relationships between voltage and current in the circuit. 1. Voltage lags current or current leads voltage, 2. Voltage leads current or current lags voltage and 3. Voltage and current are in the same phase.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the source of an AC circuit is sinusoidal. Then there is a phase difference between the voltage and current. If the phase difference between the current and voltage is zero, then both are said to be in phase, and if the phase difference is not equal to zero, then both are said to be out of phase.
In a purely capacitive circuit, the voltage and the current in the circuit are out of phase by $90^{\circ}$, the product of the voltage and current, which is the active power of the circuit is either negative or positive. If the average power is taken, then we get $0$. This is because, for one half of the cycle, the voltage and current are positive
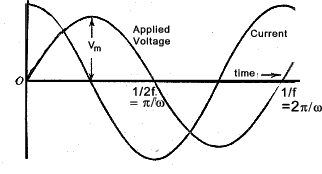
Thus, we can say that in a purely capacitive circuit, there is a phase difference of $90^{\circ}$, where current leads voltage.
Hence, we can conclude that the answer is option B. Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion
Note:
In a purely capacitive circuit, there is some energy which is stored in the capacitor as an electric field in one quarter cycle. In the next quarter, this energy is dissipated to the source again. This process continues till the source supplies to the capacitor. Hence the capacitor does not consume any power.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the source of an AC circuit is sinusoidal. Then there is a phase difference between the voltage and current. If the phase difference between the current and voltage is zero, then both are said to be in phase, and if the phase difference is not equal to zero, then both are said to be out of phase.
In a purely capacitive circuit, the voltage and the current in the circuit are out of phase by $90^{\circ}$, the product of the voltage and current, which is the active power of the circuit is either negative or positive. If the average power is taken, then we get $0$. This is because, for one half of the cycle, the voltage and current are positive

Thus, we can say that in a purely capacitive circuit, there is a phase difference of $90^{\circ}$, where current leads voltage.
Hence, we can conclude that the answer is option B. Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion
Note:
In a purely capacitive circuit, there is some energy which is stored in the capacitor as an electric field in one quarter cycle. In the next quarter, this energy is dissipated to the source again. This process continues till the source supplies to the capacitor. Hence the capacitor does not consume any power.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




