
Assertion: $k = A{e^{\left( {\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{{RT}}} \right)}}$, the Arrhenius equation represents the dependence of rate constant with temperature.
Reason: The plot of $\log k$ against $\dfrac{1}{T}$ is linear and the activation energy can be calculated with this plot.
A. Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion.
B. Both assertion and reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation for assertion.
C. Assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect.
D. Assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct.
Answer
511.8k+ views
Hint: The rate of reaction for a chemical reaction is a measure of change in concentration of reactants or the change in concentration of the products per unit time. The proportionality constant in the expression of rate of reaction is known as rate constant which is represented by k and it generally increases with rise in temperature.
Complete answer:
The overall rate of reaction depends on certain factors which are as follows:
1. The frequency with which the molecules are colliding during a chemical reaction.
2. The fraction of collisions with the minimum amount of energy which is needed to react.
3. The orientation i.e., the steric factor of the colliding molecules.
Molecules in a chemical reaction react only when they collide with each other in proper orientation. Increasing the temperature increases the energy and due to which the frequency of molecular collisions also increases.
The Arrhenius equation relates all the factors with the rate constant with the help of an expression which is as follows:
$k = A{e^{\left( {\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{{RT}}} \right)}}\;\; - (1)$
Where, k is the rate constant, A is the pre-exponential factor, ${E_a}$ is the activation energy, R is the universal gas constant and T is temperature in kelvin.
Taking natural log on both sides of equation (1):
$ \Rightarrow \ln k = \ln A{e^{\left( {\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{{RT}}} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \ln k = \ln A + \ln {e^{\left( {\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{{RT}}} \right)}}\;\;\;\;\;\;[\because \ln ab = \ln a + \ln b]$
$ \Rightarrow \ln k = \ln A - \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{RT}}\;\;\;\;\;\;[\because \ln {e^a} = a]$
Converting natural log into base 10 as follows:
\[ \Rightarrow 2.303\log k = 2.303\log A - \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{RT}}\;\;\;\;\;\;[\because \ln a = 2.303\log a]\]
\[ \Rightarrow \log k = \log A - \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303R}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{T}} \right)\;\]
The equation represents the general equation of a straight line of type $y = mx + c$, where $\log A$ is the intercept and $\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{{2.303R}}$ is the slope. Hence, the plot of $\log k$ against $\dfrac{1}{T}$ is linear and can be represented as follows:
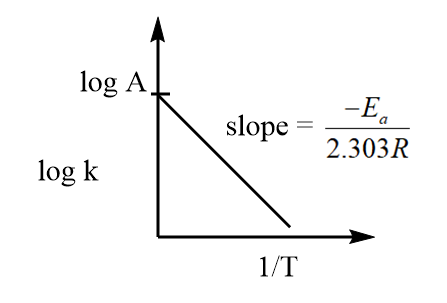
From the curve, it is clear that on changing the value of temperature, a change in rate constant is also observed i.e., the rate constant depends on temperature and by knowing the value of slope of the curve, we can determine the value of activation energy.
Thus, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that the value of rate constant increases on increasing temperature whereas decreases on increasing the value of activation energy. So, to increase the rate of reaction there are two possible methods, first is to increase the temperature of the reaction and second is to add a catalyst to decrease the activation energy which will lead to increase the rate of reaction.
Complete answer:
The overall rate of reaction depends on certain factors which are as follows:
1. The frequency with which the molecules are colliding during a chemical reaction.
2. The fraction of collisions with the minimum amount of energy which is needed to react.
3. The orientation i.e., the steric factor of the colliding molecules.
Molecules in a chemical reaction react only when they collide with each other in proper orientation. Increasing the temperature increases the energy and due to which the frequency of molecular collisions also increases.
The Arrhenius equation relates all the factors with the rate constant with the help of an expression which is as follows:
$k = A{e^{\left( {\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{{RT}}} \right)}}\;\; - (1)$
Where, k is the rate constant, A is the pre-exponential factor, ${E_a}$ is the activation energy, R is the universal gas constant and T is temperature in kelvin.
Taking natural log on both sides of equation (1):
$ \Rightarrow \ln k = \ln A{e^{\left( {\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{{RT}}} \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow \ln k = \ln A + \ln {e^{\left( {\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{{RT}}} \right)}}\;\;\;\;\;\;[\because \ln ab = \ln a + \ln b]$
$ \Rightarrow \ln k = \ln A - \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{RT}}\;\;\;\;\;\;[\because \ln {e^a} = a]$
Converting natural log into base 10 as follows:
\[ \Rightarrow 2.303\log k = 2.303\log A - \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{RT}}\;\;\;\;\;\;[\because \ln a = 2.303\log a]\]
\[ \Rightarrow \log k = \log A - \dfrac{{{E_a}}}{{2.303R}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{T}} \right)\;\]
The equation represents the general equation of a straight line of type $y = mx + c$, where $\log A$ is the intercept and $\dfrac{{ - {E_a}}}{{2.303R}}$ is the slope. Hence, the plot of $\log k$ against $\dfrac{1}{T}$ is linear and can be represented as follows:

From the curve, it is clear that on changing the value of temperature, a change in rate constant is also observed i.e., the rate constant depends on temperature and by knowing the value of slope of the curve, we can determine the value of activation energy.
Thus, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note:
It is important to note that the value of rate constant increases on increasing temperature whereas decreases on increasing the value of activation energy. So, to increase the rate of reaction there are two possible methods, first is to increase the temperature of the reaction and second is to add a catalyst to decrease the activation energy which will lead to increase the rate of reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




