
Assertion: Isopropyl chloride is a secondary alkyl halide.
Reason: chlorine is present on secondary carbon.
A.Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation to A.
B.Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation to A.
C.A is true but R is false.
D.A is false but R is true.
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint:Isopropyl chloride is the organic compound having the chemical formula ${(C{H_3})_2}CHCl$. It is a colorless and flammable liquid and is used as an industrial solvent.An alkyl halide is said to be secondary if the holgen is bonded to a secondary carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
The IUPAC name of isopropyl chloride is 2-chloropropane. According to IUPAC name, the structure of isopropyl chloride or 2-chloropropane is given as:
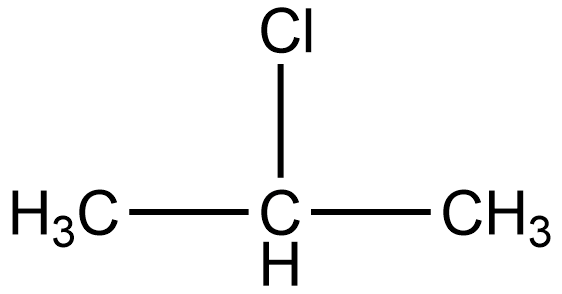
As we know the secondary halides are those in which the halogen group is attached to that carbon which is linked to two alkyl groups. In the structure of 2-chloropropane, we can see chlorine is attached to secondary carbon i.e. the carbon which is linked to two alkyls (methyl) groups.
Hence we can say here both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion also.
So the correct answer is option A.
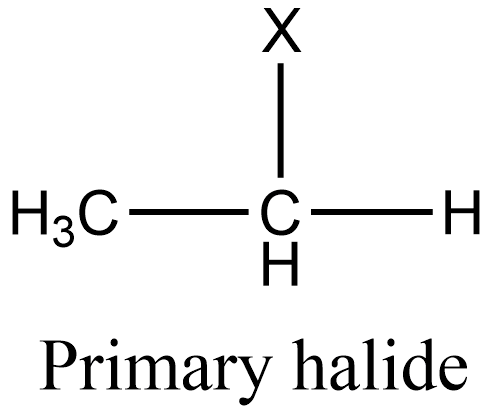
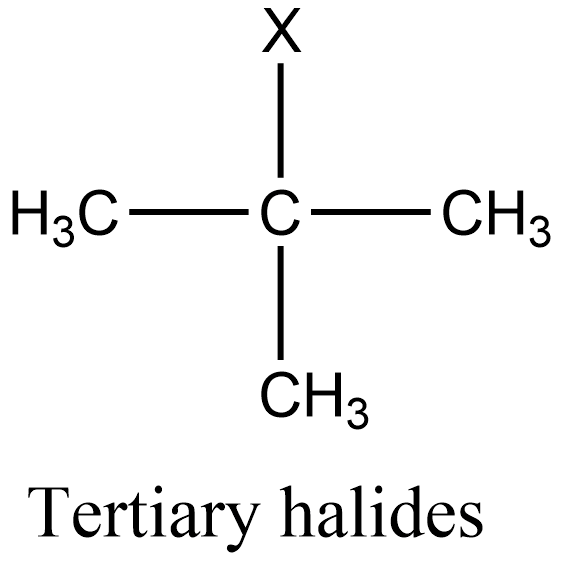
Additional information: Similarly to secondary halides, primary halides are those in which the halogen group is attached to that carbon which is linked to one alkyl group. And tertiary halides are those in which the halogen group is attached to that carbon which is linked to three alkyl groups. The general structure of primary and tertiary halides is given as:
Note:
Isopropyl chloride is a versatile solvent. It is less soluble in water. The odour of isopropyl alcohol resembles the odour of chloroform. The vapour of isopropyl alcohol is heavier than air vapour but less dense than the vapour of water. It is used for the preparation of other chemicals. it may irritate skin and eyes also. At high concentrations, it is narcotic.
Complete step by step answer:
The IUPAC name of isopropyl chloride is 2-chloropropane. According to IUPAC name, the structure of isopropyl chloride or 2-chloropropane is given as:

As we know the secondary halides are those in which the halogen group is attached to that carbon which is linked to two alkyl groups. In the structure of 2-chloropropane, we can see chlorine is attached to secondary carbon i.e. the carbon which is linked to two alkyls (methyl) groups.
Hence we can say here both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion also.
So the correct answer is option A.
Additional information: Similarly to secondary halides, primary halides are those in which the halogen group is attached to that carbon which is linked to one alkyl group. And tertiary halides are those in which the halogen group is attached to that carbon which is linked to three alkyl groups. The general structure of primary and tertiary halides is given as:


Note:
Isopropyl chloride is a versatile solvent. It is less soluble in water. The odour of isopropyl alcohol resembles the odour of chloroform. The vapour of isopropyl alcohol is heavier than air vapour but less dense than the vapour of water. It is used for the preparation of other chemicals. it may irritate skin and eyes also. At high concentrations, it is narcotic.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




