
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their basic strength:
${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}},{{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{2}}NH,{{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{3}}N,{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$
Answer
597.6k+ views
Hint: Basic strength depends on various factors like inductive effect, steric hindrance, resonance effect. In aqueous medium basic strength is affected by solvation effect and in gaseous medium it is affected by inductive effect.
Complete step by step solution:
The basic strength of amines can be easily determined by the availability of lone pairs.
In ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$, the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen is delocalised over the benzene ring due to the –R effect of the benzene ring.
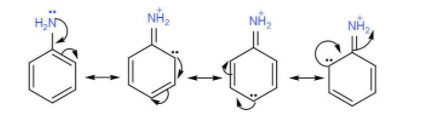
Aniline here is resonance stabilised and due to this charge delocalisation, it becomes a weak base.
Among ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}},{{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{2}}NHand{{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{3}}N$, we can predict the most basic compound by the inductive effect. It is caused due to the presence of alkyl groups which have a +I effect as they tend to donate the electron density making the compound more basic.
In the gas phase there is no solvation so the basic strength depends upon inductive effect. Higher the +I effect, higher is the basicity. The inductive effect is directly proportional to the number of alkyl groups present I.e.
Higher the number of alkyl groups present, higher will be the inductive effect caused by them and higher is the basicity.
Therefore, ${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{3}}N$ is most basic, as it has 3 alkyl groups present, causing more inductive effect therefore he nitrogen will become more electronegative hence accept proton readily.
${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{3}}N$ is the most basic followed by ${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{2}}NH$ and ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$.
Therefore, the increasing order of basicity will be-
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$<${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$<${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{2}}NH$<${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{3}}N$
However, in aqueous phase, the strength of amines depends on two factors- availability of lone pairs and strength of the conjugate acid of the amine.
The conjugate acid is stabilized by a solvation effect. More the number of water molecules solvating the amine, more is the stability of base. With increase in the number of alkyl groups, the conjugate becomes less stable as these groups hinder the water molecules to come and stabilize the molecule. However, according to this, the primary amine should be most stable but it is not as basicity also depends on +I effect. In${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{3}}N$, there is steric hindrance which decreases the solvation effect and in ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$, there is only one ethyl group which will have a lower +I.
Therefore, in aqueous medium, the basicity order is-
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$<${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{3}}N$<${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$<${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{2}}NH$
Note: It is important to remember that the basic strength is affected by the same factor as that of acidic strength as both are interdependent. Factors like electron affinity affects how strongly the compound will attract the proton and hence affects the basicity. It is also important to note here that resonance stabilised amines are weak bases because they gain stability through resonance and will not want to lose by accepting a proton.
Complete step by step solution:
The basic strength of amines can be easily determined by the availability of lone pairs.
In ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$, the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen is delocalised over the benzene ring due to the –R effect of the benzene ring.

Aniline here is resonance stabilised and due to this charge delocalisation, it becomes a weak base.
Among ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}},{{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{2}}NHand{{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{3}}N$, we can predict the most basic compound by the inductive effect. It is caused due to the presence of alkyl groups which have a +I effect as they tend to donate the electron density making the compound more basic.
In the gas phase there is no solvation so the basic strength depends upon inductive effect. Higher the +I effect, higher is the basicity. The inductive effect is directly proportional to the number of alkyl groups present I.e.
Higher the number of alkyl groups present, higher will be the inductive effect caused by them and higher is the basicity.
Therefore, ${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{3}}N$ is most basic, as it has 3 alkyl groups present, causing more inductive effect therefore he nitrogen will become more electronegative hence accept proton readily.
${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{3}}N$ is the most basic followed by ${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{2}}NH$ and ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$.
Therefore, the increasing order of basicity will be-
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$<${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$<${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{2}}NH$<${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{3}}N$
However, in aqueous phase, the strength of amines depends on two factors- availability of lone pairs and strength of the conjugate acid of the amine.
The conjugate acid is stabilized by a solvation effect. More the number of water molecules solvating the amine, more is the stability of base. With increase in the number of alkyl groups, the conjugate becomes less stable as these groups hinder the water molecules to come and stabilize the molecule. However, according to this, the primary amine should be most stable but it is not as basicity also depends on +I effect. In${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{3}}N$, there is steric hindrance which decreases the solvation effect and in ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$, there is only one ethyl group which will have a lower +I.
Therefore, in aqueous medium, the basicity order is-
${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$<${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{3}}N$<${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}N{{H}_{2}}$<${{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{2}}NH$
Note: It is important to remember that the basic strength is affected by the same factor as that of acidic strength as both are interdependent. Factors like electron affinity affects how strongly the compound will attract the proton and hence affects the basicity. It is also important to note here that resonance stabilised amines are weak bases because they gain stability through resonance and will not want to lose by accepting a proton.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




