
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their acidic strength:
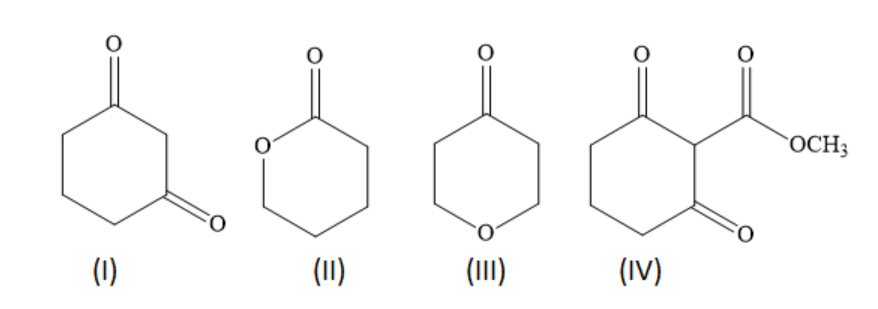
A ) III < I < IV < II
B ) II < I < IV < III
C ) I < III < IV < II
D ) II < III < I < IV

Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Determine the nature and number of different types of substituents. Here, type of substituent refers to its electron donating nature or electron withdrawing nature. Identify the inductive effect and resonance effect present.
Complete step by step answer:
Electron withdrawing groups show -I effect and electron releasing groups show +I effect. Here, ‘I’ represents an inductive effect. When electron withdrawing groups are present, the acid strength increases and when electron donating groups are present, the acid strength decreases. With increase in the number of electron withdrawing groups, the acid strength increases. With increase in the strength of -I effect of electron withdrawing groups, the acid strength increases.
Compound IV is most acidic among the given compounds. Because, the tertiary carbon atom has three strong electron withdrawing, carbonyl groups. When this tertiary carbon atom loses an electron, it forms a carbanion in which the negative charge is delocalised through resonance with three carbonyl groups. Greater is the resonance, greater is the stabilisation of the carbanion and greater is the acid strength.
After compound IV, the compound I is most acidic among the given compounds. Because, one of the secondary carbon atoms has two strong electron withdrawing, carbonyl groups. When this carbon atom loses an electron, it forms a carbanion in which the negative charge is delocalised through resonance with two carbonyl groups. Greater is the resonance, greater is the stabilisation of the carbanion and greater is the acid strength.
Among the compounds II and III, the more acidic compound is compound III as it has -I effect of carbonyl group and ether group. However in compound II, the ether group is far away, so it exerts less of -I effect.
Hence, the option D ) II < III < I < IV is the correct answer.
Note:
A strong acid can easily donate a proton. The carbanion obtained by donation of a proton is stabilised due to inductive and resonance effects. Greater is the stabilisation of the carbanion through inductive and resonance effects, greater is the acid strength of the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
Electron withdrawing groups show -I effect and electron releasing groups show +I effect. Here, ‘I’ represents an inductive effect. When electron withdrawing groups are present, the acid strength increases and when electron donating groups are present, the acid strength decreases. With increase in the number of electron withdrawing groups, the acid strength increases. With increase in the strength of -I effect of electron withdrawing groups, the acid strength increases.
Compound IV is most acidic among the given compounds. Because, the tertiary carbon atom has three strong electron withdrawing, carbonyl groups. When this tertiary carbon atom loses an electron, it forms a carbanion in which the negative charge is delocalised through resonance with three carbonyl groups. Greater is the resonance, greater is the stabilisation of the carbanion and greater is the acid strength.
After compound IV, the compound I is most acidic among the given compounds. Because, one of the secondary carbon atoms has two strong electron withdrawing, carbonyl groups. When this carbon atom loses an electron, it forms a carbanion in which the negative charge is delocalised through resonance with two carbonyl groups. Greater is the resonance, greater is the stabilisation of the carbanion and greater is the acid strength.
Among the compounds II and III, the more acidic compound is compound III as it has -I effect of carbonyl group and ether group. However in compound II, the ether group is far away, so it exerts less of -I effect.
Hence, the option D ) II < III < I < IV is the correct answer.
Note:
A strong acid can easily donate a proton. The carbanion obtained by donation of a proton is stabilised due to inductive and resonance effects. Greater is the stabilisation of the carbanion through inductive and resonance effects, greater is the acid strength of the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




