
Arrange the bond angle order of $ N{O_2},N{O_{_2}}^ - ,N{O_2}^ + {\text{ and }}N{O_3}^ - $ in descending order.
Answer
509.7k+ views
Hint :On adding or removing electrons from the nitrogen oxides their bond angles get significantly affected because the bond angles depend upon hybridization of the central atom (nitrogen in this case) as well as the presence of lone pairs or unpaired electron on the atom.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Bond angle is the angle formed by the three orbitals that overlap to form two adjacent bonds.
All the nitrogen oxides and corresponding ions consist of only two types of atoms namely nitrogen and oxygen. Nitrogen has a total of five electrons in its outermost shell and oxygen has a total of six electrons in its outermost shell. The hybridization and geometries of nitrogen oxides can be explained as follows:
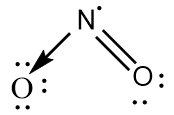
$ N{O_2} $ : The central atom is $ s{p^2} $ hybridized with one nitrogen-oxygen double bond and one coordinate covalent bond. One unpaired electron is present on the nitrogen atom. The bond angle is greater than $ {120^ \circ } $ and the geometry is bent.
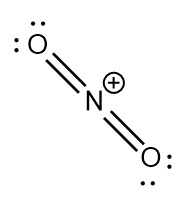
$ N{O_2}^ + $ : The central atom is $ sp $ hybridized with two nitrogen-oxygen double bonds. Due to the positive charge there is no unpaired electron on the nitrogen atom. The bond angle is exactly $ {180^ \circ } $ and the molecule is linear.
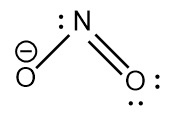
$ N{O_{_2}}^ - $ : The central atom is $ s{p^2} $ hybridized with one nitrogen-oxygen double bond and one coordinate covalent bond. Due to the negative charge there is a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. The bond angle is lesser than $ {120^ \circ } $ and the geometry is bent.
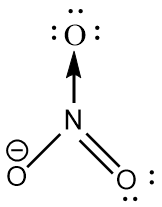
$ N{O_3}^ - $ : The central atom is $ s{p^2} $ hybridized with one nitrogen-oxygen double bond, one nitrogen-oxygen single bond and one coordinate covalent bond. The negative charge is on oxygen. The bond angle is exactly $ {120^ \circ } $ and the molecule has trigonal planar geometry.
Hence the descending order of bond angles is as follows:
$ N{O_2}^ + > N{O_2} > N{O_3}^ - > N{O_{_2}}^ - $
Note :
Nitrogen cannot extend its valency up to five due to the absence of vacant d-orbitals. Oxygen on the other hand can form a total of two covalent bonds or complete its octet by accepting a pair of electrons through a coordinate covalent donation.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Bond angle is the angle formed by the three orbitals that overlap to form two adjacent bonds.
All the nitrogen oxides and corresponding ions consist of only two types of atoms namely nitrogen and oxygen. Nitrogen has a total of five electrons in its outermost shell and oxygen has a total of six electrons in its outermost shell. The hybridization and geometries of nitrogen oxides can be explained as follows:
$ N{O_2} $ : The central atom is $ s{p^2} $ hybridized with one nitrogen-oxygen double bond and one coordinate covalent bond. One unpaired electron is present on the nitrogen atom. The bond angle is greater than $ {120^ \circ } $ and the geometry is bent.

$ N{O_2}^ + $ : The central atom is $ sp $ hybridized with two nitrogen-oxygen double bonds. Due to the positive charge there is no unpaired electron on the nitrogen atom. The bond angle is exactly $ {180^ \circ } $ and the molecule is linear.

$ N{O_{_2}}^ - $ : The central atom is $ s{p^2} $ hybridized with one nitrogen-oxygen double bond and one coordinate covalent bond. Due to the negative charge there is a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. The bond angle is lesser than $ {120^ \circ } $ and the geometry is bent.

$ N{O_3}^ - $ : The central atom is $ s{p^2} $ hybridized with one nitrogen-oxygen double bond, one nitrogen-oxygen single bond and one coordinate covalent bond. The negative charge is on oxygen. The bond angle is exactly $ {120^ \circ } $ and the molecule has trigonal planar geometry.

Hence the descending order of bond angles is as follows:
$ N{O_2}^ + > N{O_2} > N{O_3}^ - > N{O_{_2}}^ - $
Note :
Nitrogen cannot extend its valency up to five due to the absence of vacant d-orbitals. Oxygen on the other hand can form a total of two covalent bonds or complete its octet by accepting a pair of electrons through a coordinate covalent donation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




