
Arrange following compounds in their acidic strength order:
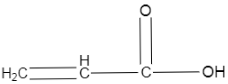
($I$)
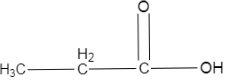
$(II)$
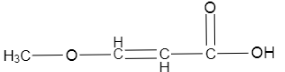
$(III)$



Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint:In organic compounds, the strength of acids can be easily determined by making their conjugate bases. If the conjugate bases are stable, then the acidic strength will be higher.
There are various ways by which the conjugate base could gain stability, one of them is a double bond on the adjacent carbon, as it will get involved in resonance with the conjugate base, making the electrons more degenerate.
Complete step-by-step answer:In order to comment on the acidic strength of any structure or a compound, we need to know what acids are, by definition. We will use the definition of acids which is based in terms of proton release, in this question. Acids can be defined as the species which readily liberate their proton in the solution, in order to form a stable conjugate base. Now, in order to understand the concept of conjugate base, we will consider an example. Suppose we have an acid, hydrochloric acid, the conjugate base would be the part which is left after we remove the proton from it, meaning, the corresponding conjugate base of hydrochloric acid is chloride ion.
Now, consider the options given in the question, it shows three of the structures having a common group which is carboxylic acid. Since, it is common in all three of them we cannot compare their acidic strength on the basis of carboxylic acid only. So, we will look for the other criterias which may affect the acidic strength in all three of them.
In the first option we can see that a double bond is present in the adjacent carbon of the carboxylic acid, which will help stabilise the conjugate base of this structure, by the use of resonance.
In the second option, the carboxylic acid is present on a simple ethane, without any substituents. So, it will be less acidic than the first one, obviously because it doesn’t have anything to stabilize the conjugate base. Also, alkyl groups are electron donating, which contributes to the lesser acidic strength of this structure.
Now, in the last one we can see that a methoxy group is attached at the other end of the carbon chain and also a double bond is present on the carbon which is adjacent to carboxylic acid. Now, we know that electron withdrawing groups increase the acidic strength of a structure. Since, the methoxy group is electron withdrawing, it is safe to say that it will also contribute to higher acidic strength of the structure.
So, the order of acidic strength becomes $III$ $>$ $I$ $>$ $II$.
Note:The acidic strength of compounds containing carboxylic acid depends on the nature of substituent, meaning, if it is attached to an electron withdrawing group, the acidic strength will increase and vice versa.
It also depends on the stability of the conjugate base, in other words, the more stable the conjugate base is, the more acidic the corresponding acid will be.
There are various ways by which the conjugate base could gain stability, one of them is a double bond on the adjacent carbon, as it will get involved in resonance with the conjugate base, making the electrons more degenerate.
Complete step-by-step answer:In order to comment on the acidic strength of any structure or a compound, we need to know what acids are, by definition. We will use the definition of acids which is based in terms of proton release, in this question. Acids can be defined as the species which readily liberate their proton in the solution, in order to form a stable conjugate base. Now, in order to understand the concept of conjugate base, we will consider an example. Suppose we have an acid, hydrochloric acid, the conjugate base would be the part which is left after we remove the proton from it, meaning, the corresponding conjugate base of hydrochloric acid is chloride ion.
Now, consider the options given in the question, it shows three of the structures having a common group which is carboxylic acid. Since, it is common in all three of them we cannot compare their acidic strength on the basis of carboxylic acid only. So, we will look for the other criterias which may affect the acidic strength in all three of them.
In the first option we can see that a double bond is present in the adjacent carbon of the carboxylic acid, which will help stabilise the conjugate base of this structure, by the use of resonance.
In the second option, the carboxylic acid is present on a simple ethane, without any substituents. So, it will be less acidic than the first one, obviously because it doesn’t have anything to stabilize the conjugate base. Also, alkyl groups are electron donating, which contributes to the lesser acidic strength of this structure.
Now, in the last one we can see that a methoxy group is attached at the other end of the carbon chain and also a double bond is present on the carbon which is adjacent to carboxylic acid. Now, we know that electron withdrawing groups increase the acidic strength of a structure. Since, the methoxy group is electron withdrawing, it is safe to say that it will also contribute to higher acidic strength of the structure.
So, the order of acidic strength becomes $III$ $>$ $I$ $>$ $II$.
Note:The acidic strength of compounds containing carboxylic acid depends on the nature of substituent, meaning, if it is attached to an electron withdrawing group, the acidic strength will increase and vice versa.
It also depends on the stability of the conjugate base, in other words, the more stable the conjugate base is, the more acidic the corresponding acid will be.
Recently Updated Pages
Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

The coating formed on the metals such as iron silver class 12 chemistry CBSE

Metals are refined by using different methods Which class 12 chemistry CBSE

What do you understand by denaturation of proteins class 12 chemistry CBSE

Assertion Nitrobenzene is used as a solvent in FriedelCrafts class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




