
Aromatic aldehydes are less reactive than aliphatic aldehydes in nucleophilic addition reaction. Give reason.
Answer
532.2k+ views
Hint: To solve this question we have to use the concept of resonance effect to show why aromatic aldehydes are less reactive to nucleophiles than aliphatic aldehydes. This happens due to the electron donating resonance effect that is called the +R effect. This increases the electron density and repels nucleophiles.
Complete answer:
From your chemistry lessons you have learned about the resonance effect. Resonance effect is defined as the polarity produced in the molecule due to the interaction between the pi bond and the lone pair of electrons or it can also be produced due to the interaction between two adjacent atoms and two pi bonds.
Now, aliphatic aldehyde and aromatic aldehyde are two broad classes of the aldehydes. The difference in the interaction between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. In the aliphatic aldehyde the bonds present between the carbon and hydrogen are weak so, they can be easily broken and are quite reactive while in aromatic aldehydes the carbon atoms are arranged in the form of a flat ring therefore the interaction between carbon atoms are stronger and difficult to break and are less reactive also.
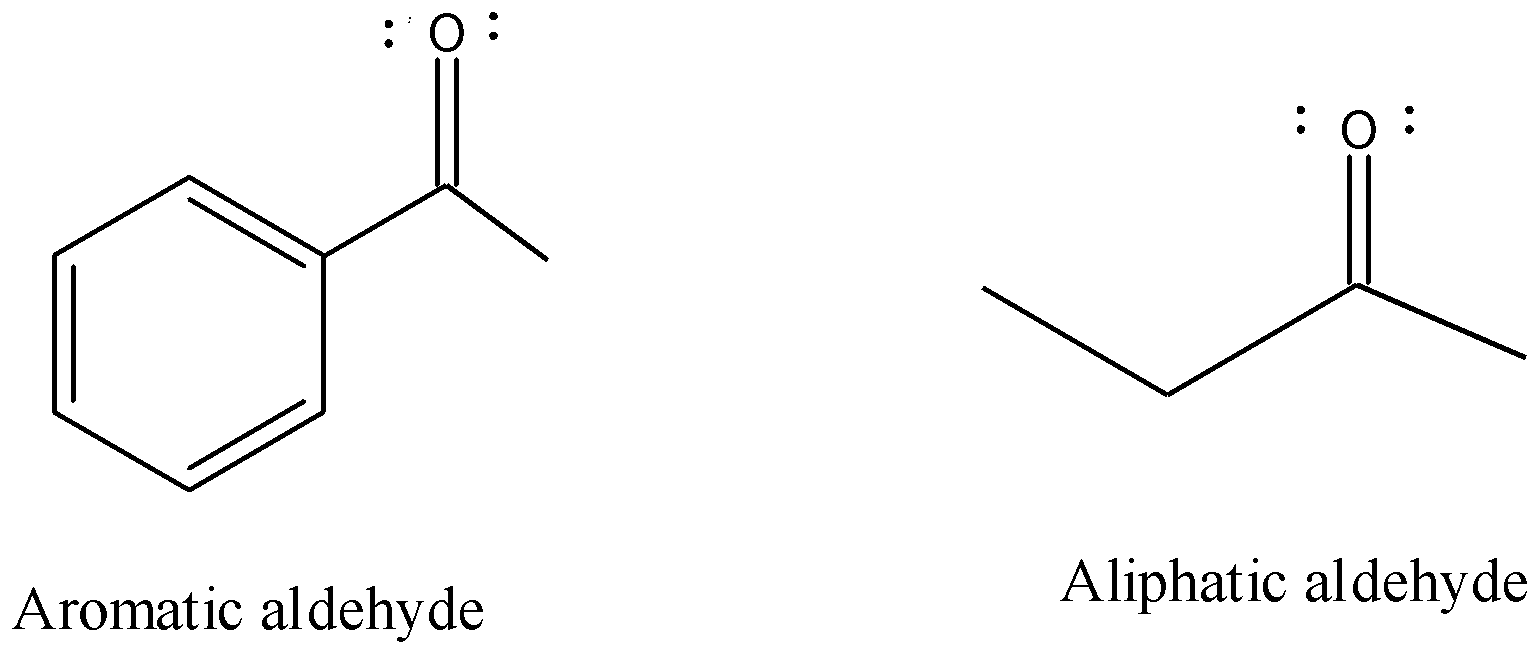
So, the aliphatic aldehyde are reactive in nucleophilic addition reaction because the bonds between the carbon and hydrogen can easily be broken but the aromatic aldehydes are less reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction because the bonds are strong and due to resonance stabilized by carbon ring. This happens due to the electron donating resonance effect that is called the +R effect. This increases the electron density of the carbonyl carbon and thus repel the nucleophiles.
Thus we can say that aromatic aldehydes are less reactive due to resonance effect.
Note: Resonance stabilised compounds are more stable and inter in nature as compared to the aliphatic compounds. Aromatic aldehydes are sterically hindered and conjugated. Nucleophilic addition reaction refers to the addition reaction in which nucleophile reacts with electrophilic double or triple bond.
Complete answer:
From your chemistry lessons you have learned about the resonance effect. Resonance effect is defined as the polarity produced in the molecule due to the interaction between the pi bond and the lone pair of electrons or it can also be produced due to the interaction between two adjacent atoms and two pi bonds.
Now, aliphatic aldehyde and aromatic aldehyde are two broad classes of the aldehydes. The difference in the interaction between the carbon and hydrogen atoms. In the aliphatic aldehyde the bonds present between the carbon and hydrogen are weak so, they can be easily broken and are quite reactive while in aromatic aldehydes the carbon atoms are arranged in the form of a flat ring therefore the interaction between carbon atoms are stronger and difficult to break and are less reactive also.

So, the aliphatic aldehyde are reactive in nucleophilic addition reaction because the bonds between the carbon and hydrogen can easily be broken but the aromatic aldehydes are less reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction because the bonds are strong and due to resonance stabilized by carbon ring. This happens due to the electron donating resonance effect that is called the +R effect. This increases the electron density of the carbonyl carbon and thus repel the nucleophiles.
Thus we can say that aromatic aldehydes are less reactive due to resonance effect.
Note: Resonance stabilised compounds are more stable and inter in nature as compared to the aliphatic compounds. Aromatic aldehydes are sterically hindered and conjugated. Nucleophilic addition reaction refers to the addition reaction in which nucleophile reacts with electrophilic double or triple bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




