
Area bounded by $y={{e}^{2x}}$ and lines x = 0, y = 0 and $x=\dfrac{e}{2}$ is given by
A. $\dfrac{1}{2}\int\limits_{0}^{2}{\ln ydy}$
B. $\dfrac{{{e}^{e}}-1}{2}$
C. ${{e}^{2}}$
D. None of these
Answer
615.3k+ views
Hint: First of all draw the area under the given curve to clearly visualize the question. Then, use $\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f(x)}={{e}^{2x}}$, a =0 and $b=\dfrac{e}{2}$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here we have to find the area bounded by $y={{e}^{2x}}$ and the lines x = 0, y = 0 and $x=\dfrac{e}{2}$. Before proceeding with the question, let us see how to find the area under a curve. Let the area be bounded by a curve, y = f(x), here the x-axis and the ordinates, x = a and x = b is given by $A=\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f(x)dx=\int\limits_{a}^{b}{ydx}}$.
Now, let us consider our question. Here let us first see the area under x = 0 and $x=\dfrac{e}{2}$ diagrammatically.
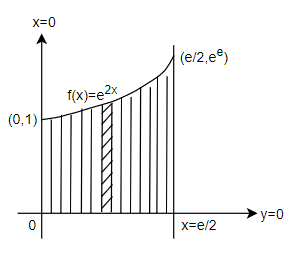
Basically, we have to find the shaded portion. So, we get the area as, \[A=\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f(x)dx}\]. By substituting$f(x)={{e}^{2x}}$, a = 0 and $b=\dfrac{e}{2}$ we get, \[A=\int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{e}{2}}{{{e}^{2x}}dx}\]. We know that $\int\limits_{p}^{q}{{{e}^{ax}}}dx=\int\limits_{p}^{q}{\dfrac{{{e}^{ax}}}{a}}$. So we get, \[A=\int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{e}{2}}{\dfrac{{{e}^{2x}}}{2}dx}\]
$A=\dfrac{1}{2}[{{e}^{2\left( \dfrac{e}{2} \right)}}-{{e}^{2\left( 0 \right)}}]$
$A=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{e}^{e}}-{{e}^{0}} \right)$
We know that ${{e}^{0}}=1$ so we get,
$A=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{e}^{e}}-1 \right)$
Hence, we get area between$y={{e}^{2x}}$, x = 0, y = 0 and $x=\dfrac{e}{2}$ as $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{e}^{e}}-1 \right)$ or $\dfrac{{{e}^{e}}-1}{2}$.
Therefore, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: In this question, some students may make the mistake of taking ${{e}^{x}}$ instead of${{e}^{2x}}$, which is wrong, so the question must be read properly. Also, the students must note that the given formula is only for y = f(x) and that there is a slightly different formula for x = f(y). Also for y = f(x), we take vertical strips for the area under the curve while for x = f(y), we take horizontal strips for the area under the curve.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here we have to find the area bounded by $y={{e}^{2x}}$ and the lines x = 0, y = 0 and $x=\dfrac{e}{2}$. Before proceeding with the question, let us see how to find the area under a curve. Let the area be bounded by a curve, y = f(x), here the x-axis and the ordinates, x = a and x = b is given by $A=\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f(x)dx=\int\limits_{a}^{b}{ydx}}$.

Now, let us consider our question. Here let us first see the area under x = 0 and $x=\dfrac{e}{2}$ diagrammatically.

Basically, we have to find the shaded portion. So, we get the area as, \[A=\int\limits_{a}^{b}{f(x)dx}\]. By substituting$f(x)={{e}^{2x}}$, a = 0 and $b=\dfrac{e}{2}$ we get, \[A=\int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{e}{2}}{{{e}^{2x}}dx}\]. We know that $\int\limits_{p}^{q}{{{e}^{ax}}}dx=\int\limits_{p}^{q}{\dfrac{{{e}^{ax}}}{a}}$. So we get, \[A=\int\limits_{0}^{\dfrac{e}{2}}{\dfrac{{{e}^{2x}}}{2}dx}\]
$A=\dfrac{1}{2}[{{e}^{2\left( \dfrac{e}{2} \right)}}-{{e}^{2\left( 0 \right)}}]$
$A=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{e}^{e}}-{{e}^{0}} \right)$
We know that ${{e}^{0}}=1$ so we get,
$A=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{e}^{e}}-1 \right)$
Hence, we get area between$y={{e}^{2x}}$, x = 0, y = 0 and $x=\dfrac{e}{2}$ as $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{e}^{e}}-1 \right)$ or $\dfrac{{{e}^{e}}-1}{2}$.
Therefore, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: In this question, some students may make the mistake of taking ${{e}^{x}}$ instead of${{e}^{2x}}$, which is wrong, so the question must be read properly. Also, the students must note that the given formula is only for y = f(x) and that there is a slightly different formula for x = f(y). Also for y = f(x), we take vertical strips for the area under the curve while for x = f(y), we take horizontal strips for the area under the curve.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




