
Are these halides primary, Secondary or tertiary? How is this determined?
A. 2-chlorobutane
B. 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
C. 1-chloro-2-butene
D. 1-chloro-2-methylpropane
E. 1-chloroadamantane
Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: In primary halide, the halogen is attached to primary carbon. In secondary halide the halogen is attached to secondary carbon and in tertiary halide the halogen is attached to tertiary carbon atoms.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is asked to find the given compounds in the options are primary, secondary or tertiary halides.
- Coming to the given options. Option A, 2-chlorobutane.
- We should know the structure of 2-chlorobutane to find which type of halide it is.
- The structure of 2-chlorobutane is as follows.
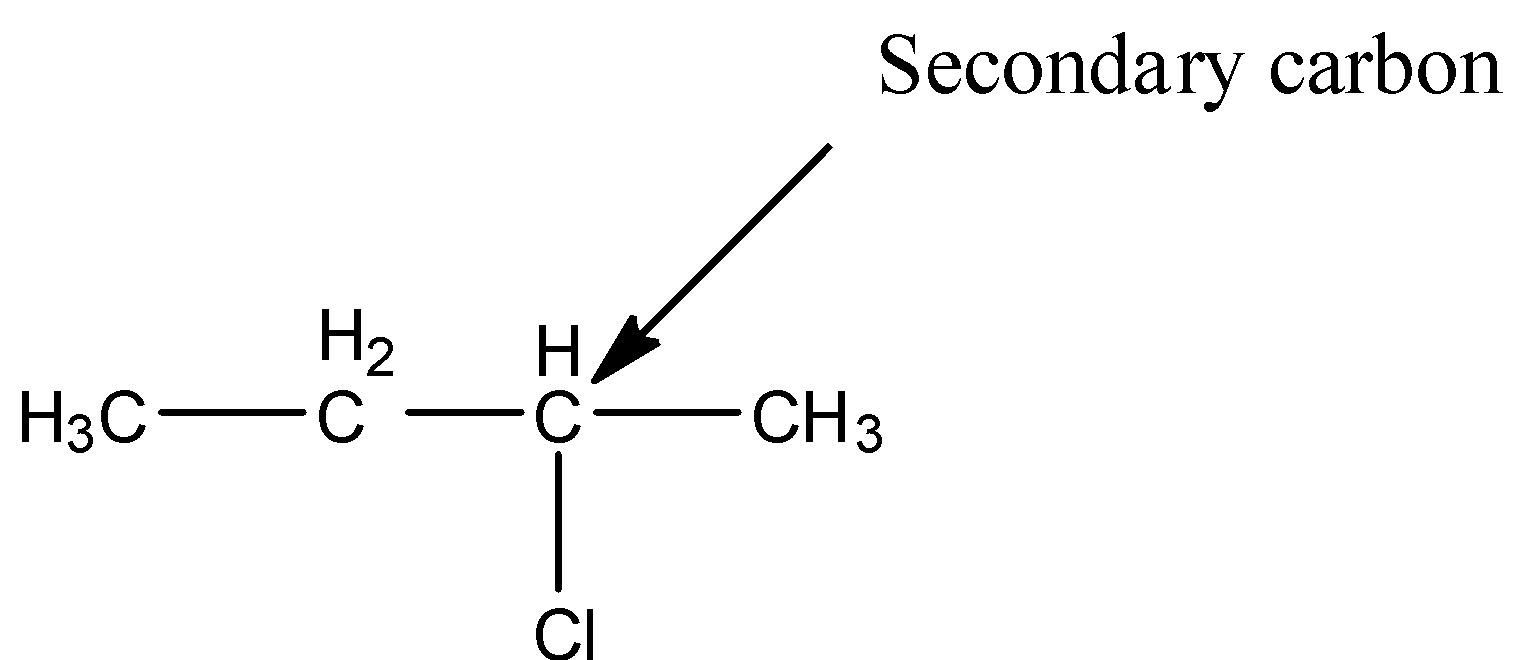
- In the above structure the chlorine is attached to secondary carbon then the halide is called secondary halide.
- Coming to option B, 2-chloro-2-methylpropane.
- The structure of 2-chloro-2-methylpropane is as follows.
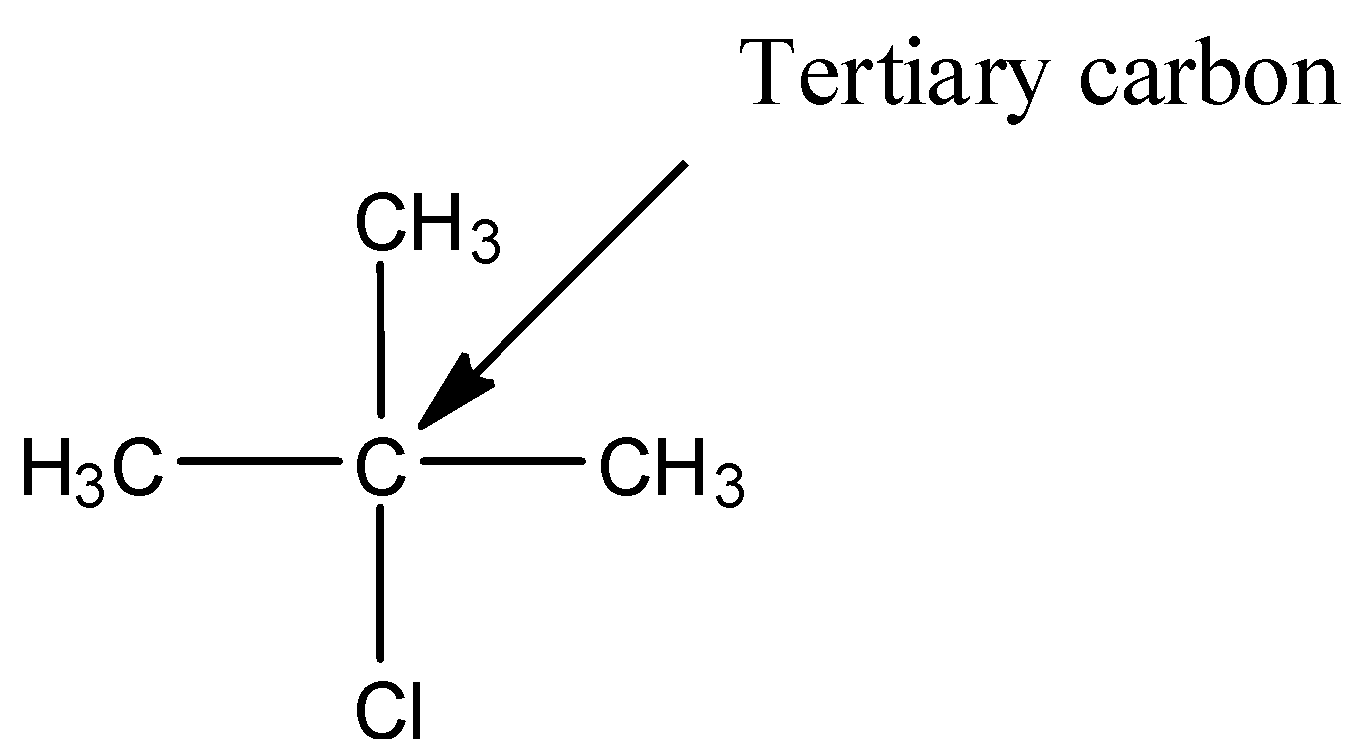
- In the above structure the chlorine is attached to tertiary carbon then the halide is called tertiary halide.
- Coming to option C, 1-chloro-2-butene.
- The structure of 1-chloro-2-butene is as follows.
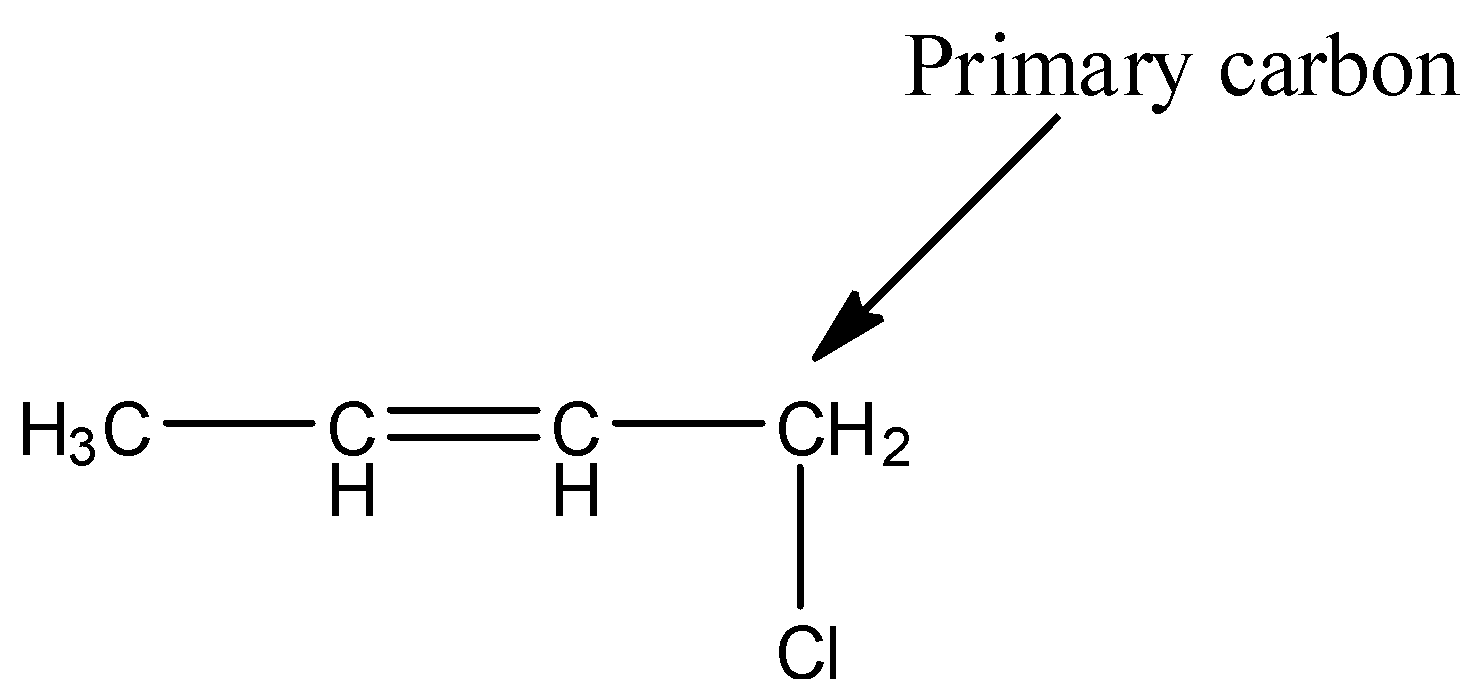
- In the above structure the chlorine is attached to primary carbon then the halide is called primary halide.
- Coming to the option D, 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
- The structure of 1-chloro-2-methylpropane is as follows.
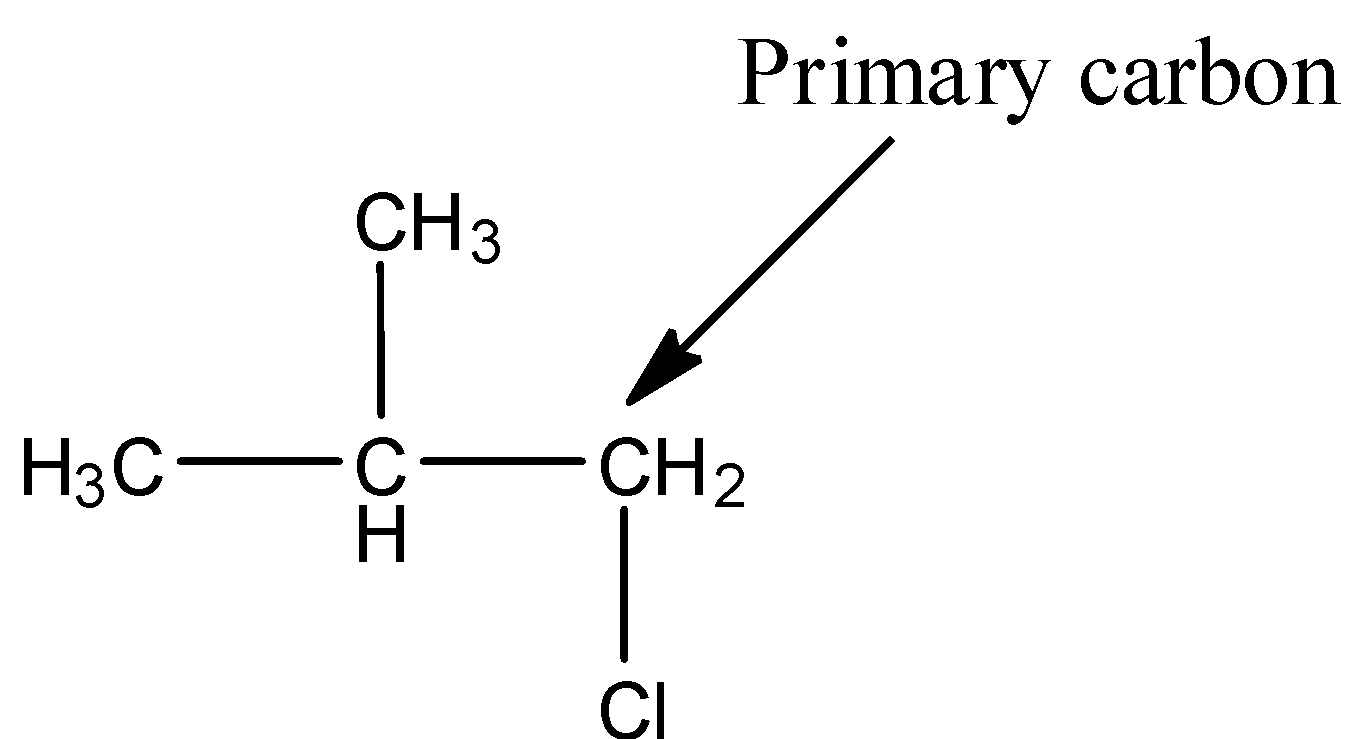
- In the above structure the chlorine is attached to primary carbon then the halide is called primary halide.
- Coming to option E, 1-chloroadamantane.
- The structure of 1-chloroadamantane is as follows.
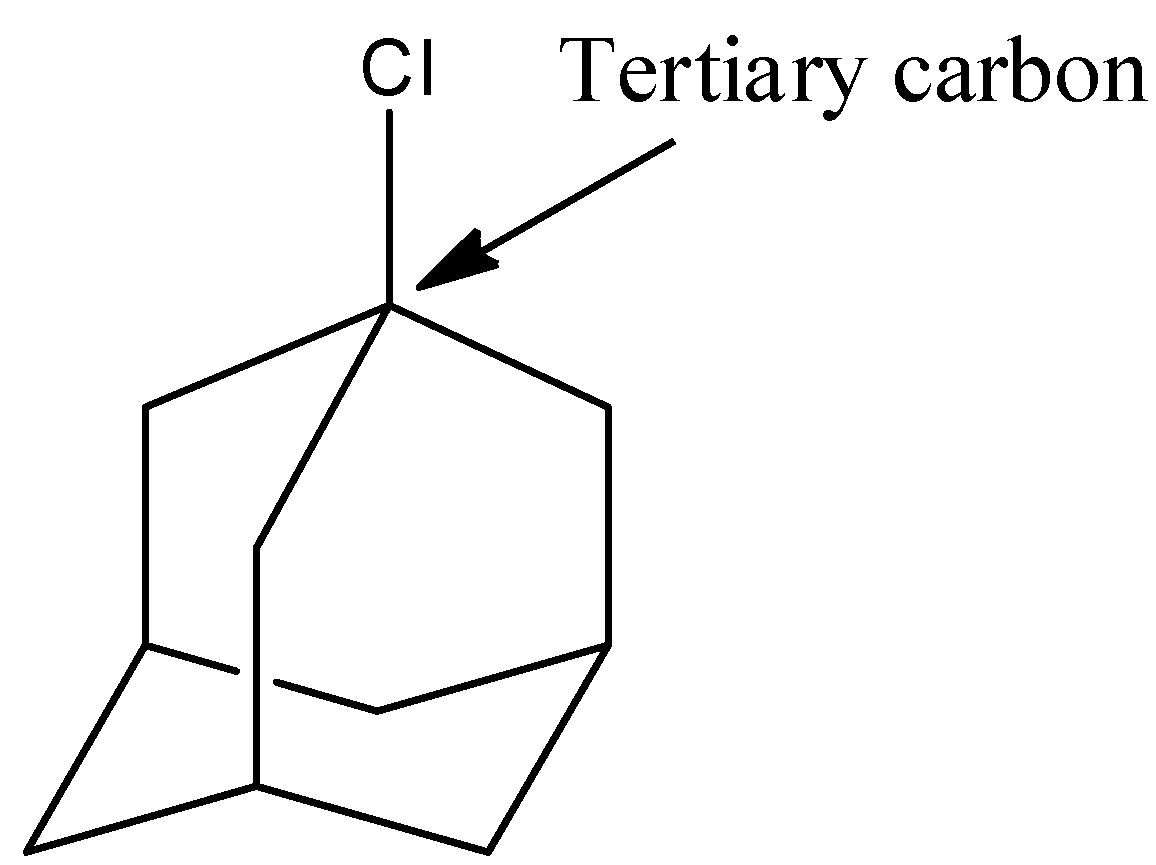
- In the above structure the chlorine is attached to tertiary carbon then the halide is called tertiary halide.
Note:
Only there is a chance to form three types of alkyl halides by organic compounds and they are primary, secondary and tertiary alkyl halides. Tertiary alkyl halides undergo ${{S}_{N}}1$ reaction and form the respective derivatives easily.
Complete answer:
- In the question it is asked to find the given compounds in the options are primary, secondary or tertiary halides.
- Coming to the given options. Option A, 2-chlorobutane.
- We should know the structure of 2-chlorobutane to find which type of halide it is.
- The structure of 2-chlorobutane is as follows.

- In the above structure the chlorine is attached to secondary carbon then the halide is called secondary halide.
- Coming to option B, 2-chloro-2-methylpropane.
- The structure of 2-chloro-2-methylpropane is as follows.

- In the above structure the chlorine is attached to tertiary carbon then the halide is called tertiary halide.
- Coming to option C, 1-chloro-2-butene.
- The structure of 1-chloro-2-butene is as follows.

- In the above structure the chlorine is attached to primary carbon then the halide is called primary halide.
- Coming to the option D, 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
- The structure of 1-chloro-2-methylpropane is as follows.

- In the above structure the chlorine is attached to primary carbon then the halide is called primary halide.
- Coming to option E, 1-chloroadamantane.
- The structure of 1-chloroadamantane is as follows.

- In the above structure the chlorine is attached to tertiary carbon then the halide is called tertiary halide.
Note:
Only there is a chance to form three types of alkyl halides by organic compounds and they are primary, secondary and tertiary alkyl halides. Tertiary alkyl halides undergo ${{S}_{N}}1$ reaction and form the respective derivatives easily.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




