
What are the steps associated with the process of constructing a hybrid orbital diagram?
Answer
480.6k+ views
Hint: The hybrid orbital diagram describes and shows the sigma and pi bonding present in a compound. With the help of this diagram the number of sigma and pi bonds can be calculated. To draw the hybrid orbital diagram, we need to know the hybridisation of the central atom present.
Complete answer:
We will take a molecule for reference and know the process of constructing a hybrid orbital diagram.
Consider the Ethylene molecule, also known as Ethene. It has two carbon atoms with a double bond present in between the two carbons. The molecular formula is $ {H_2}C = C{H_2} $. The steps of constructing a hybrid orbital diagram are as follows:
Step 1: Draw the Lewis structure of the ethene molecule.
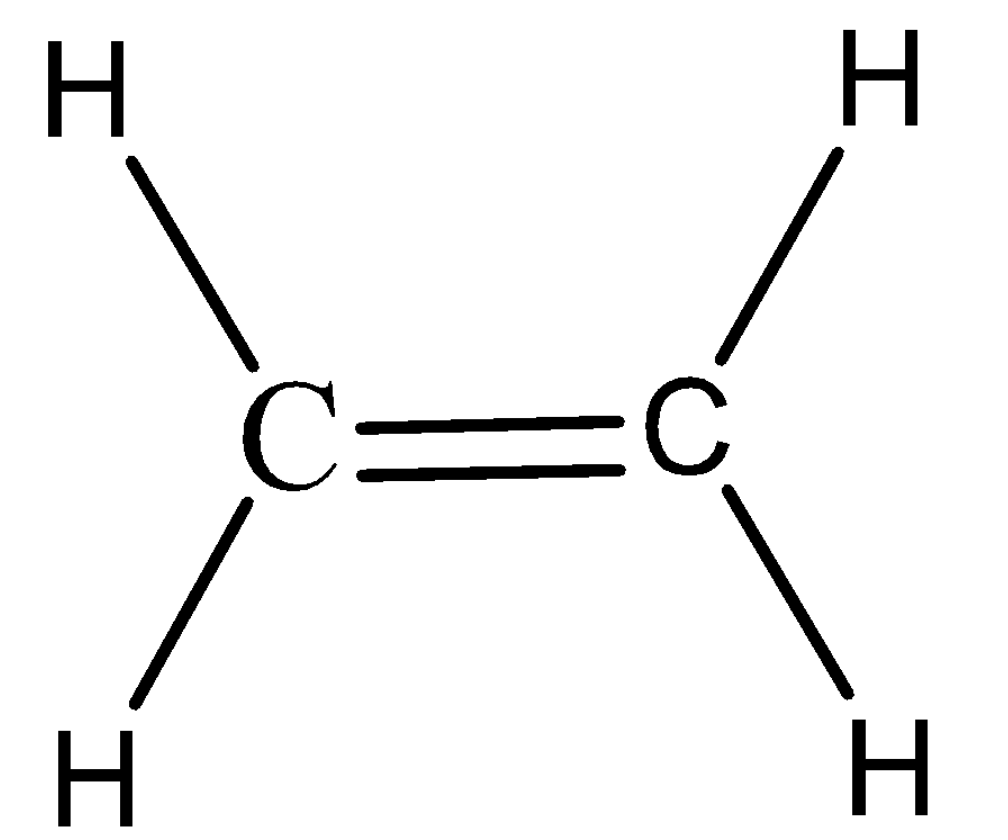
Step 2: We will determine the geometry around each central atom i.e. Carbon using the VSEPR theory. Here the carbon is attached to a double bond and two hydrogens. Therefore, we can say that it has a $ A{X_3} $ system , hence the geometry is Trigonal Planar.
Step 3: Determine the hybridization of the central atom using the geometry. Here the geometry is Trigonal Planar, hence the hybridisation will be $ s{p^2} $ . Each carbon atom in the ethene molecule has a $ s{p^2} $ hybridisation.
Step 4. Draw the two Carbon atoms side by side of each other and bring the next carbon and Hydrogen close to each other, such that they can overlap to form sigma and pi bonds. The sigma and pi bonding of ethene can be shown below:
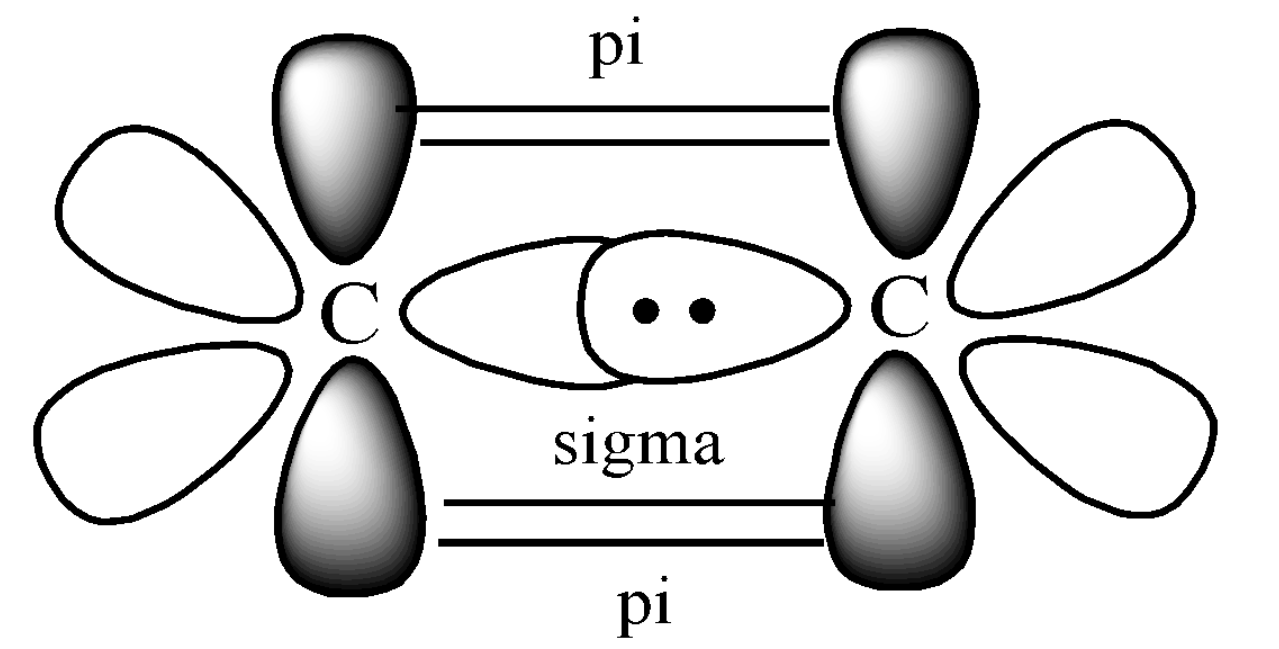
Here, the C-C head-on collision forms the sigma bond and the perpendicular overlap of the p orbitals forms the pi bond. Hence, we can say that ethylene has one sigma and one pi bond present between the two Carbon atoms. The perpendicular p-orbital will always form a pi bond, whereas the orbital in the plane will form a sigma bond only. This is the hybrid orbital diagram of ethene. We follow the same process for any molecule.
Note:
Sigma bonds are formed due to head-to-head collisions of orbitals that reside in the same plane. Pi bonds are formed by lateral overlap of orbitals which are perpendicular to the plane. Sigma bonds are stronger than pi bonds because of this reason only.
Complete answer:
We will take a molecule for reference and know the process of constructing a hybrid orbital diagram.
Consider the Ethylene molecule, also known as Ethene. It has two carbon atoms with a double bond present in between the two carbons. The molecular formula is $ {H_2}C = C{H_2} $. The steps of constructing a hybrid orbital diagram are as follows:
Step 1: Draw the Lewis structure of the ethene molecule.

Step 2: We will determine the geometry around each central atom i.e. Carbon using the VSEPR theory. Here the carbon is attached to a double bond and two hydrogens. Therefore, we can say that it has a $ A{X_3} $ system , hence the geometry is Trigonal Planar.
Step 3: Determine the hybridization of the central atom using the geometry. Here the geometry is Trigonal Planar, hence the hybridisation will be $ s{p^2} $ . Each carbon atom in the ethene molecule has a $ s{p^2} $ hybridisation.
Step 4. Draw the two Carbon atoms side by side of each other and bring the next carbon and Hydrogen close to each other, such that they can overlap to form sigma and pi bonds. The sigma and pi bonding of ethene can be shown below:

Here, the C-C head-on collision forms the sigma bond and the perpendicular overlap of the p orbitals forms the pi bond. Hence, we can say that ethylene has one sigma and one pi bond present between the two Carbon atoms. The perpendicular p-orbital will always form a pi bond, whereas the orbital in the plane will form a sigma bond only. This is the hybrid orbital diagram of ethene. We follow the same process for any molecule.
Note:
Sigma bonds are formed due to head-to-head collisions of orbitals that reside in the same plane. Pi bonds are formed by lateral overlap of orbitals which are perpendicular to the plane. Sigma bonds are stronger than pi bonds because of this reason only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




