
What are the rules of transformation: specifically of dilation, rotation, reflection and translation?
Answer
529.8k+ views
Hint: First we will understand the meaning of the terms dilation, rotation, reflection and translation one by one with the necessary parameters required to perform these transformations. Then we will see the rules of these four transformations. We will limit these transformations in a 2-D plane only.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we have been asked to mention and explain the rules of transformations namely: dilation, rotation, reflection and translation. Let us see each term one by one and with the rules and necessary conditions.
(1) Dilation: Dilation means enlargement or shrinkage of a figure. The extent of dilation is known as the factor of dilation. There are two necessary parameters to be chosen for the dilation.
(i) Center of dilation
(ii) Factor of dilation
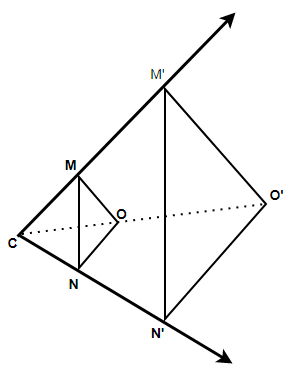
Here, we have to connect the center of dilation with the points on the figure needed to be stretched or shrunk. If the dilation factor is greater than 1 then enlargement will take place and if the factor is between 0 and 1 then shrinkage will take place.
(2) Rotation: For rotation of a point on a figure we have two important parameters to be chosen.
(i) Center of rotation
(ii) Angle of rotation
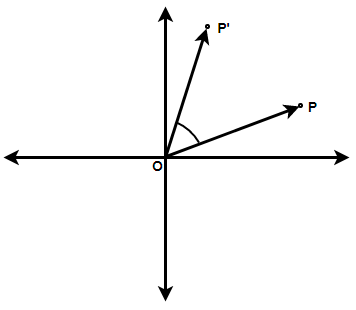
Here, we have to choose a point around which the rotation will take place. We have to connect a line joining the center of rotation and the point to be rotated. Then we have to rotate this line segment with a fixed angle.
(3) Reflection: For the reflection of any figure we have only one necessary parameter to be chosen, that is the axis of rotation.
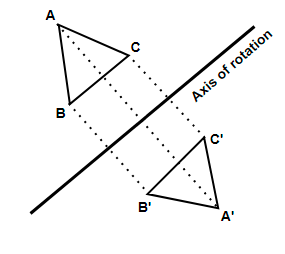
Here, we have to draw a perpendicular on the axis of rotation from the point whose reflection is to be taken. Now, we have to stretch the perpendicular line on the other side of the axis with the same length to get the reflected image.
(4) Translation: For the translation of a figure we have to consider two necessary parameters.
(i) Direction of the translation
(ii) Length of the translation
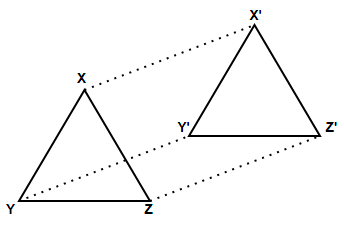
Here, we have to fix a direction along which the shift will take place. All the points on the figure to be shifted will be moved parallel along this direction with a fixed distance.
Note: Note that these transformation rules are used in drawing the graphs of certain mathematical functions which are then helpful in solving the questions of the topic ‘area under curve ‘. The rules of translation, reflection are used in plane mirrors in Physics. The rule of dilation can be related with the magnification by the concave or convex mirrors and planes.
Complete step by step solution:
Here we have been asked to mention and explain the rules of transformations namely: dilation, rotation, reflection and translation. Let us see each term one by one and with the rules and necessary conditions.
(1) Dilation: Dilation means enlargement or shrinkage of a figure. The extent of dilation is known as the factor of dilation. There are two necessary parameters to be chosen for the dilation.
(i) Center of dilation
(ii) Factor of dilation

Here, we have to connect the center of dilation with the points on the figure needed to be stretched or shrunk. If the dilation factor is greater than 1 then enlargement will take place and if the factor is between 0 and 1 then shrinkage will take place.
(2) Rotation: For rotation of a point on a figure we have two important parameters to be chosen.
(i) Center of rotation
(ii) Angle of rotation

Here, we have to choose a point around which the rotation will take place. We have to connect a line joining the center of rotation and the point to be rotated. Then we have to rotate this line segment with a fixed angle.
(3) Reflection: For the reflection of any figure we have only one necessary parameter to be chosen, that is the axis of rotation.

Here, we have to draw a perpendicular on the axis of rotation from the point whose reflection is to be taken. Now, we have to stretch the perpendicular line on the other side of the axis with the same length to get the reflected image.
(4) Translation: For the translation of a figure we have to consider two necessary parameters.
(i) Direction of the translation
(ii) Length of the translation

Here, we have to fix a direction along which the shift will take place. All the points on the figure to be shifted will be moved parallel along this direction with a fixed distance.
Note: Note that these transformation rules are used in drawing the graphs of certain mathematical functions which are then helpful in solving the questions of the topic ‘area under curve ‘. The rules of translation, reflection are used in plane mirrors in Physics. The rule of dilation can be related with the magnification by the concave or convex mirrors and planes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




