
What are the products of hydrolysis of sugar?
Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint: Sugar is actually a polymer. Hydrolysis cleaves a sugar into smaller units. It relates to carbohydrates.
Complete step-by-step answer:
So, what is sugar? Carbohydrates are commonly called sugar. Along with proteins and fats, carbohydrates are one of the macronutrients that our body requires to maintain all its structure and function. The body’s go-to substance for energy is carbohydrate. The plasma membranes of all our cells contain carbohydrate molecules that support its structure. The cell walls of plants are also composed of sugar, specifically cellulose. These are the compounds which make fruits sweet in taste. Carbohydrates or sugars are therefore omnipresent substances.
There are many types of substances that we commonly refer to when we say “sugar”, some of them are table sugar (sucrose), milk sugar (lactose) and malt sugar (maltose). Sugars are large molecules made up of monosaccharides and disaccharides. If we take the examples above then:
- Sucrose is a dimer of glucose (6-membered ring) and fructose (5-membered ring)
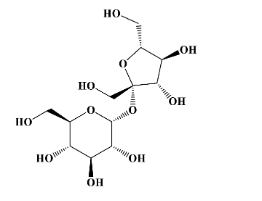
- Lactose is a dimer of glucose (top molecule) and galactose (bottom molecule)
- Maltose is a dimer of glucose
Similarly starch and glycogen are polymers of glucose.
Hydrolysis is the process of cleavage of molecules with the help of water molecules. It can be carried out in an acidic or basic medium. Hydrolysis of sugars breaks them into smaller molecules by cleaving the glycosidic bonds that hold the monomer units together. A glycosidic bond is formed between two monosaccharides when they are near enough to each other with the leaving of a water molecule. It is a condensation reaction. So when water is added to them in the reaction mixture they separate to their former states.
Hydrolysis of sugar results in forming of smaller units which may be polysaccharides, disaccharides or the smallest of all- monosaccharides. A typical hydrolysis reaction is shown below:
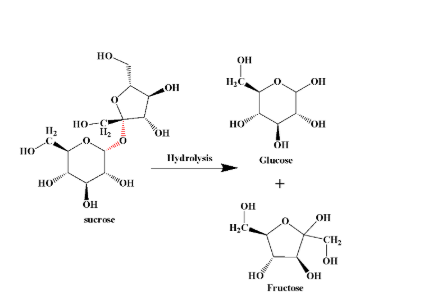
(The bond in red colour is the glycosidic bond that breaks during hydrolysis)
Note: Hydrolysis is not limited to only sugars. It is a very crucial chemical reaction both inside our bodies and also in the organic laboratories. Other macronutrients such as proteins and fats do not undergo hydrolysis to break into smaller units. They have different chemical reactions to achieve this.
Complete step-by-step answer:
So, what is sugar? Carbohydrates are commonly called sugar. Along with proteins and fats, carbohydrates are one of the macronutrients that our body requires to maintain all its structure and function. The body’s go-to substance for energy is carbohydrate. The plasma membranes of all our cells contain carbohydrate molecules that support its structure. The cell walls of plants are also composed of sugar, specifically cellulose. These are the compounds which make fruits sweet in taste. Carbohydrates or sugars are therefore omnipresent substances.
There are many types of substances that we commonly refer to when we say “sugar”, some of them are table sugar (sucrose), milk sugar (lactose) and malt sugar (maltose). Sugars are large molecules made up of monosaccharides and disaccharides. If we take the examples above then:
- Sucrose is a dimer of glucose (6-membered ring) and fructose (5-membered ring)

- Lactose is a dimer of glucose (top molecule) and galactose (bottom molecule)
- Maltose is a dimer of glucose
Similarly starch and glycogen are polymers of glucose.
Hydrolysis is the process of cleavage of molecules with the help of water molecules. It can be carried out in an acidic or basic medium. Hydrolysis of sugars breaks them into smaller molecules by cleaving the glycosidic bonds that hold the monomer units together. A glycosidic bond is formed between two monosaccharides when they are near enough to each other with the leaving of a water molecule. It is a condensation reaction. So when water is added to them in the reaction mixture they separate to their former states.
Hydrolysis of sugar results in forming of smaller units which may be polysaccharides, disaccharides or the smallest of all- monosaccharides. A typical hydrolysis reaction is shown below:

(The bond in red colour is the glycosidic bond that breaks during hydrolysis)
Note: Hydrolysis is not limited to only sugars. It is a very crucial chemical reaction both inside our bodies and also in the organic laboratories. Other macronutrients such as proteins and fats do not undergo hydrolysis to break into smaller units. They have different chemical reactions to achieve this.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




