
What are the possible resonance structures of $ C{H_3} - \,CH\, = \,CH\, - \,CH\, = \,O $ and $ C{H_3}\, - \,CO{O^ - } $ ? What is the order of stability of the contributing resonance structures?
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint :A group of two or more Lewis Structures that collectively explain the electronic bonding of a single polyatomic species, including fractional bonds and fractional charges, is known as a resonance structure.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Remember that the electrons will pass to the more electronegative or positive atom.
(a)But-2en-al
2-Butenal, also known as crotonaldehyde, is a member of the enal family of organic compounds. Since there is no such thing as a positive atom, but because $ O $ is the most electronegative, let us transfer electrons to it.
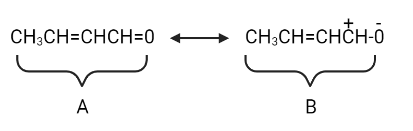
Let's move electrons to the carbon atom now that it has a positive charge.
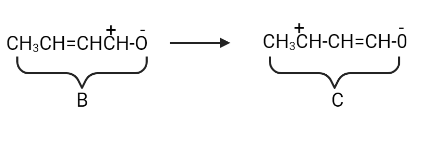
Structure $ A $ contributes the most and has the lowest energy. Structures $ B $ and $ C $ have a higher energy level and contribute less.
(b) Acetate ion
The removal of a proton from the carboxyl group of acetic acid produces acetate, a monocarboxylic acid anion.
There is no positive atom in this case, but the other $ O $ atom is an electronegative atom. Let us transfer the electrons in that direction.
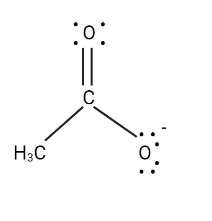
To get the third structure shown below, transfer the electrons in the carbonyl group to the carbonyl $ O $ atom.
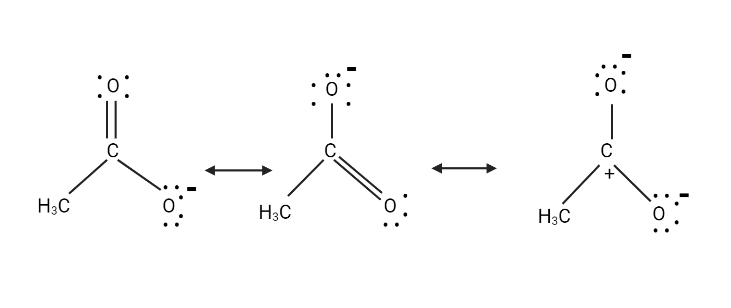
Of the three structures above, the first two structures are similar and have the same amount of energy. Since the third structure has three charges instead of one, it is just a minor contributor.
Note :
The basic aim of resonance structures is to demonstrate that molecules can transfer electrons and charges to different atoms. Since the charge (or bond) is now delocalized and not "forced" onto an atom that does not want it, resonance makes a molecule more stable.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Remember that the electrons will pass to the more electronegative or positive atom.
(a)But-2en-al
2-Butenal, also known as crotonaldehyde, is a member of the enal family of organic compounds. Since there is no such thing as a positive atom, but because $ O $ is the most electronegative, let us transfer electrons to it.

Let's move electrons to the carbon atom now that it has a positive charge.

Structure $ A $ contributes the most and has the lowest energy. Structures $ B $ and $ C $ have a higher energy level and contribute less.
(b) Acetate ion
The removal of a proton from the carboxyl group of acetic acid produces acetate, a monocarboxylic acid anion.
There is no positive atom in this case, but the other $ O $ atom is an electronegative atom. Let us transfer the electrons in that direction.

To get the third structure shown below, transfer the electrons in the carbonyl group to the carbonyl $ O $ atom.

Of the three structures above, the first two structures are similar and have the same amount of energy. Since the third structure has three charges instead of one, it is just a minor contributor.
Note :
The basic aim of resonance structures is to demonstrate that molecules can transfer electrons and charges to different atoms. Since the charge (or bond) is now delocalized and not "forced" onto an atom that does not want it, resonance makes a molecule more stable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




