
What are the major and minor products obtained in the reaction of \[\left( E \right) - 3{\text{ }}methyl - 2{\text{ }}pentene\] with\[HBr\]?
A)
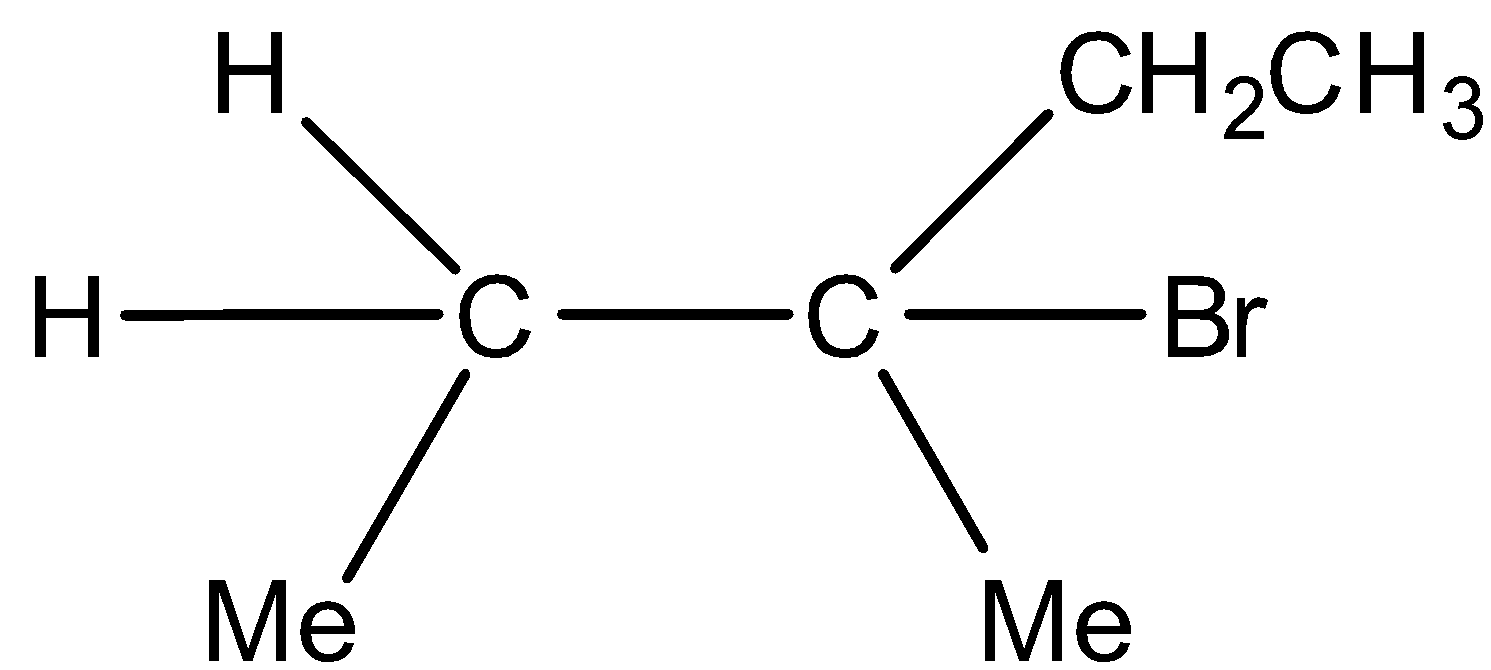 Major product and
Major product and
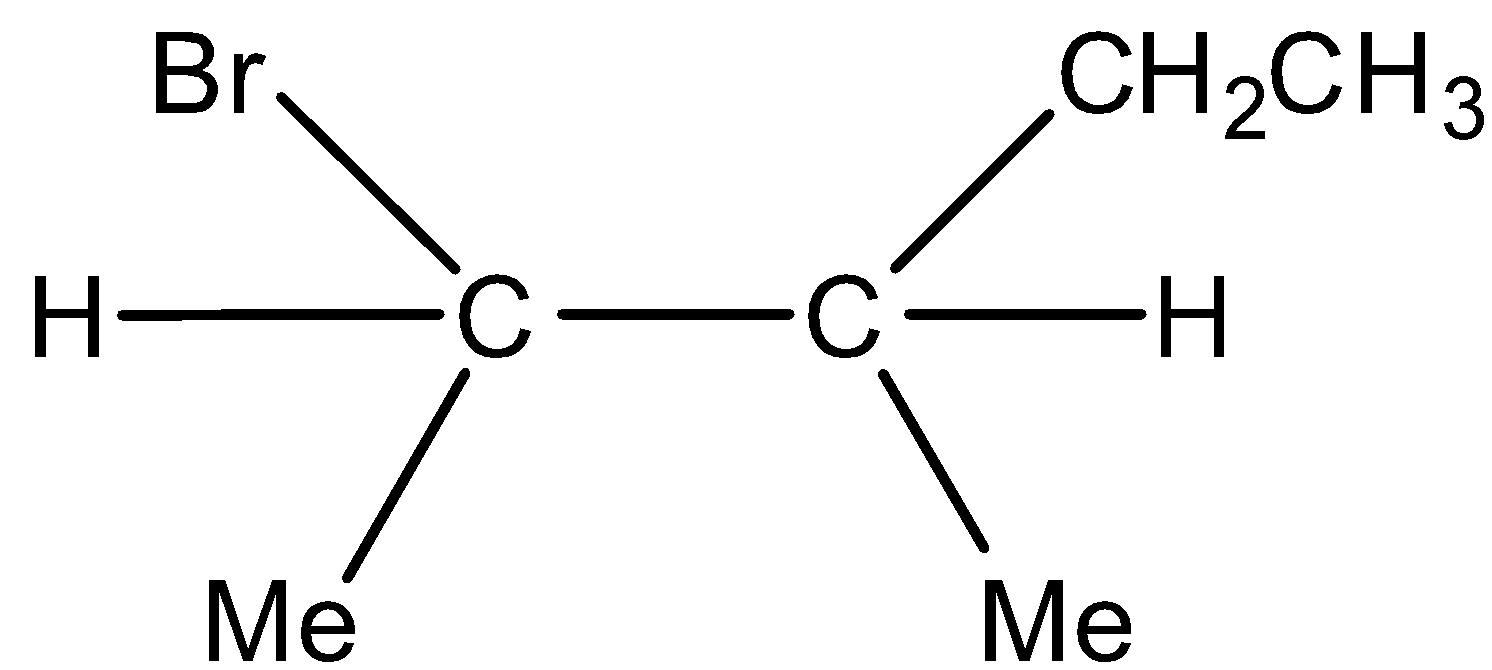 Minor product
Minor product
B) Both major and minor will be same
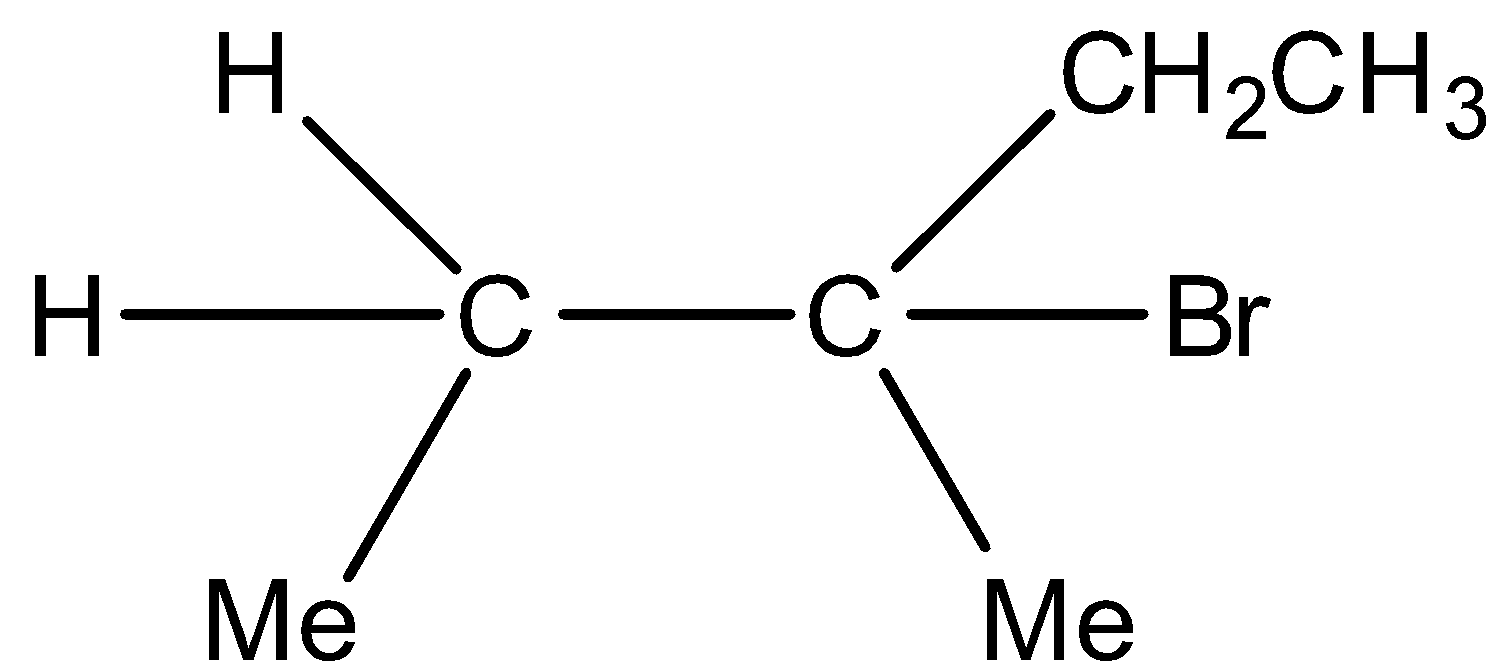
C)
 Major product and
Major product and
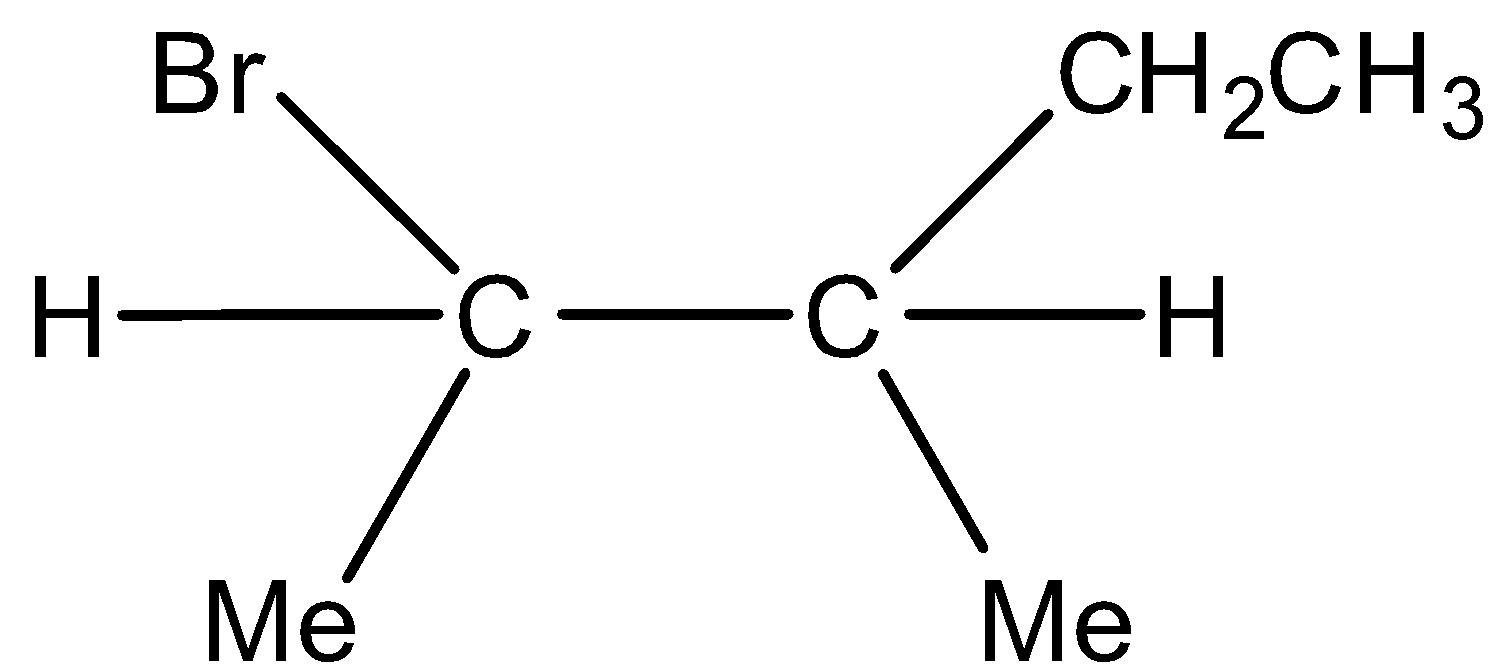
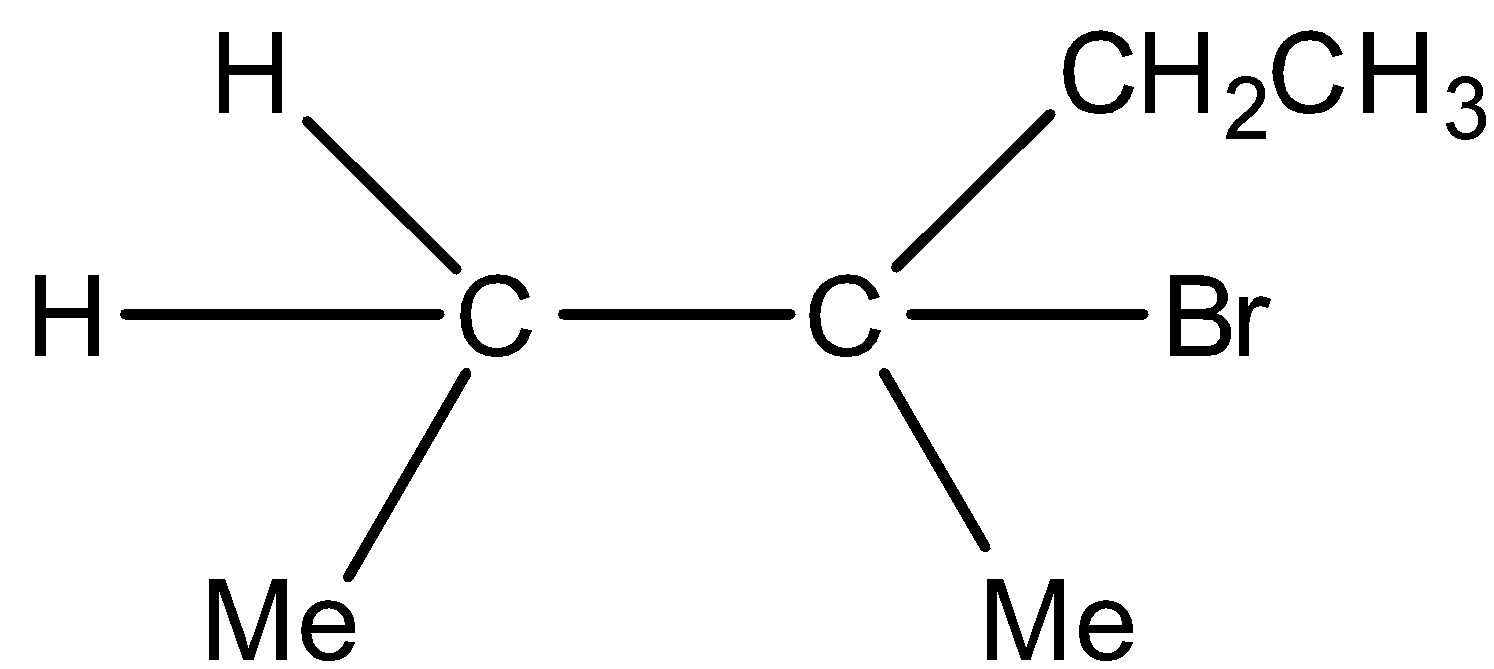 Minor product
Minor product
D) None of the above





Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: We have to remember that the order of stability of a carbocation : \[3^\circ > 2^\circ > 1^\circ \]
Stability of carbocation is crucial in finding the major and minor products in this type of questions. So you must have knowledge of this before.
Complete step by step answer:
We can draw the structure of \[\left( E \right) - 3 - methyl - 2 - pentene\] as,
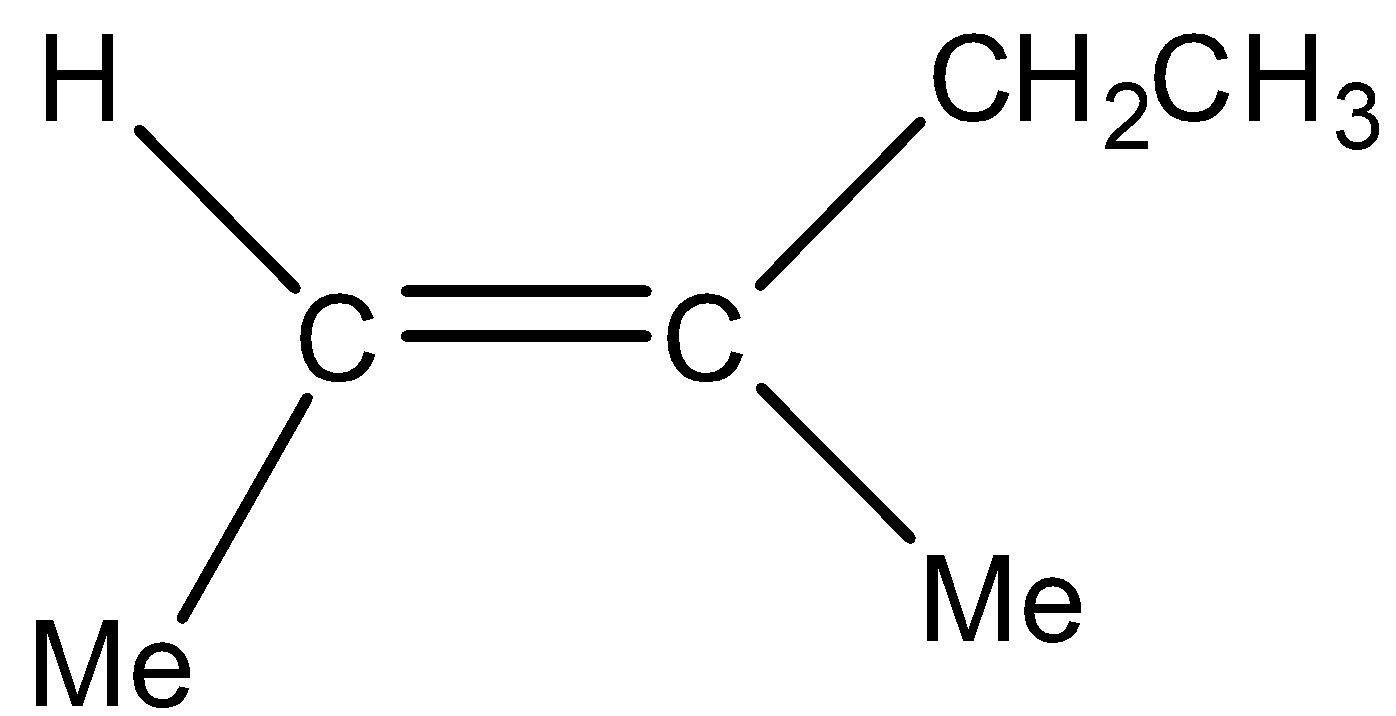
Reaction of \[\left( E \right) - 3 - methyl - 2 - pentene\] with \[HBr\] is a Markovnikov’s addition reaction which involves the presence of an alkene and\[HBr\]. In this addition, firstly an alkene will break itself into carbocations on which \[HBr\]reacts. Now H will get added to the one carbon which has a higher number of Hydrogen atoms whereas Br gets attached to the carbon that has a lower number of Hydrogen atoms or no hydrogen atom. Out of the two carbocations secondary carbocation is more stable as compared to primary carbocation.
Therefore the major product will be secondary carbocation substitution with\[HBr\].
Reaction mechanism will proceed like:
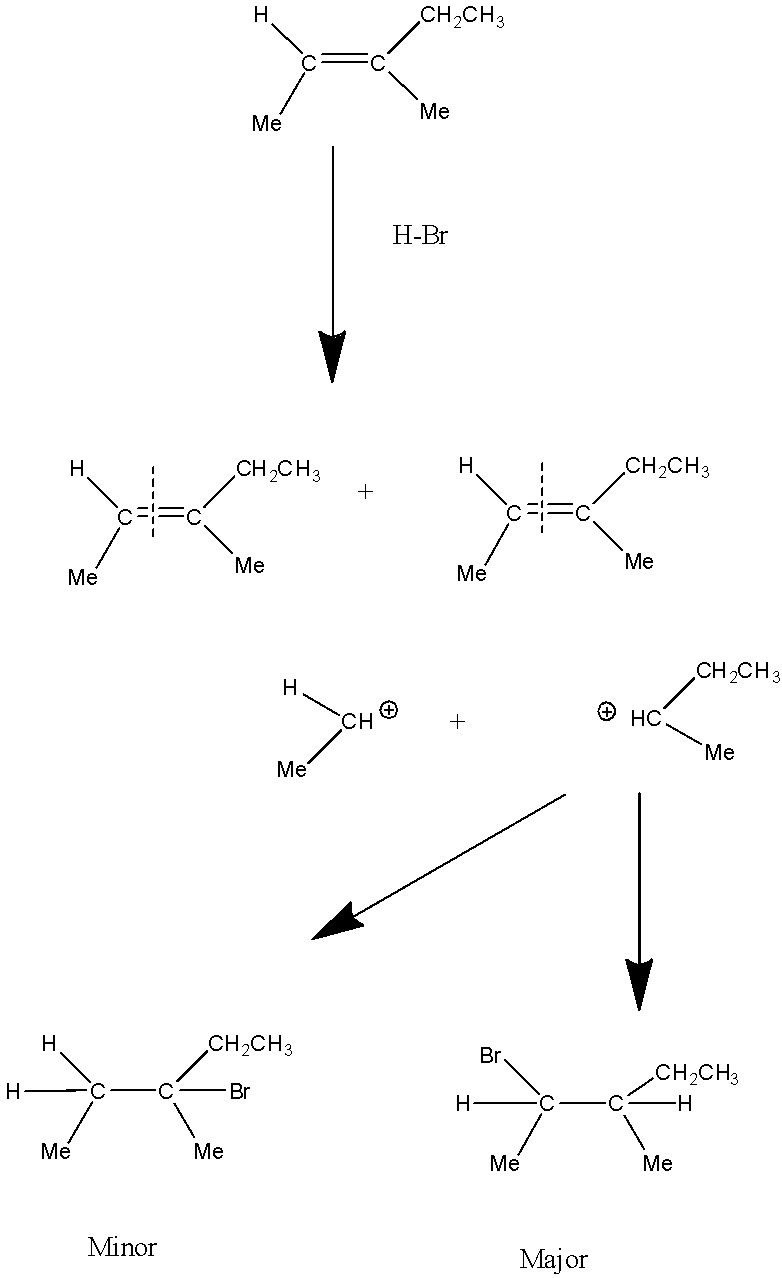
Option A) this is an incorrect option as vice versa true in this case.
Option B) This is an incorrect option as major and minor products cannot be the same.
Option C) this is a correct option as the major product formed in this reaction is due the stability of carbocation which is more in case of tertiary than secondary. And the other one i.e. secondary carbocation will have a minor product.
Option D) this is an incorrect option as we got option A as a correct option.
Hence, the correct option is ‘Option A’
Note: We have to remember that anti markovnikov addition is just the reverse of markovnikov addition in which the hydrogen atom will attack the carbon atom having lower number of H atoms and the halide will attack the one having higher number of Hydrogen atoms.
Stability of carbocation is crucial in finding the major and minor products in this type of questions. So you must have knowledge of this before.
Complete step by step answer:
We can draw the structure of \[\left( E \right) - 3 - methyl - 2 - pentene\] as,

Reaction of \[\left( E \right) - 3 - methyl - 2 - pentene\] with \[HBr\] is a Markovnikov’s addition reaction which involves the presence of an alkene and\[HBr\]. In this addition, firstly an alkene will break itself into carbocations on which \[HBr\]reacts. Now H will get added to the one carbon which has a higher number of Hydrogen atoms whereas Br gets attached to the carbon that has a lower number of Hydrogen atoms or no hydrogen atom. Out of the two carbocations secondary carbocation is more stable as compared to primary carbocation.
Therefore the major product will be secondary carbocation substitution with\[HBr\].
Reaction mechanism will proceed like:

Option A) this is an incorrect option as vice versa true in this case.
Option B) This is an incorrect option as major and minor products cannot be the same.
Option C) this is a correct option as the major product formed in this reaction is due the stability of carbocation which is more in case of tertiary than secondary. And the other one i.e. secondary carbocation will have a minor product.
Option D) this is an incorrect option as we got option A as a correct option.
Hence, the correct option is ‘Option A’
Note: We have to remember that anti markovnikov addition is just the reverse of markovnikov addition in which the hydrogen atom will attack the carbon atom having lower number of H atoms and the halide will attack the one having higher number of Hydrogen atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




