
How are the following conversions brought?
i.benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol
ii. benzyl alcohol to benzoic acid
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: The concept of nucleophilic substitution reaction as well as the oxidation of organic compounds to form aldehydes/ketones or carboxylic acids is to be used in this question.
Complete Solution :
- In order to answer this question, we need to learn about the nucleophilic reaction as well as the oxidation reaction, to form acids. Nucleophilic substitution bimolecular or ${{S}_{N}}2$ is a single step bimolecular reaction in which the incoming nucleophile attacks the C-atom of substrate in a direction opposite to the outgoing nucleophile. The reaction passes through a transition state in which both the incoming and outgoing nucleophiles are bonded to the same C-atom. In the transition state, the C-atom is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised with a p-orbital whose one lobe overlaps with an orbital of incoming nucleophile and the other lobe overlaps with an orbital of outgoing nucleophile. The three non-reacting atoms or groups attached to the C-atom are nearly coplanar at an angle of ${{120}^{0}}$. The reaction is completed when the outgoing nucleophile leaves with the bond pair of electrons and simultaneously the incoming nucleophile binds to the C-atom. As the reaction progresses, the configuration of the C-atom under attack is inverted. An ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction is always accompanied by inversion of configuration. The inversion in configuration implies change in configuration from R to S or S to R (provided the incoming nucleophile and outgoing nucleophile have same priority) and not from (+) to (-) or (-) to (+).
- Primary alcohols are easily oxidised to carboxylic acids with oxidants such as $KMn{{O}_{4}}$, in neutral, acidic or alkaline media or by $Cr{{O}_{3}}/{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$ in acidic media. Now, let us come to the question and see the reactions. In (i), an ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction is taking place.
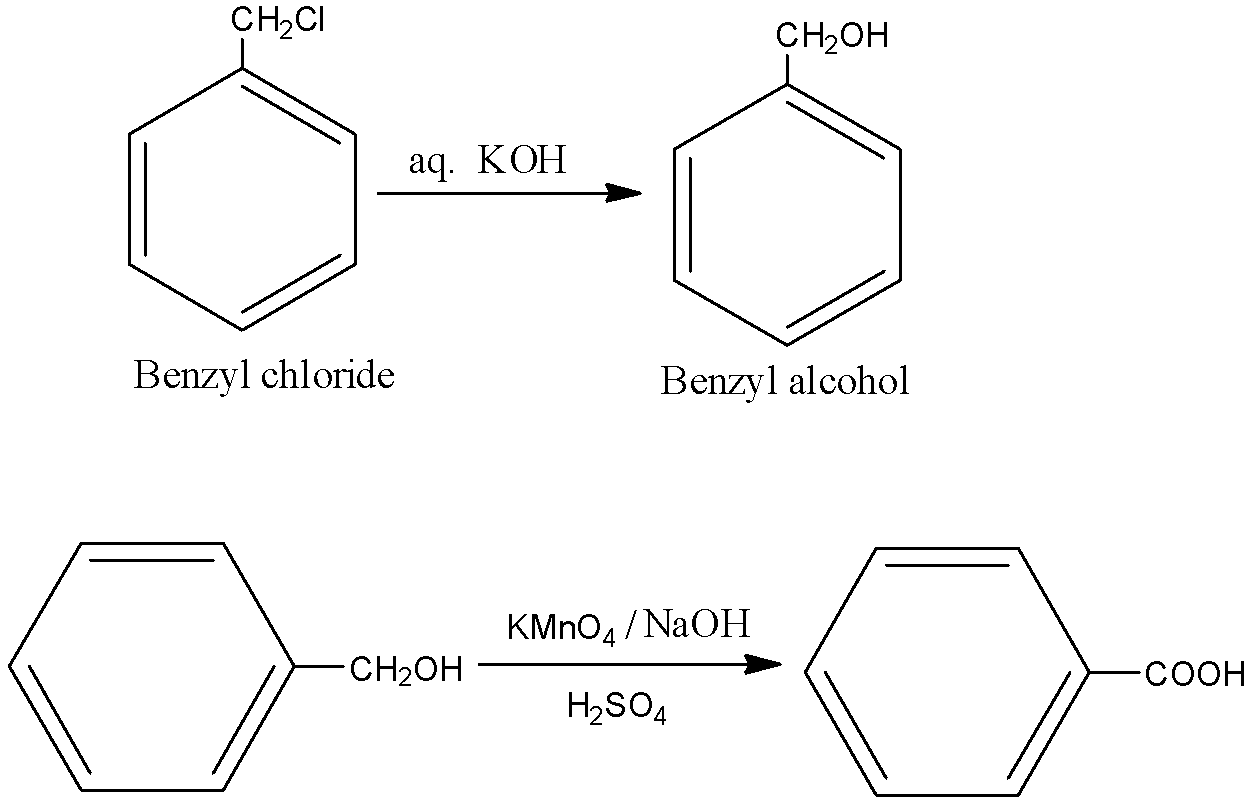
Hence with the above reagents, we obtain the desired products.
Note: Steric hindrance plays a very vital role in an ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction. As steric hindrance increases the rate of ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction decreases. Thus for the same halogen the reactivity order of alkyl halides towards ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction is as under.
- Methyl halide > primary Alkyl halide > secondary Alkyl halide > tertiary Alkyl halide
Complete Solution :
- In order to answer this question, we need to learn about the nucleophilic reaction as well as the oxidation reaction, to form acids. Nucleophilic substitution bimolecular or ${{S}_{N}}2$ is a single step bimolecular reaction in which the incoming nucleophile attacks the C-atom of substrate in a direction opposite to the outgoing nucleophile. The reaction passes through a transition state in which both the incoming and outgoing nucleophiles are bonded to the same C-atom. In the transition state, the C-atom is $s{{p}^{2}}$ hybridised with a p-orbital whose one lobe overlaps with an orbital of incoming nucleophile and the other lobe overlaps with an orbital of outgoing nucleophile. The three non-reacting atoms or groups attached to the C-atom are nearly coplanar at an angle of ${{120}^{0}}$. The reaction is completed when the outgoing nucleophile leaves with the bond pair of electrons and simultaneously the incoming nucleophile binds to the C-atom. As the reaction progresses, the configuration of the C-atom under attack is inverted. An ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction is always accompanied by inversion of configuration. The inversion in configuration implies change in configuration from R to S or S to R (provided the incoming nucleophile and outgoing nucleophile have same priority) and not from (+) to (-) or (-) to (+).
- Primary alcohols are easily oxidised to carboxylic acids with oxidants such as $KMn{{O}_{4}}$, in neutral, acidic or alkaline media or by $Cr{{O}_{3}}/{{K}_{2}}C{{r}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$ in acidic media. Now, let us come to the question and see the reactions. In (i), an ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction is taking place.

Hence with the above reagents, we obtain the desired products.
Note: Steric hindrance plays a very vital role in an ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction. As steric hindrance increases the rate of ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction decreases. Thus for the same halogen the reactivity order of alkyl halides towards ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction is as under.
- Methyl halide > primary Alkyl halide > secondary Alkyl halide > tertiary Alkyl halide
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




