
What are the bond angles in the central atoms of the following: NSF, $O{{F}_{2}}$, and $IB{{r}_{2}}^{-}$ ?
Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: Bond angle of any atom in a molecule is affected by the lone pairs of electrons as well as the bonds that the atoms form in that molecule. Multiple bonds are shorter in length.
Complete answer:
Bond angle is the measure of the angle between adjacent atoms in a molecule. The bond angle decides the geometry on any molecule. These angles are affected by the lone pair of electrons on the atom.
For determining the bond angles, we look at the Lewis structures of the given compounds. The bond angles are expressed as,
For NSF,
The Lewis structure of NSF is, $\ddot{N}\equiv \ddot{S}-\underset{\scriptscriptstyle\centerdot\centerdot}{\ddot{F}}:$ , this shows that there is 1 lone pair of electron each on N and S, while 3 lone pair of electrons on F. This makes the type of the molecule to be $A{{X}_{2}}E$ type, so the molecular shape becomes bent, as
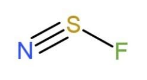
Due to the bent shape, the bond angle of the central atom is $120{}^\circ $, but due to repulsion of lone pair it decreases to nearly $117{}^\circ $.
For $O{{F}_{2}}$,
The Lewis structure is, $:\underset{\scriptscriptstyle\centerdot\centerdot}{\ddot{F}}-\underset{\scriptscriptstyle\centerdot\centerdot}{\ddot{O}}-\underset{\scriptscriptstyle\centerdot\centerdot}{\ddot{F}}:$, this shows 3 lone pair of electrons on both the F atoms, and 2 lone pairs on O. This makes the type of the molecule to be $A{{X}_{2}}{{E}_{2}}$, so the molecular shape becomes bent, as
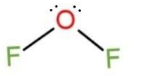
Due to bent shape, the bond angle of the central atom is $109.5{}^\circ $, but it decreases to nearly $103{}^\circ $ due to repulsion in electrons.
For $IB{{r}_{2}}^{-}$,
The Lewis structure is, ${{[:\underset{\scriptscriptstyle\centerdot\centerdot}{\ddot{B}}r-\underset{\scriptscriptstyle\centerdot\centerdot}{}-\underset{\scriptscriptstyle\centerdot\centerdot}{\ddot{B}}r:]}^{-}}$ , this shows, 3 lone pair of electrons on both the Br, and 3 lone pair on $I$. This makes the molecule to be of $A{{X}_{2}}{{E}_{3}}$ type, with trigonal bi-pyramidal geometry, as
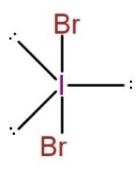
The bond pairs are on axial positions, while lone pairs on equatorial position, this makes the bond angle of the central atom to be $180{}^\circ $.
Hence, the bond angles of central atoms of molecules NSF, $O{{F}_{2}}$, and $IB{{r}_{2}}^{-}$ are near $117{}^\circ $, near $109.5{}^\circ $, and $180{}^\circ $respectively.
Note: The types of molecules and their geometry according to the number of bond pairs and lone pairs is well explained in the VSEPR, valence shell electron pair repulsion theory.
Complete answer:
Bond angle is the measure of the angle between adjacent atoms in a molecule. The bond angle decides the geometry on any molecule. These angles are affected by the lone pair of electrons on the atom.
For determining the bond angles, we look at the Lewis structures of the given compounds. The bond angles are expressed as,
For NSF,
The Lewis structure of NSF is, $\ddot{N}\equiv \ddot{S}-\underset{\scriptscriptstyle\centerdot\centerdot}{\ddot{F}}:$ , this shows that there is 1 lone pair of electron each on N and S, while 3 lone pair of electrons on F. This makes the type of the molecule to be $A{{X}_{2}}E$ type, so the molecular shape becomes bent, as

Due to the bent shape, the bond angle of the central atom is $120{}^\circ $, but due to repulsion of lone pair it decreases to nearly $117{}^\circ $.
For $O{{F}_{2}}$,
The Lewis structure is, $:\underset{\scriptscriptstyle\centerdot\centerdot}{\ddot{F}}-\underset{\scriptscriptstyle\centerdot\centerdot}{\ddot{O}}-\underset{\scriptscriptstyle\centerdot\centerdot}{\ddot{F}}:$, this shows 3 lone pair of electrons on both the F atoms, and 2 lone pairs on O. This makes the type of the molecule to be $A{{X}_{2}}{{E}_{2}}$, so the molecular shape becomes bent, as

Due to bent shape, the bond angle of the central atom is $109.5{}^\circ $, but it decreases to nearly $103{}^\circ $ due to repulsion in electrons.
For $IB{{r}_{2}}^{-}$,
The Lewis structure is, ${{[:\underset{\scriptscriptstyle\centerdot\centerdot}{\ddot{B}}r-\underset{\scriptscriptstyle\centerdot\centerdot}{}-\underset{\scriptscriptstyle\centerdot\centerdot}{\ddot{B}}r:]}^{-}}$ , this shows, 3 lone pair of electrons on both the Br, and 3 lone pair on $I$. This makes the molecule to be of $A{{X}_{2}}{{E}_{3}}$ type, with trigonal bi-pyramidal geometry, as

The bond pairs are on axial positions, while lone pairs on equatorial position, this makes the bond angle of the central atom to be $180{}^\circ $.
Hence, the bond angles of central atoms of molecules NSF, $O{{F}_{2}}$, and $IB{{r}_{2}}^{-}$ are near $117{}^\circ $, near $109.5{}^\circ $, and $180{}^\circ $respectively.
Note: The types of molecules and their geometry according to the number of bond pairs and lone pairs is well explained in the VSEPR, valence shell electron pair repulsion theory.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a labelled diagram of the human heart and label class 11 biology CBSE

What is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p class 11 chemistry CBSE




