
What are structural isomers? Name the first member of alkanes that shows structural isomerism.
Answer
504.3k+ views
Hint: A structural isomer of a compound (also known as a constitutional isomer in IUPAC terminology) is a compound having the same number of atoms of each element but logically different bonds between them. Previously, the word "metamer" was used to describe the same idea.
Complete answer:
A structural isomer, also known as a constitutional isomer, is an organic molecule that has the same chemical formula but differs in structure. The most extreme kind of isomerism is structural isomerism. It differs from stereoisomerism, which has the identical atoms and bonding system but a distinct relative spatial arrangement of the atoms. Differences between isotopes of the same element are generally overlooked. In other cases, however, distinct isotopes of the same element may be treated as separate elements. In the second example, structural isotopomers are two molecules with the same number of atoms of each isotope but different bonding schemes.
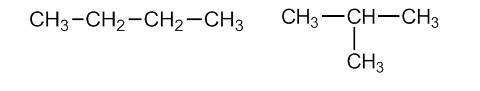
Butane is the first member of alkanes that shows structural isomerism.
Both molecules must have the same molecular formula, but the atom arrangement must be different. Take a look at the structures of n-butane and isobutane, for example. $ {C_4}{H_{10}} $ is the same chemical formula for each of these compounds. Atomic connection is the ability of atoms to communicate with one another (carbon atoms). In the case of n-butane, all carbon atoms are in a straight chain, but there is a side chain in the case of isobutane. As a result, they have distinct atom connections and are constitutional isomers of one another.
Note:
Compounds with the same molecular formula but distinct structural formulae are known as constitutional isomers. In other words, constitutional isomers differ in the way atoms in molecules are connected. We must count the number of each atom in each molecule to determine whether they are constitutional isomers of each other.
Complete answer:
A structural isomer, also known as a constitutional isomer, is an organic molecule that has the same chemical formula but differs in structure. The most extreme kind of isomerism is structural isomerism. It differs from stereoisomerism, which has the identical atoms and bonding system but a distinct relative spatial arrangement of the atoms. Differences between isotopes of the same element are generally overlooked. In other cases, however, distinct isotopes of the same element may be treated as separate elements. In the second example, structural isotopomers are two molecules with the same number of atoms of each isotope but different bonding schemes.
Butane is the first member of alkanes that shows structural isomerism.
Both molecules must have the same molecular formula, but the atom arrangement must be different. Take a look at the structures of n-butane and isobutane, for example. $ {C_4}{H_{10}} $ is the same chemical formula for each of these compounds. Atomic connection is the ability of atoms to communicate with one another (carbon atoms). In the case of n-butane, all carbon atoms are in a straight chain, but there is a side chain in the case of isobutane. As a result, they have distinct atom connections and are constitutional isomers of one another.

Note:
Compounds with the same molecular formula but distinct structural formulae are known as constitutional isomers. In other words, constitutional isomers differ in the way atoms in molecules are connected. We must count the number of each atom in each molecule to determine whether they are constitutional isomers of each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




