
How are frictional forces measured?
Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: Friction is the resistance to motion when an object is moving relative to another and the friction is of two type static and kinetic. The force of friction depends mainly on two factors- material the object and how tightly they are pushed against each other.
Complete step by step solution:
The maximum force that can be applied by a surface on an object is defined as a force of friction and is calculated by –
${{F}_{f}}={{\mu }_{f}}N$
Here ${{F}_{f}}$ = Force of friction, ${{\mu }_{f}}$ = coefficient of friction of given surface and $N$= Normal force.
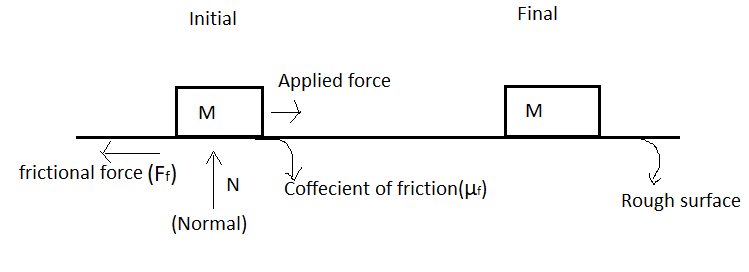
Normal force: Surface exerts a force which prevents solid objects passing through each other known as normal force and it is calculated by mass of an object $M$ and acceleration due to gravity $g$.
$N=M\cdot g$
But, in the case of an inclined surface the normal force depends on the angle of inclination as well and is given by, $N=M\cdot g\cdot \cos (\theta )$.
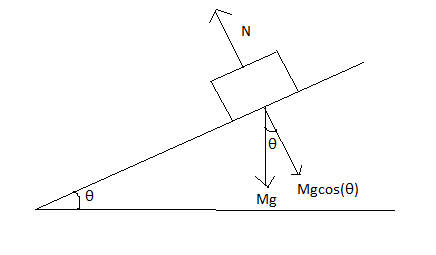
Now for calculating frictional force ,let us suppose an object is deaccelerating with $a$and stops after some time $t$ and the mass of the object is $M$ so, frictional force exerted on the object after is given by,
$F=M\cdot a$, and we know that pressure is weight per unit area so,
$P=\dfrac{M\cdot g}{A}$, here $P$=pressure per unit area and $A$is surface area of block which is in contact of surface,
Now we can calculate friction coefficient which is defined as frictional force per unit pressure on ground.
$\mu =\dfrac{F}{P}=\dfrac{M\cdot a\cdot A}{M\cdot g}=\dfrac{a.A}{g}$
So, by this coefficient of friction we can measure frictional force exerted on an object and by following this method we can calculate it for different situations and objects.
Additional information:
Static friction: static friction occurs when we try to move on object from its state of rest to motion, as we increase the amount of force static friction force will increase and try to match the force but eventually force will exceed the maximum static force and the object moves(${{\mu }_{s}}$ is coefficient of static friction).
Kinetic friction: when an object is in state of motion on the surface, I experiences a force opposite to the direction of motion known as kinetic friction (${{\mu }_{k}}$ is coefficient of kinetic friction).
Note:
There are four types of coefficient of friction which comes under the category of dry friction-
1) Static friction
2) Kinetic friction
3) Rolling friction and,
4) Sliding friction
But, in ideal problems we only deal with the static and kinetic. You can determine the coefficient by direct measurements or by clever indirect means.
Complete step by step solution:
The maximum force that can be applied by a surface on an object is defined as a force of friction and is calculated by –
${{F}_{f}}={{\mu }_{f}}N$
Here ${{F}_{f}}$ = Force of friction, ${{\mu }_{f}}$ = coefficient of friction of given surface and $N$= Normal force.

Normal force: Surface exerts a force which prevents solid objects passing through each other known as normal force and it is calculated by mass of an object $M$ and acceleration due to gravity $g$.
$N=M\cdot g$
But, in the case of an inclined surface the normal force depends on the angle of inclination as well and is given by, $N=M\cdot g\cdot \cos (\theta )$.

Now for calculating frictional force ,let us suppose an object is deaccelerating with $a$and stops after some time $t$ and the mass of the object is $M$ so, frictional force exerted on the object after is given by,
$F=M\cdot a$, and we know that pressure is weight per unit area so,
$P=\dfrac{M\cdot g}{A}$, here $P$=pressure per unit area and $A$is surface area of block which is in contact of surface,
Now we can calculate friction coefficient which is defined as frictional force per unit pressure on ground.
$\mu =\dfrac{F}{P}=\dfrac{M\cdot a\cdot A}{M\cdot g}=\dfrac{a.A}{g}$
So, by this coefficient of friction we can measure frictional force exerted on an object and by following this method we can calculate it for different situations and objects.
Additional information:
Static friction: static friction occurs when we try to move on object from its state of rest to motion, as we increase the amount of force static friction force will increase and try to match the force but eventually force will exceed the maximum static force and the object moves(${{\mu }_{s}}$ is coefficient of static friction).
Kinetic friction: when an object is in state of motion on the surface, I experiences a force opposite to the direction of motion known as kinetic friction (${{\mu }_{k}}$ is coefficient of kinetic friction).
Note:
There are four types of coefficient of friction which comes under the category of dry friction-
1) Static friction
2) Kinetic friction
3) Rolling friction and,
4) Sliding friction
But, in ideal problems we only deal with the static and kinetic. You can determine the coefficient by direct measurements or by clever indirect means.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




