
How are electric vector (\[\overrightarrow E \]), magnetic vector ($\overrightarrow B $) velocity vector ($\overrightarrow c $) oriented in an electromagnetic wave?
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint Electromagnetic waves are transverse in nature. Oscillations of the electric vector and magnetic vectors are perpendicular to the direction of the wave or path of propagation.
Complete step-by-step solution
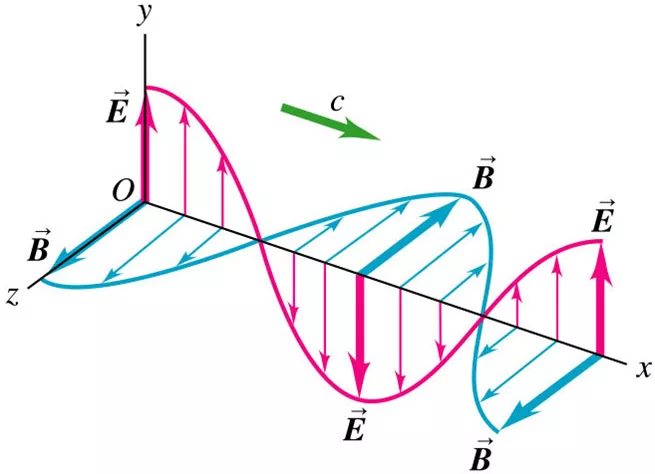
For a transverse wave like electromagnetic waves the electric vector and magnetic vector are always perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of propagation. Since electromagnetic waves propagate with speed of light, both electric vector and magnetic vector oscillates perpendicular to the velocity vector.
The direction of propagation of electromagnetic waves is the direction of $\overrightarrow {E \times B} $. If an electromagnetic wave is travelling in the positive x-axis then the direction of the electric vector is along the y-axis and the magnetic vector is along the z-axis direction.
Note Electromagnetic waves can travel through empty space. Electromagnetic waves can be produced by oscillating charges or by transition of electrons from different energy levels of the atom.
Examples of electromagnetic waves are: Radio waves, microwaves, infrared, ultraviolet rays, x-rays, gamma rays and visible light.
Complete step-by-step solution

For a transverse wave like electromagnetic waves the electric vector and magnetic vector are always perpendicular to each other and perpendicular to the direction of propagation. Since electromagnetic waves propagate with speed of light, both electric vector and magnetic vector oscillates perpendicular to the velocity vector.
The direction of propagation of electromagnetic waves is the direction of $\overrightarrow {E \times B} $. If an electromagnetic wave is travelling in the positive x-axis then the direction of the electric vector is along the y-axis and the magnetic vector is along the z-axis direction.
Note Electromagnetic waves can travel through empty space. Electromagnetic waves can be produced by oscillating charges or by transition of electrons from different energy levels of the atom.
Examples of electromagnetic waves are: Radio waves, microwaves, infrared, ultraviolet rays, x-rays, gamma rays and visible light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




