
What are chelates? Give one example and write the importance of chelate?
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint:A ligand is a molecule or an ion that is attached to the metal atom by a coordinate bonding. It donates its electron pair to form a complex. Ligands can be anionic, cationic, or neutral. Ligand acts as a Lewis base and the central metal atom acts as Lewis acid. The examples of ligands are ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}^{\text{ + }}}$, ${{\text{F}}^{\text{ - }}}$, ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$, etc, There are different types of ligands called as monodentate, bidentate, polydentate depending on the binding sites. If the ligand is bonded to the metal through one atom, it is called a monodentate ligand. Bidentate ligands have 2 atoms that can bind to the central atom at 2 points. This means that it can donate 2 pairs of electrons.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, we know what a bidentate ligand is. Here, the Ligand has 2 donor sites.
Example:- en- ethylenediamine.
${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{--C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{--C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{--N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$
We know there is one lone pair of electrons on both the N atoms.
Thus, both the N can be coordinated to the central metal atom.
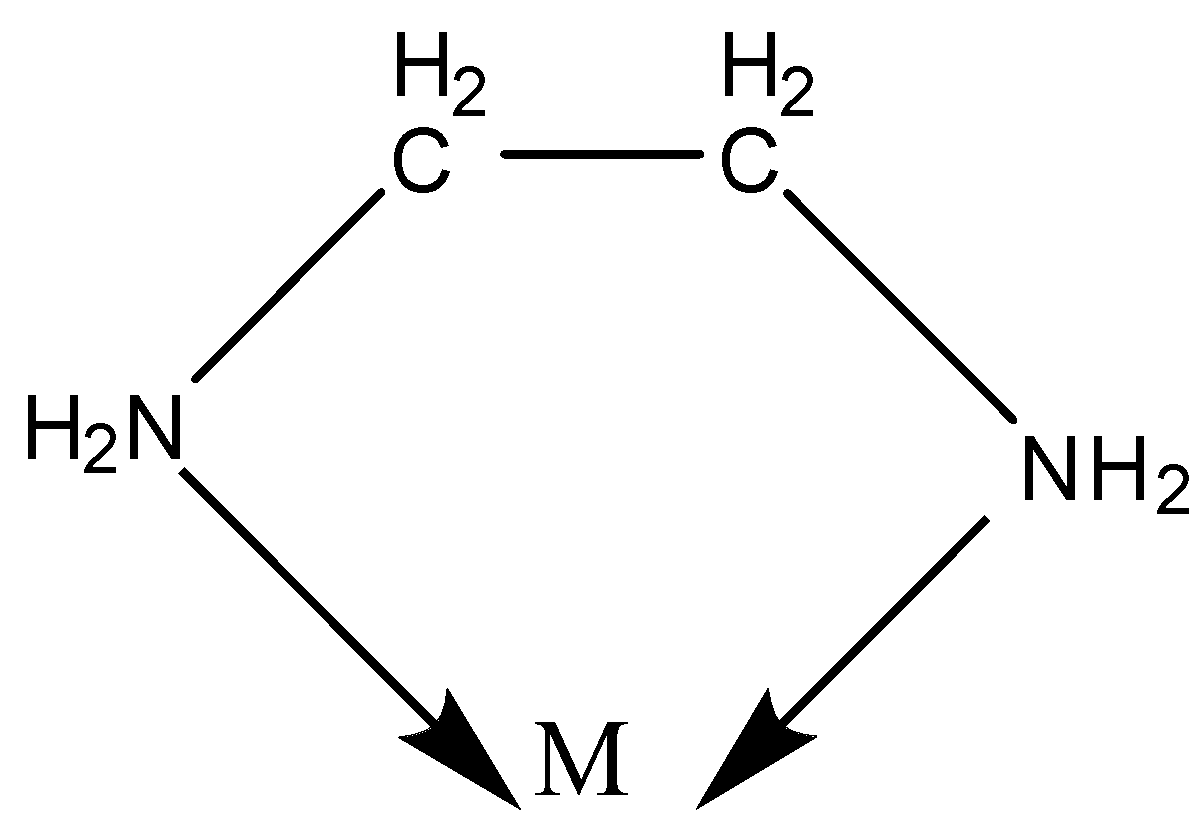
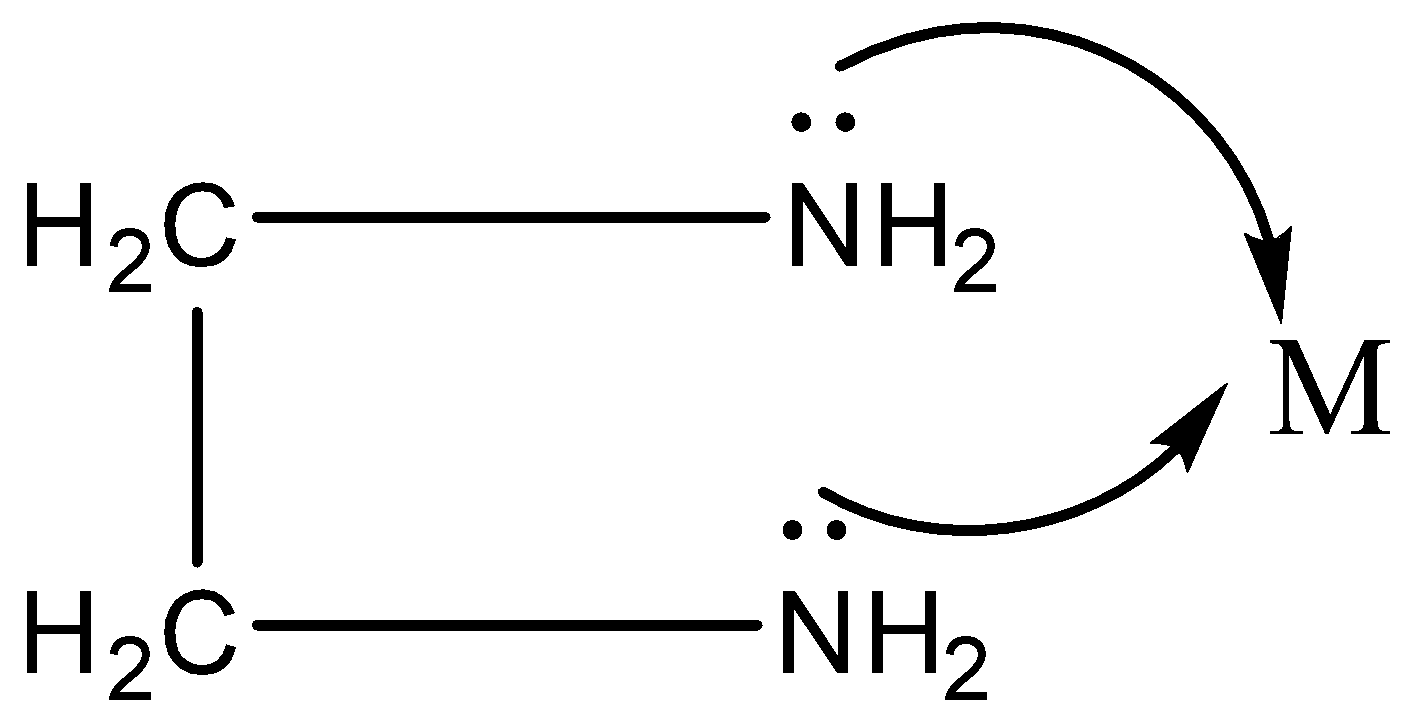
Another example of the polydentate ligand is ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) which is a hexadentate ligand. It leads to the formation of the ring.
Chelation is a process in which a bidentate or a polydentate ligand binds to the metal atom to form a ring.
The complex formed by this process is called a chelate.
The polydentate ligand which leads to chelation is called a chelating agent.
The importance of chelate is:-
It is used in chelation therapy to remove toxic substances from the body (in lead poisoning)
It is used as a contrast agent in MRI scanning.
It is used in chemical water treatments to remove metals.
They can also be used to separate lanthanides and actinides.
Note: As we discussed monodentate ligand donates a lone pair of electrons and bind to the central atom at one point. ${{\text{[Cu(N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{]}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}$. Here each ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ group is linked to the metal by only one atom. In the above complexes, ” $ \to $ ” shows the coordinate bond. A complex $[CaN{a_2}EDTA]$ is given to a person who has consumed lead. The lead present in the bloodstream forms a complex $[PbN{a_2}EDTA]$ and Ca is left behind. $[PbN{a_2}EDTA]$ is more stable and complex and excreted. The chelating complex also has an application in agriculture.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, we know what a bidentate ligand is. Here, the Ligand has 2 donor sites.
Example:- en- ethylenediamine.
${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{--C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{--C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{--N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$
We know there is one lone pair of electrons on both the N atoms.
Thus, both the N can be coordinated to the central metal atom.


Another example of the polydentate ligand is ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) which is a hexadentate ligand. It leads to the formation of the ring.
Chelation is a process in which a bidentate or a polydentate ligand binds to the metal atom to form a ring.
The complex formed by this process is called a chelate.
The polydentate ligand which leads to chelation is called a chelating agent.
The importance of chelate is:-
It is used in chelation therapy to remove toxic substances from the body (in lead poisoning)
It is used as a contrast agent in MRI scanning.
It is used in chemical water treatments to remove metals.
They can also be used to separate lanthanides and actinides.
Note: As we discussed monodentate ligand donates a lone pair of electrons and bind to the central atom at one point. ${{\text{[Cu(N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{]}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}$. Here each ${\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$ group is linked to the metal by only one atom. In the above complexes, ” $ \to $ ” shows the coordinate bond. A complex $[CaN{a_2}EDTA]$ is given to a person who has consumed lead. The lead present in the bloodstream forms a complex $[PbN{a_2}EDTA]$ and Ca is left behind. $[PbN{a_2}EDTA]$ is more stable and complex and excreted. The chelating complex also has an application in agriculture.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




