
What are chelates? Give an example and write the importance of chelate.
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint:
When polydentate ligands bond with the central atom and form an organic compound is called chelate. There are so many examples of chelates. It is a heterocyclic compound which reacts to form a chelate and form a ring by forming one or more hydrogen bonds. It works by binding metal in the bloodstream.
Complete step by step answer:
Chelate, any of a class of coordination or complex compounds consisting of a central metal atom attached to a large molecule, called a ligand, in a cyclic or ring structure.
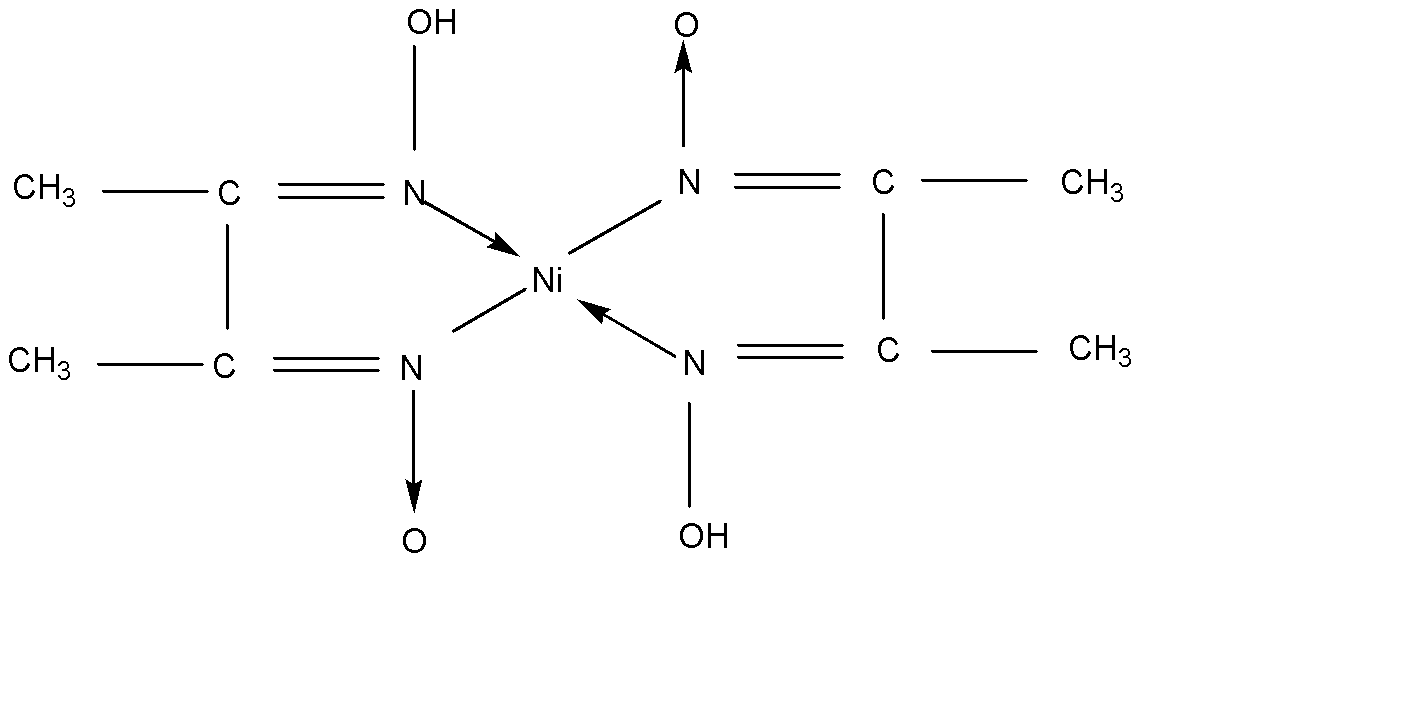
There are so many examples of chelate. Here we try to understand about chelates with example:
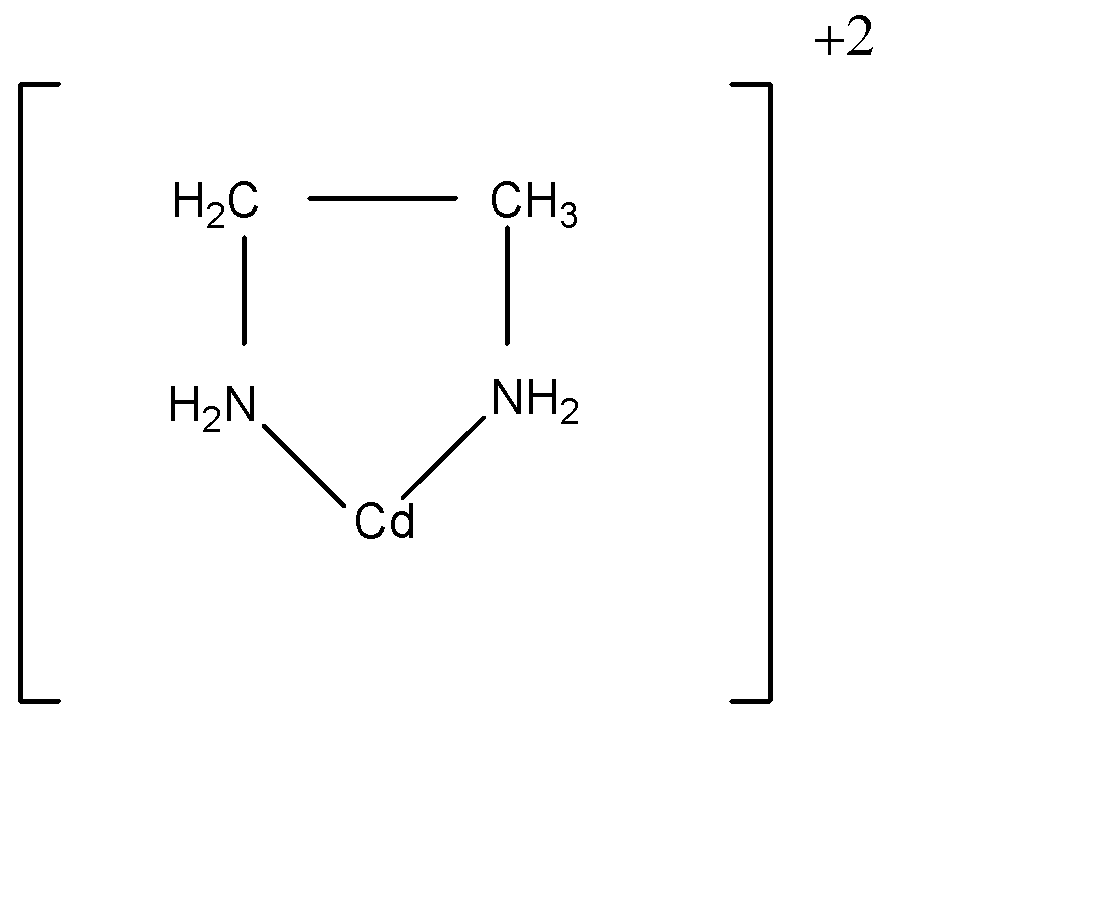
The other example of chelate is:
Ethylene diamine ligand has two points of attachment to the cadmium ion, thus forming a ring; it is known as a bidentate ligand. Ligands that can attach to the same metal ion at two or more points are known as polydentate ligands.
Importance of chelate:
1.It attaches minerals to other substances, such as organic in order to increase their bioavailability.
2.It is useful for softening hard water.
3.It is used in separation of lanthanides and actinides.
4.It is based upon the target heavy metal like iron, copper, mercury and lead being the major targets.
5.It is useful for providing nutritional supplements.
Note:Chelate any class of complex compounds consisting of ligands and metal atoms and form a chelate ring. Chelates are stable complexes of metal ions with organic substance as a result of ring shaped bonds. The stability is a result of the bond between the chelator, which has more than one pair of free electrons, and the central metal ion.
When polydentate ligands bond with the central atom and form an organic compound is called chelate. There are so many examples of chelates. It is a heterocyclic compound which reacts to form a chelate and form a ring by forming one or more hydrogen bonds. It works by binding metal in the bloodstream.
Complete step by step answer:
Chelate, any of a class of coordination or complex compounds consisting of a central metal atom attached to a large molecule, called a ligand, in a cyclic or ring structure.
There are so many examples of chelate. Here we try to understand about chelates with example:

The other example of chelate is:

Ethylene diamine ligand has two points of attachment to the cadmium ion, thus forming a ring; it is known as a bidentate ligand. Ligands that can attach to the same metal ion at two or more points are known as polydentate ligands.
Importance of chelate:
1.It attaches minerals to other substances, such as organic in order to increase their bioavailability.
2.It is useful for softening hard water.
3.It is used in separation of lanthanides and actinides.
4.It is based upon the target heavy metal like iron, copper, mercury and lead being the major targets.
5.It is useful for providing nutritional supplements.
Note:Chelate any class of complex compounds consisting of ligands and metal atoms and form a chelate ring. Chelates are stable complexes of metal ions with organic substance as a result of ring shaped bonds. The stability is a result of the bond between the chelator, which has more than one pair of free electrons, and the central metal ion.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




