
Archaebacteria differ from eubacteria in which one of the following respects?
(a) Their cell wall lack peptidoglycan
(b) They inhabit extreme environment
(c) They have unique 16s RNA.
(d) All of the above.
Answer
530.3k+ views
Hint: Archaebacteria range from different bacteria (eubacteria) in having a different cell wall structure and this characteristic is reason for their survival in intense conditions.
Complete answer:To answer this question, at first, we have to know the difference between archaebacteria and eubacteria. Archaebacteria typically have the identical shape, size, vitamins and look like microorganisms (bacteria). They multiply by using binary fission. However, archaebacteria cell walls do not comprise peptidoglycan. They additionally have an exceptional membrane lipid bond as compared to the bacteria and eukarya. Archaeal membrane lipids have ether bonds whereas microorganisms like bacteria has ester-related lipids.
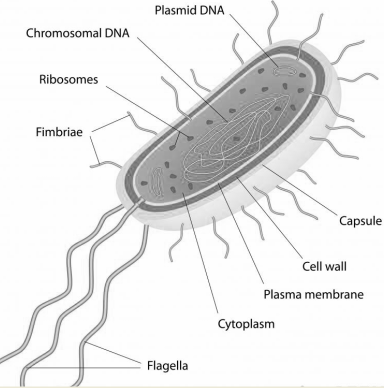
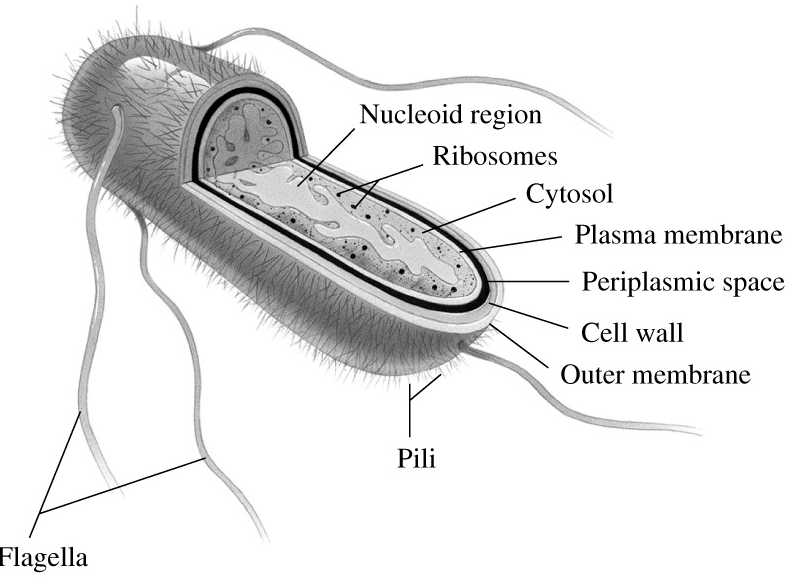
Fig- Archaebacteria and eubacteria structure.
Now lets us find the solution from given options -
The cell wall of archaea consists of S-layers and lacks peptidoglycan molecules with the exception of methanobacteria who have pseudopeptidoglycan in their cell wall. Eubacteria are enclosed by a cell wall. The wall is made of cross-connected chains of peptidoglycan, a polymer that mixes amino acids and sugar chains.
Rather than having one primary set of adaptations that works for all environments, Archaea have developed separate protein functions that are adapted for each environment. These archaebacteria and eubacteria can live in excessive salt concentration, excessive temperature, excessive pressure etc.
Additional information: The 16S rRNA gene is used for phylogenetic research as it is highly conserved among extraordinary species of microorganisms like bacteria and archaea. Botharchaebacteria and eubacteria have genetically extraordinary 16S rRNA.
Thus, the right answer is, ‘All of the above’.
Note:The mode of reproduction, food and cellular structure of archaebacteria resembles a regular eubacteria. Their cell walls, composed of a few polymers, however do not consist of peptidoglycan unlike eubacteria. Lipids in their cytoplasmic membranes are ether connected unlike eubacteria which comprise glycerol ester lipids of their cell membrane.
Complete answer:To answer this question, at first, we have to know the difference between archaebacteria and eubacteria. Archaebacteria typically have the identical shape, size, vitamins and look like microorganisms (bacteria). They multiply by using binary fission. However, archaebacteria cell walls do not comprise peptidoglycan. They additionally have an exceptional membrane lipid bond as compared to the bacteria and eukarya. Archaeal membrane lipids have ether bonds whereas microorganisms like bacteria has ester-related lipids.


Fig- Archaebacteria and eubacteria structure.
Now lets us find the solution from given options -
The cell wall of archaea consists of S-layers and lacks peptidoglycan molecules with the exception of methanobacteria who have pseudopeptidoglycan in their cell wall. Eubacteria are enclosed by a cell wall. The wall is made of cross-connected chains of peptidoglycan, a polymer that mixes amino acids and sugar chains.
Rather than having one primary set of adaptations that works for all environments, Archaea have developed separate protein functions that are adapted for each environment. These archaebacteria and eubacteria can live in excessive salt concentration, excessive temperature, excessive pressure etc.
Additional information: The 16S rRNA gene is used for phylogenetic research as it is highly conserved among extraordinary species of microorganisms like bacteria and archaea. Botharchaebacteria and eubacteria have genetically extraordinary 16S rRNA.
Thus, the right answer is, ‘All of the above’.
Note:The mode of reproduction, food and cellular structure of archaebacteria resembles a regular eubacteria. Their cell walls, composed of a few polymers, however do not consist of peptidoglycan unlike eubacteria. Lipids in their cytoplasmic membranes are ether connected unlike eubacteria which comprise glycerol ester lipids of their cell membrane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




