
Arachidonic acid is a
(a)Non-essential fatty acid
(b)Saturated fatty acid
(c)Monounsaturated fatty acid
(d)Polyunsaturated fatty acid
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The given molecule is a 20-carbon chain organic acid molecule with four cis double bonds. The degree of saturation can be determined by the presence and the number of double bonds present in the carbon chain.
Complete answer:
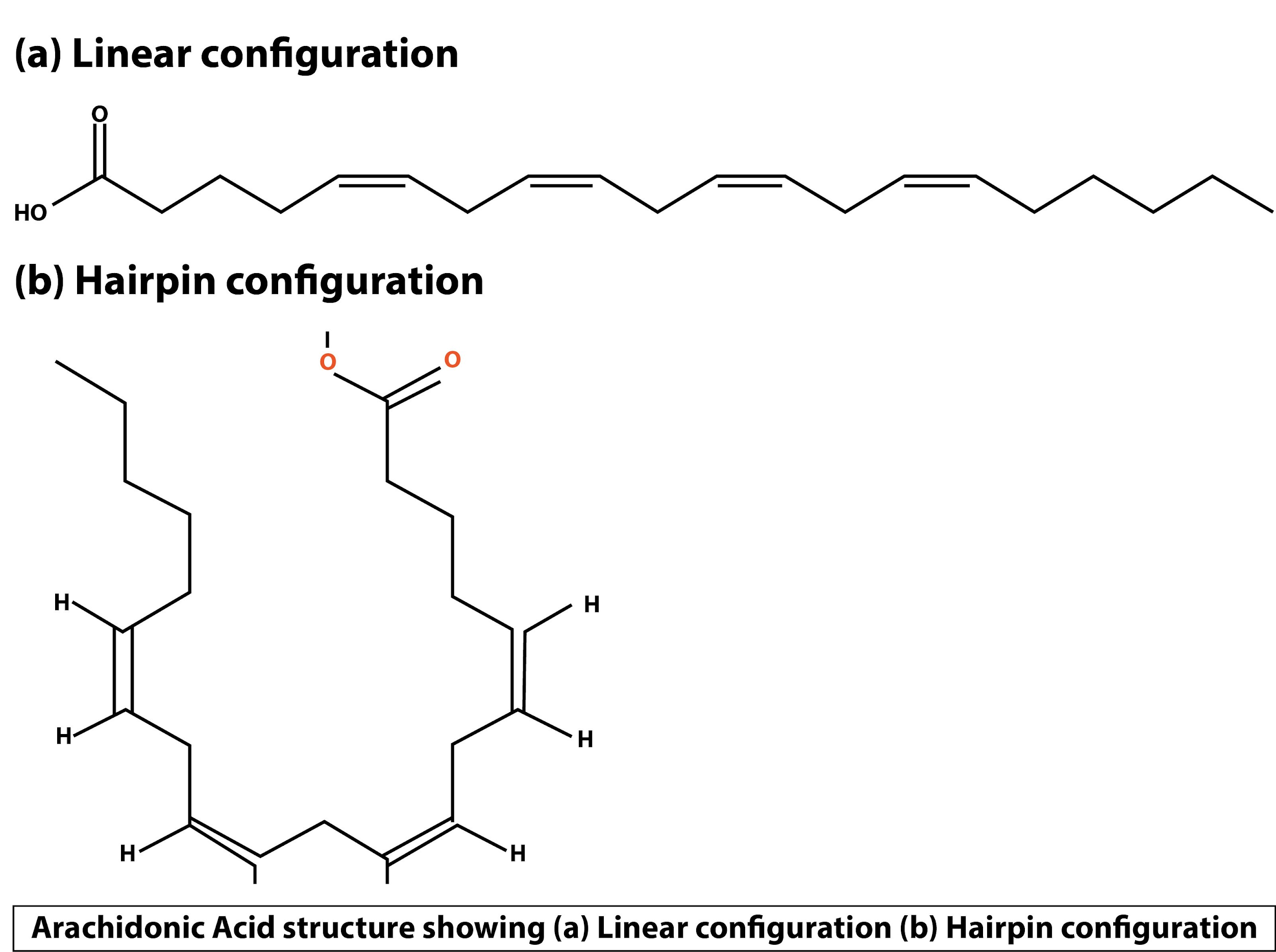
Arachidonic acid is a 20-carbon chain fatty acid which has four cis double bonds, making it a polyunsaturated fatty acid. It contains a carboxylic acid group.
- It is present in the phospholipids, such as phosphatidylinositide, of the membranes of the body’s cells. It is present most abundantly in skeletal muscles of the body. It is also widely present in the brain and liver.
Additional Information: - Arachidonic acid is not an essential fatty acid but it becomes essential when the body lacks linoleic acid or the body is somehow not able to convert linoleic acid to arachidonic acid. It is known as a conditionally essential fatty acid.
- Arachidonic acid in the body is involved in the body’s cellular signaling as a lipid second messenger. It is also involved in vasodilation.
- It is obtained from the metabolism of plant-based linoleic acid. Linoleic acid undergoes desaturation and elongation to form arachidonic acid.
- Non-essential fatty acids are those fatty acids that the body can synthesize from our diet.
- Saturated fatty acids are organic acids containing saturated carbons. They contain an even number of carbon atoms.
- Monounsaturated fatty acids have only one double bond in their chain.
So, the correct answer is ‘polyunsaturated fatty acid’.
Note: - The IUPAC name of arachidonic acid is (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic acid.
-Other names of arachidonic acid are 5,8,11,14-all-cis-Eicosatetraenoic acid, all-cis-5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic acid, and Arachidonate.
Complete answer:
Arachidonic acid is a 20-carbon chain fatty acid which has four cis double bonds, making it a polyunsaturated fatty acid. It contains a carboxylic acid group.
- It is present in the phospholipids, such as phosphatidylinositide, of the membranes of the body’s cells. It is present most abundantly in skeletal muscles of the body. It is also widely present in the brain and liver.
Additional Information: - Arachidonic acid is not an essential fatty acid but it becomes essential when the body lacks linoleic acid or the body is somehow not able to convert linoleic acid to arachidonic acid. It is known as a conditionally essential fatty acid.
- Arachidonic acid in the body is involved in the body’s cellular signaling as a lipid second messenger. It is also involved in vasodilation.
- It is obtained from the metabolism of plant-based linoleic acid. Linoleic acid undergoes desaturation and elongation to form arachidonic acid.
- Non-essential fatty acids are those fatty acids that the body can synthesize from our diet.
- Saturated fatty acids are organic acids containing saturated carbons. They contain an even number of carbon atoms.
- Monounsaturated fatty acids have only one double bond in their chain.
So, the correct answer is ‘polyunsaturated fatty acid’.
Note: - The IUPAC name of arachidonic acid is (5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)-5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic acid.
-Other names of arachidonic acid are 5,8,11,14-all-cis-Eicosatetraenoic acid, all-cis-5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic acid, and Arachidonate.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




