
Antibodies are which type of proteins?
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: Antibodies, or immunoglobulins, are glycoprotein molecules generated by plasma cells (white blood cells). They are an important aspect of the immune response because they recognise and attach to certain antigens, such as bacteria or viruses, and help to destroy them.
Immunoglobulins also have two functions: as antigen receptors on cell surfaces that allow for cell signalling and activation, and as soluble effector molecules that can bind and destroy antigens at a distance.
IgM antibodies are the most powerful antibodies. They are the first type of antibody produced in response to an infection and are detected in blood and lymph fluid. Other immune system cells are also triggered to destroy foreign substances. IgM antibodies account for roughly 5% to 10% of all antibodies in the body.
Complete answer:
Immunoglobulins are glycoprotein that are associated with the immune system and are called antibodies. Each antibody is made up of two heavy chains and two light chains that are linked together to form a "Y" shaped molecule.
Immunoglobulin (Ig) is another name for an antibody (Ab) (Ig). Plasma cells create these big, Y-shaped blood proteins. They attach to and infiltrate foreign particles. Antibodies attack these particles because they are alien bodies.
Antigens are foreign pathogens that infiltrate the body and can elicit an immune response from our immune system by forming a complex with a bigger molecule or by attaching to antibodies for a specific immunological response. As a result, antigens trigger the immune system's manufacture of antibodies.
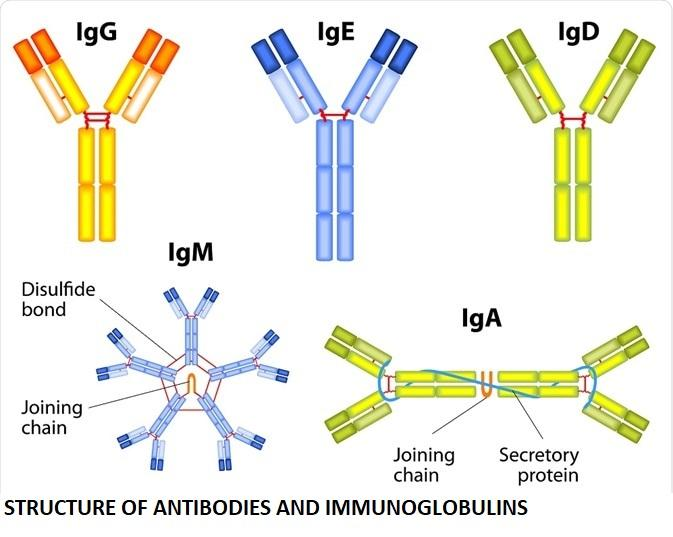
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins (Ig), are divided into five isotypes. This categorization is based on their H chains. Antibodies come in a variety of forms, including: IgM, IgG, IgA, IgD,IdE
The following are some of the most important roles of antibodies:
Identifies pathogens and binds to them.
In the case of bacterial pathogens, it activates the immune system.
Viral pathogens are directly attacked.
Helps with phagocytosis.
Note:
Structure of antibody-
An antibody is made up of four polypeptide subunits and has a Y-shaped structure. Each subunit has two light and heavy chains that are identical.
Each heavy chain's N-terminus creates an antigen-binding domain with a light chain. The arms of the "Y" shape are made up of two antigen-binding domains. Fragment antigen-binding (Fab) domains are what they're called.
The heavy chains' C-terminus produces the 'fragment crystallisation' (Fc) domain, which aids contact with effector cells.
Disulfide and non-covalent linkages hold all four polypeptide subunits together.
A variable area and three consistent sections are found in the heavy chains of antibodies. Each antibody has two antigen-binding sites that are identical yet differ in the antibodies.
Immunoglobulins also have two functions: as antigen receptors on cell surfaces that allow for cell signalling and activation, and as soluble effector molecules that can bind and destroy antigens at a distance.
IgM antibodies are the most powerful antibodies. They are the first type of antibody produced in response to an infection and are detected in blood and lymph fluid. Other immune system cells are also triggered to destroy foreign substances. IgM antibodies account for roughly 5% to 10% of all antibodies in the body.
Complete answer:
Immunoglobulins are glycoprotein that are associated with the immune system and are called antibodies. Each antibody is made up of two heavy chains and two light chains that are linked together to form a "Y" shaped molecule.
Immunoglobulin (Ig) is another name for an antibody (Ab) (Ig). Plasma cells create these big, Y-shaped blood proteins. They attach to and infiltrate foreign particles. Antibodies attack these particles because they are alien bodies.
Antigens are foreign pathogens that infiltrate the body and can elicit an immune response from our immune system by forming a complex with a bigger molecule or by attaching to antibodies for a specific immunological response. As a result, antigens trigger the immune system's manufacture of antibodies.
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins (Ig), are divided into five isotypes. This categorization is based on their H chains. Antibodies come in a variety of forms, including: IgM, IgG, IgA, IgD,IdE
The following are some of the most important roles of antibodies:
Identifies pathogens and binds to them.
In the case of bacterial pathogens, it activates the immune system.
Viral pathogens are directly attacked.
Helps with phagocytosis.

Note:
Structure of antibody-
An antibody is made up of four polypeptide subunits and has a Y-shaped structure. Each subunit has two light and heavy chains that are identical.
Each heavy chain's N-terminus creates an antigen-binding domain with a light chain. The arms of the "Y" shape are made up of two antigen-binding domains. Fragment antigen-binding (Fab) domains are what they're called.
The heavy chains' C-terminus produces the 'fragment crystallisation' (Fc) domain, which aids contact with effector cells.
Disulfide and non-covalent linkages hold all four polypeptide subunits together.
A variable area and three consistent sections are found in the heavy chains of antibodies. Each antibody has two antigen-binding sites that are identical yet differ in the antibodies.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




