
An organic compound \[X\] of molecular formula ${C_2}{H_4}{O_2}$ gives brisk effervescence with $NaHC{O_3}$ . Give the name of the formula of $X$
Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint: We will first try to draw the structural formula of the organic compound. Also, we know Brisk effervescence means release of bubbles. Brisk effervescence is observed when there is a release of the gas called carbon dioxide. Since two atoms of oxygen are present, two structural isomers are possible namely a carboxylic acid or an ester.
Complete solution:
So, the two functional isomers formed are:
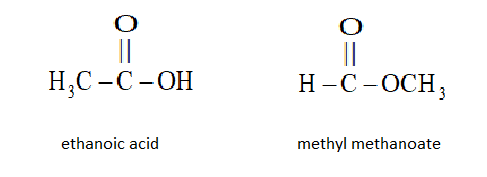
A carboxylic acid and an ester will be formed.
We know that esters do not react with $NaHC{O_3}$ while carboxylic acids will react with $NaHC{O_3}$ and to the brisk effervescence of carbon dioxide.
Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate to form sodium acetate and water with the release of carbon dioxide.
$2C{H_3}COOH + 2NaHC{O_3} \to 2C{H_3}COONa + C{O_2} + {H_2}O$
This is a very common test used for the identification of carboxylic acid in functional group analysis.
Let us have a look on how to write the IUPAC name of the compound:
Here we see that since two carbon atoms are present so the root word will be ‘eth’. And also, a single bond is present between carbon and hydrogen atoms so the root word will become ethane. It is an acid so, ‘oic’ will be used as the suffix. Hence the name of the acid is ethanoic acid.
Therefore, the compound \[X\] of molecular formula ${C_2}{H_4}{O_2}$ is ethanoic acid also known as acetic acid.
Note:We know that here the reaction is taking place between an acid and a base so the reaction will be named as the neutralization reaction. In neutralization reaction acid reacts with base to form salt and water. Hence in the above reaction the salt which is being formed is sodium acetate salt with the release of water and carbon dioxide.
Complete solution:
So, the two functional isomers formed are:
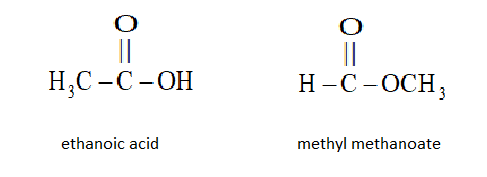
A carboxylic acid and an ester will be formed.
We know that esters do not react with $NaHC{O_3}$ while carboxylic acids will react with $NaHC{O_3}$ and to the brisk effervescence of carbon dioxide.
Ethanoic acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate to form sodium acetate and water with the release of carbon dioxide.
$2C{H_3}COOH + 2NaHC{O_3} \to 2C{H_3}COONa + C{O_2} + {H_2}O$
This is a very common test used for the identification of carboxylic acid in functional group analysis.
Let us have a look on how to write the IUPAC name of the compound:
Here we see that since two carbon atoms are present so the root word will be ‘eth’. And also, a single bond is present between carbon and hydrogen atoms so the root word will become ethane. It is an acid so, ‘oic’ will be used as the suffix. Hence the name of the acid is ethanoic acid.
Therefore, the compound \[X\] of molecular formula ${C_2}{H_4}{O_2}$ is ethanoic acid also known as acetic acid.
Note:We know that here the reaction is taking place between an acid and a base so the reaction will be named as the neutralization reaction. In neutralization reaction acid reacts with base to form salt and water. Hence in the above reaction the salt which is being formed is sodium acetate salt with the release of water and carbon dioxide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




