
An organic compound (A) with molecular formula, \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{O}}\] forms an orange-red precipitate with 2,4-DNP reagent and gives yellow precipitate on heating with iodine in the presence of sodium hydroxide. lt neither reduces Tollens' or Fehling's reagent, nor does it decolourise bromine water or Baeyer's reagent. On drastic oxidation with chromic acid, it gives a carboxylic acid (B) having molecular formula, \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_2}\] . Identify the compounds (A) and (B) and explain the reactions involved.
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint:From the given molecular formula, calculate the degree of unsaturation. You can confirm the presence of the carbonyl group by the reaction with 2,4-DNP. You can use the test with Tollen’s reagent or with Fehling’s solution to confirm absence of an aldehyde group. From the product obtained on vigorous oxidation, you can determine the structure of the starting material.
Complete answer:
The organic compound has the molecular formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{O}}\]
The molecular formula of the corresponding saturated compound is \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{18}}}}{\text{O}}\] .
Calculate the degree of unsaturation:
\[\dfrac{{18 - 8}}{2} = \dfrac{{10}}{2} = 5\]
A benzene nucleus has a degree of unsaturation of 4. A benzene nucleus has one ring and three carbon-carbon double bonds.
Thus, the given compound with degree of unsaturation of 5 has a benzene nucleus and a double bond.
The compound (A) forms an orange-red precipitate with 2,4-DNP reagent. This confirms the presence of the carbonyl group. The compound (A) gives yellow precipitate on heating with iodine in the presence of sodium hydroxide. This confirms the presence of methyl keto groups.
The compound (A) neither reduces Tollens' or Fehling's reagent. It confirms the absence of the aldehyde group.
The compound (A) neither decolourises bromine water nor Baeyer's reagent. It confirms the absence of carbon-carbon double or triple bonds.
From this information, you can conclude that the compound is acetophenone.
When you subject acetophenone to vigorous oxidation, you obtain benzoic acid (compound (B) with molecular formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_2}\] .
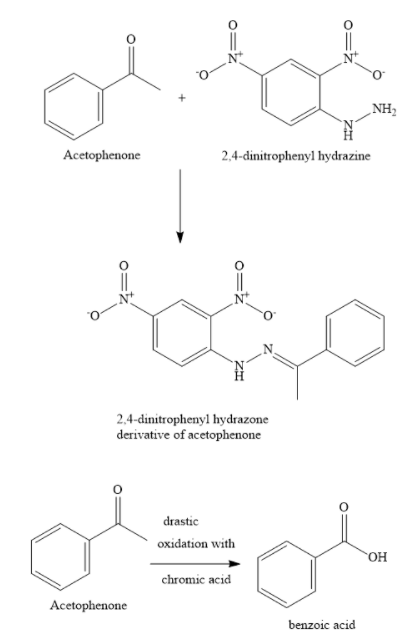
Hence, the compound (A) is acetophenone and the compound (B) is benzoic acid.
Note:
An aldehyde (or a ketone) reacts with 2,4-DNP to form a 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazone derivative. Here, 2,4-DNP reagent means 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine. Aldehydes are oxidized by Tollen’s reagent to give black silver mirror. Tollen’s reagent is an ammoniacal silver nitrate solution. Ketones do not react with Tollen’s reagent. Silver mirror test is used to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones.
Complete answer:
The organic compound has the molecular formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{8}}}{\text{O}}\]
The molecular formula of the corresponding saturated compound is \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{18}}}}{\text{O}}\] .
Calculate the degree of unsaturation:
\[\dfrac{{18 - 8}}{2} = \dfrac{{10}}{2} = 5\]
A benzene nucleus has a degree of unsaturation of 4. A benzene nucleus has one ring and three carbon-carbon double bonds.
Thus, the given compound with degree of unsaturation of 5 has a benzene nucleus and a double bond.
The compound (A) forms an orange-red precipitate with 2,4-DNP reagent. This confirms the presence of the carbonyl group. The compound (A) gives yellow precipitate on heating with iodine in the presence of sodium hydroxide. This confirms the presence of methyl keto groups.
The compound (A) neither reduces Tollens' or Fehling's reagent. It confirms the absence of the aldehyde group.
The compound (A) neither decolourises bromine water nor Baeyer's reagent. It confirms the absence of carbon-carbon double or triple bonds.
From this information, you can conclude that the compound is acetophenone.
When you subject acetophenone to vigorous oxidation, you obtain benzoic acid (compound (B) with molecular formula \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{7}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_2}\] .

Hence, the compound (A) is acetophenone and the compound (B) is benzoic acid.
Note:
An aldehyde (or a ketone) reacts with 2,4-DNP to form a 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazone derivative. Here, 2,4-DNP reagent means 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine. Aldehydes are oxidized by Tollen’s reagent to give black silver mirror. Tollen’s reagent is an ammoniacal silver nitrate solution. Ketones do not react with Tollen’s reagent. Silver mirror test is used to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




