
An organic compound A having molecular formula \[{C_6}{H_6}O\] gives a violet colour with neutral \[FeC{l_3}\] solution. A on treatment with $C{O_2}$ and NaOH at 400K under pressure gives B on acidification gives a compound C. The compound C reacts with acetyl chloride to give D which is a popular pain killer. Deduce structure of A, B, C and D.
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: Phenol react with $C{O_2}$ and NaOH at 400K under pressure gives Salicylic acid (i.e. Kolbe–Schmitt reaction)
Complete step by step answer:
Given question can be represented as:
A\[ + FeC{l_3} \to \] Violet colour
A$\xrightarrow[{400K}]{{C{O_2},NaOH}}B\xrightarrow{{Acidification}}C\xrightarrow{{{\text{Acetyl Chloride}}}}D$
Here the formation of a given violet compound on reaction with\[FeC{l_3}\] i.e. first step confirms that the given compound has a phenolic group. Second reaction of A to form B, C and then to D is the Kolbe-Schmitt reaction.
Step-1
In this step phenol reacts with \[FeC{l_3}\] and forms a violet colour compound. This reaction is an identification reaction for phenolic groups.
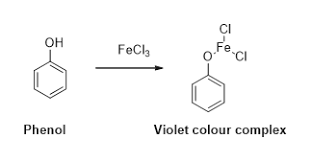
So the compound A is Phenol.
Step-2
This is a typical Kolbe Schmitt reaction in which an addition reaction occurs. This is a carboxylation reaction in which the sodium phenoxide forms first then it will react with carbon dioxide and form sodium salicylate. Sodium salicylate will form salicylic acid on acidification by sulphuric acid. The reaction occurs as the image showing below:
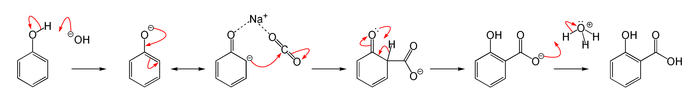
So the compound B is sodium salicylate and C is salicylic acid.
Step-3
On acetylation salicylic acid Acetyl salicylic acid formation takes place which is commonly known as aspirin i.e. a pain killer.
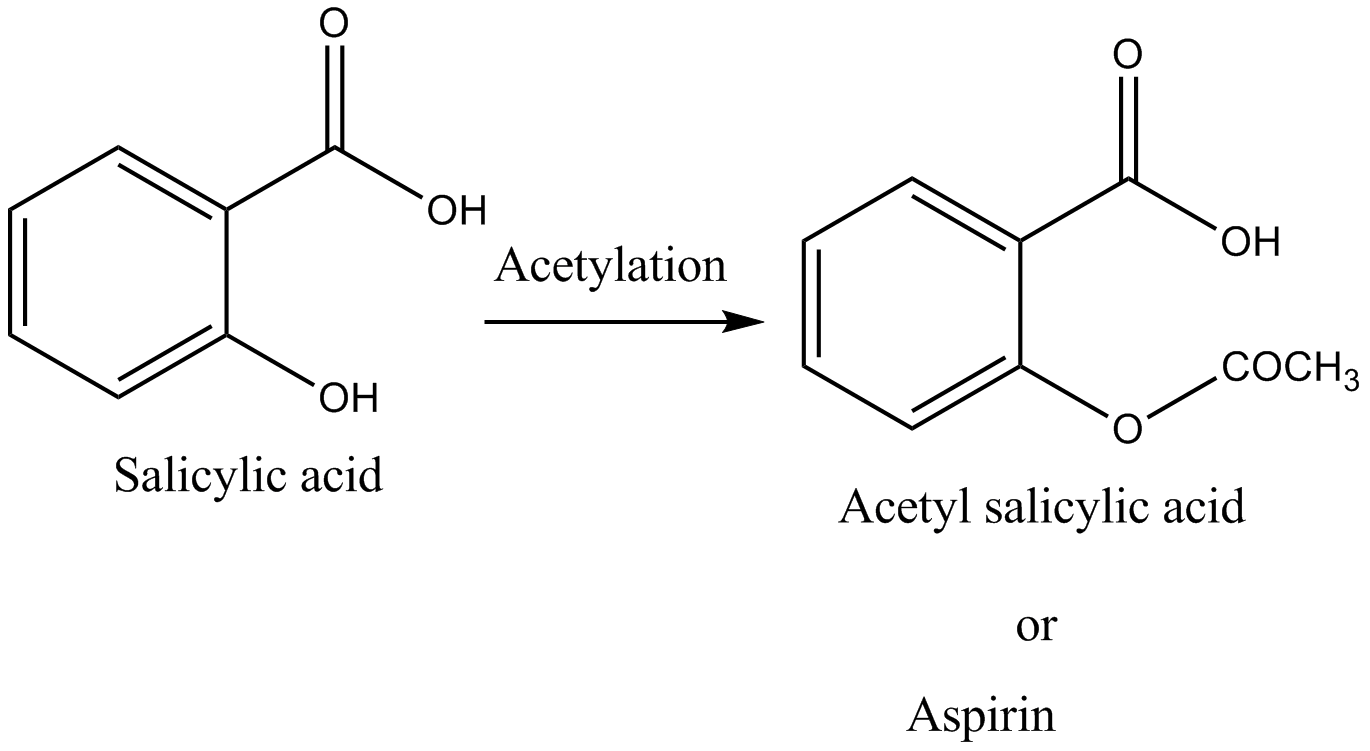
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Just identify the starting product and the end product very carefully. Starting with phenol given the type of reaction it is and identification of the painkiller aspirin will help in finding the final product.
Complete step by step answer:
Given question can be represented as:
A\[ + FeC{l_3} \to \] Violet colour
A$\xrightarrow[{400K}]{{C{O_2},NaOH}}B\xrightarrow{{Acidification}}C\xrightarrow{{{\text{Acetyl Chloride}}}}D$
Here the formation of a given violet compound on reaction with\[FeC{l_3}\] i.e. first step confirms that the given compound has a phenolic group. Second reaction of A to form B, C and then to D is the Kolbe-Schmitt reaction.
Step-1
In this step phenol reacts with \[FeC{l_3}\] and forms a violet colour compound. This reaction is an identification reaction for phenolic groups.

So the compound A is Phenol.
Step-2
This is a typical Kolbe Schmitt reaction in which an addition reaction occurs. This is a carboxylation reaction in which the sodium phenoxide forms first then it will react with carbon dioxide and form sodium salicylate. Sodium salicylate will form salicylic acid on acidification by sulphuric acid. The reaction occurs as the image showing below:

So the compound B is sodium salicylate and C is salicylic acid.
Step-3
On acetylation salicylic acid Acetyl salicylic acid formation takes place which is commonly known as aspirin i.e. a pain killer.

So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Just identify the starting product and the end product very carefully. Starting with phenol given the type of reaction it is and identification of the painkiller aspirin will help in finding the final product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




