
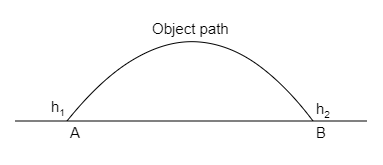
An object thrown at a certain angle to the ground moves in a curved path and falls back to the ground. The initial and the final points of the path of the object lie on the same horizontal line. What is the work done by the force of gravity on the object?
Answer
585.6k+ views
HintThe work done by the force of gravity on the object is determined by using the relation between the work done by the force of gravity on the object and the change in potential energy of the object. The initial and final points of the path of the object lie in the same horizontal point, by using this information also the solution can be easily determined.
Formulae Used:
The relation between the work done by the force of gravity on the object and the change in potential energy of the object is,
${W_g} = - \Delta P.E$
Where, ${W_g}$ is the work done by the force of gravity and $\Delta P.E$ is the change in potential energy.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The potential energy is equal to the product of mass, acceleration due to gravity and the height.
$P.E = mgh$
Where, $m$ is the mass, $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and $h$ is the height.
Now,
${W_g} = - \Delta P.E\,.................\left( 1 \right)$
The change in potential energy is also written as,
${W_g} = - \left( {mg{h_1} - mg{h_2}} \right)\,............\left( 2 \right)$
Here, ${h_1}$ and ${h_2}$ are the initial and final height of the object.
It is given that the initial and the final points of the path of the object lie on the same horizontal line. So, ${h_1} = {h_2}$
By substituting ${h_1} = {h_2}$ in the equation (2), then
${W_g} = - \left( {mg{h_2} - mg{h_2}} \right)$
By subtracting, then the above equation is written as,
${W_g} = 0$
Hence, the work done by the force of gravity on the object is equal to zero.
Note:- Here the mass of the object and acceleration due to gravity are same, then the height also same, so the terms will cancel each other. This question can be solved by another method also, by using the work, force and displacement relation. As the object moves back to the same horizontal line, then displacement is zero, so the work done also is zero.
Formulae Used:
The relation between the work done by the force of gravity on the object and the change in potential energy of the object is,
${W_g} = - \Delta P.E$
Where, ${W_g}$ is the work done by the force of gravity and $\Delta P.E$ is the change in potential energy.

Complete step-by-step solution:
The potential energy is equal to the product of mass, acceleration due to gravity and the height.
$P.E = mgh$
Where, $m$ is the mass, $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and $h$ is the height.
Now,
${W_g} = - \Delta P.E\,.................\left( 1 \right)$
The change in potential energy is also written as,
${W_g} = - \left( {mg{h_1} - mg{h_2}} \right)\,............\left( 2 \right)$
Here, ${h_1}$ and ${h_2}$ are the initial and final height of the object.
It is given that the initial and the final points of the path of the object lie on the same horizontal line. So, ${h_1} = {h_2}$
By substituting ${h_1} = {h_2}$ in the equation (2), then
${W_g} = - \left( {mg{h_2} - mg{h_2}} \right)$
By subtracting, then the above equation is written as,
${W_g} = 0$
Hence, the work done by the force of gravity on the object is equal to zero.
Note:- Here the mass of the object and acceleration due to gravity are same, then the height also same, so the terms will cancel each other. This question can be solved by another method also, by using the work, force and displacement relation. As the object moves back to the same horizontal line, then displacement is zero, so the work done also is zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




