
An object of height 5 cm is placed at 30 cm distance on the principal axis in front of a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm. Find the image distance and size of the image.
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Since the object is located between the focus and centre of curvature of the concave mirror, the image will be formed away from the centre of curvature ($\text{v>40 cm}$) and the image will be real, inverted, and magnified.
Complete step by step solution:
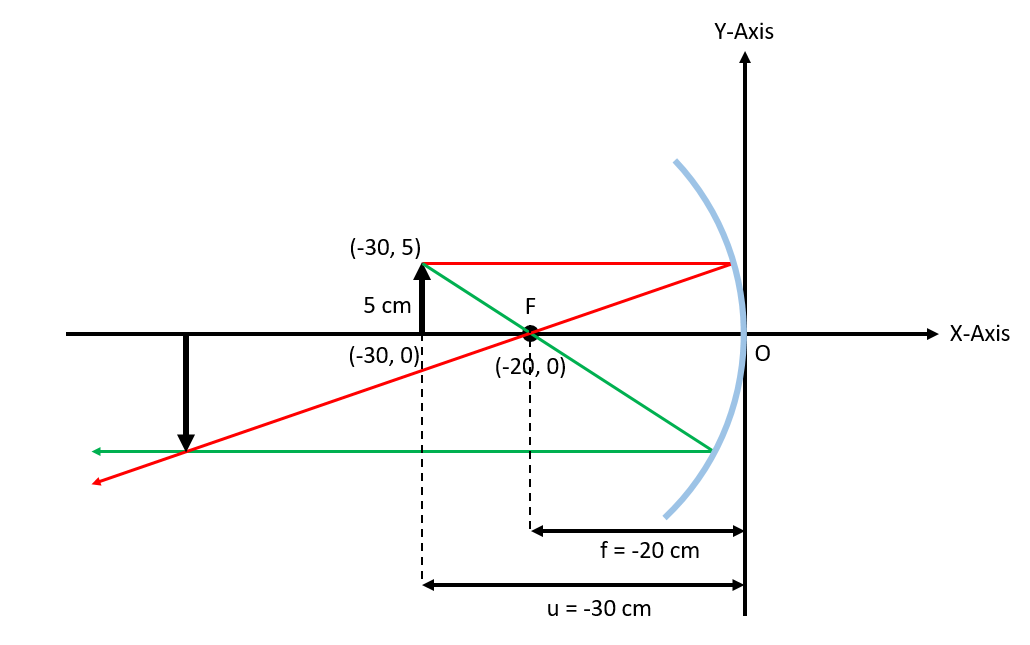
Let us draw an X-Y plane and place a concave lens of focal length 20 cm with its optical centre at the origin, such that the curved side is towards the negative Y-axis. Now we place an object of height 5 cm at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre on the principal axis. The coordinates of the focus and the object are (-20, 0) and (-30, 0), respectively. Now to draw the ray diagram, first we take a ray parallel to the principal axis (red line) and a second ray passing through the focus (green line). These two rays, after reflection from the mirror, converge at a point to form the image of the object. As seen in the ray diagram above, the image is formed behind the object and the characteristic of this image is real and inverted. To calculate the image distance, we will use the mirror’s formula, which is
$\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Since both the focus and the object are on the negative side of the Y-axis, therefore
$\begin{align}
& f=-20\,cm \\
& u=-30\,cm \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the values of f and u in the above equation and equating, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{-30}=\dfrac{1}{-20} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{30}-\dfrac{1}{20} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{20-30}{600} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=-\dfrac{10}{600} \\
& \Rightarrow v=-60\,cm \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the image is formed on the negative side of the Y-axis and at a distance of 60 cm from the optical centre of the mirror.
For the next part, we see from the ray diagram that the image formed will be bigger than the object. Therefore, the image formed is magnified. Magnification (m) is calculated using the formula
$m=\dfrac{\text{Image Height}}{\text{Object Height}}=\dfrac{-v}{u}$
We will use this formula to calculate the image height. We know the object height, u and v therefore, the image height will be
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\text{Image Height}}{5}=\dfrac{60}{-30} \\
& \text{Image Height}=-10\,cm \\
\end{align}$
$\therefore$ The image formed is inverted with a height of 10 cm.
Note:
In the ray diagram based questions, students generally get confused with the sign convention and commit silly mistakes. To avoid such confusions, plotting the ray diagram on an X-Y plane (as it’s done in this question) is the best method to solve such questions.
Complete step by step solution:

Let us draw an X-Y plane and place a concave lens of focal length 20 cm with its optical centre at the origin, such that the curved side is towards the negative Y-axis. Now we place an object of height 5 cm at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre on the principal axis. The coordinates of the focus and the object are (-20, 0) and (-30, 0), respectively. Now to draw the ray diagram, first we take a ray parallel to the principal axis (red line) and a second ray passing through the focus (green line). These two rays, after reflection from the mirror, converge at a point to form the image of the object. As seen in the ray diagram above, the image is formed behind the object and the characteristic of this image is real and inverted. To calculate the image distance, we will use the mirror’s formula, which is
$\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Since both the focus and the object are on the negative side of the Y-axis, therefore
$\begin{align}
& f=-20\,cm \\
& u=-30\,cm \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the values of f and u in the above equation and equating, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{-30}=\dfrac{1}{-20} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{30}-\dfrac{1}{20} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{20-30}{600} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=-\dfrac{10}{600} \\
& \Rightarrow v=-60\,cm \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the image is formed on the negative side of the Y-axis and at a distance of 60 cm from the optical centre of the mirror.
For the next part, we see from the ray diagram that the image formed will be bigger than the object. Therefore, the image formed is magnified. Magnification (m) is calculated using the formula
$m=\dfrac{\text{Image Height}}{\text{Object Height}}=\dfrac{-v}{u}$
We will use this formula to calculate the image height. We know the object height, u and v therefore, the image height will be
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\text{Image Height}}{5}=\dfrac{60}{-30} \\
& \text{Image Height}=-10\,cm \\
\end{align}$
$\therefore$ The image formed is inverted with a height of 10 cm.
Note:
In the ray diagram based questions, students generally get confused with the sign convention and commit silly mistakes. To avoid such confusions, plotting the ray diagram on an X-Y plane (as it’s done in this question) is the best method to solve such questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




