
An object $4cm$ high is placed at a distance a $6cm$ in front of a concave mirror of focal length $12cm$. Find the position, nature and size of the image.
Answer
523.3k+ views
Hint: The distance between the mirror and object is less than the focal length. Thus the is placed between the focal and the pole.
Formula used: Mirror Formula $\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}$
Magnification: $m = - \dfrac{v}{u}$and $m = \dfrac{{{h_i}}}{{{h_o}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Observe the image.
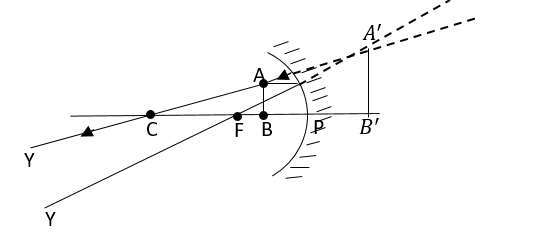
Here, P is called the pole of concave lens.
C is called the radius of curvature.
F is called the focal.
A ‘B’ is the height of image formed,${h_i}$
How image is formed:
Objective the diagram
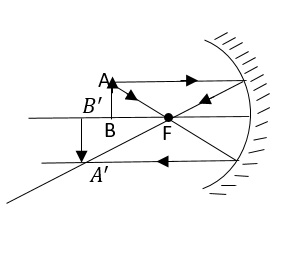
In this diagram we can observe the rays pass through point A, get reflected from the concave mirror and intersect at point${A^1}$.
This${A^1}{B^1}$gives the image of AB and it formed at the point of intersection of the rays coming from AB, after reflecting from the concave lenses.
One more thing to objective here is, that the rays from A pass through the focal, before or after reflection. This happens because the object is behind the terms.
But in the given question, the object is placed between the focal and the pole. Therefore, we can observe in the first diagram that the rays do not intersect after reflection. The point x and Y show us that the distance between them will keep on increasing and they will not intersect.
In such a case, real images do not form. Then, we assume that the rays would intersect to the other side of the concave lens. (which is shown by the dotted lines).
So, the image${A^1}{B^1}$is formed to the night side of the pole, and the image is virtual and erect.
Now, by mirror formula, we have
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}$
Where, \[f\]is focal length.
\[V\]is distance of image from pole
$u$is distance of object from the pole
Before solving this equation, we need to sing conversion.
In sign conversion, we assume.
That the horizontal lengths to the left side of the pole will have negative signs and to the right hand side of the pole will have positive signs.
Vertical length above the line of pole is positive and below the line of pole is negative.
Therefore, after applying the sign convention, the mirror formula is
$\dfrac{{ - 1}}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{12}} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{6}$
After re-arranging we get
$\dfrac{1}{V} = - \dfrac{1}{{12}} + \dfrac{1}{6}$
Cross multiplying
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{{ - 1 + 2}}{{12}}$ (took LCM of denominates)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{12}}$
By taking reciprocal, we get
$V = 12cm$
Therefore, the image will be termed distance$12cm$from pole to the right hand side.
Metrification of image is given by
$m = - \dfrac{v}{u}$
$ \Rightarrow m = - \dfrac{{12}}{{ - 6}}$
$ \Rightarrow m = + 2$
Also, $m = \dfrac{{{h_i}}}{{{h_o}}}$
$ \Rightarrow 2 = \dfrac{{{h_i}}}{{{h_4}}}(\therefore {h_o} = 4cm)$
By cross multiplication, we get
${h_i} = 8cm$
Hence, the size of the image will be$8cm$in upward direction (erect image).
Note:Sign convention is very important always remember to apply sign convention before solving such question positive value of lengths, does not mean that the length is negative. The positive or negative sign only shows the direction of object, tower and image with respect to the pole.
Formula used: Mirror Formula $\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}$
Magnification: $m = - \dfrac{v}{u}$and $m = \dfrac{{{h_i}}}{{{h_o}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Observe the image.

Here, P is called the pole of concave lens.
C is called the radius of curvature.
F is called the focal.
A ‘B’ is the height of image formed,${h_i}$
How image is formed:
Objective the diagram

In this diagram we can observe the rays pass through point A, get reflected from the concave mirror and intersect at point${A^1}$.
This${A^1}{B^1}$gives the image of AB and it formed at the point of intersection of the rays coming from AB, after reflecting from the concave lenses.
One more thing to objective here is, that the rays from A pass through the focal, before or after reflection. This happens because the object is behind the terms.
But in the given question, the object is placed between the focal and the pole. Therefore, we can observe in the first diagram that the rays do not intersect after reflection. The point x and Y show us that the distance between them will keep on increasing and they will not intersect.
In such a case, real images do not form. Then, we assume that the rays would intersect to the other side of the concave lens. (which is shown by the dotted lines).
So, the image${A^1}{B^1}$is formed to the night side of the pole, and the image is virtual and erect.
Now, by mirror formula, we have
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}$
Where, \[f\]is focal length.
\[V\]is distance of image from pole
$u$is distance of object from the pole
Before solving this equation, we need to sing conversion.
In sign conversion, we assume.
That the horizontal lengths to the left side of the pole will have negative signs and to the right hand side of the pole will have positive signs.
Vertical length above the line of pole is positive and below the line of pole is negative.
Therefore, after applying the sign convention, the mirror formula is
$\dfrac{{ - 1}}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{12}} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{6}$
After re-arranging we get
$\dfrac{1}{V} = - \dfrac{1}{{12}} + \dfrac{1}{6}$
Cross multiplying
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{{ - 1 + 2}}{{12}}$ (took LCM of denominates)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{{12}}$
By taking reciprocal, we get
$V = 12cm$
Therefore, the image will be termed distance$12cm$from pole to the right hand side.
Metrification of image is given by
$m = - \dfrac{v}{u}$
$ \Rightarrow m = - \dfrac{{12}}{{ - 6}}$
$ \Rightarrow m = + 2$
Also, $m = \dfrac{{{h_i}}}{{{h_o}}}$
$ \Rightarrow 2 = \dfrac{{{h_i}}}{{{h_4}}}(\therefore {h_o} = 4cm)$
By cross multiplication, we get
${h_i} = 8cm$
Hence, the size of the image will be$8cm$in upward direction (erect image).
Note:Sign convention is very important always remember to apply sign convention before solving such question positive value of lengths, does not mean that the length is negative. The positive or negative sign only shows the direction of object, tower and image with respect to the pole.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




