
An LED operates under which biasing condition?
A. Forward bias
B. Reverse bias
C. Can operate both in forward and reverse bias
D. No biasing is required
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: We are asked to find which biasing condition LED works. We know that LED is a source of light that is based on a simple p-n junction diode. When we pass current through an LED the holes and the electrons combine together and emit light. To find the condition of bias in an LED we need to know about the bias in the p-n junction.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that LED or light emitting diodes is a light source that is based on semiconductors.
We also know that LED is a simple p-n junction diode.
In the case of a p-n junction diode, we know that it only allows the flow of current in the forward direction and also restricts the flow of current in the reverse direction.
Therefore a p-n junction diode works under the forward bias condition.
Since LED or light emitting diode is a p-n junction diode, we can say that LED operates under forward bias.
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note:
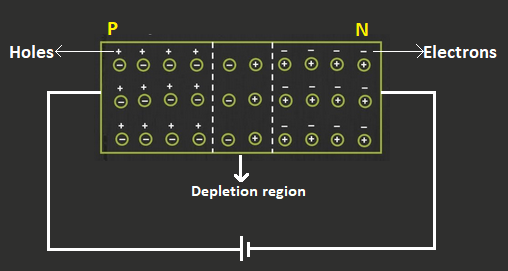
The above figure shows us a p-n junction diode.
The p-n junction diode is a combination of p-type semiconductor and a n-type semiconductor.
Hence it has a p- side, a n-side and a depletion region.
Majority charge carriers on the p-side are holes and on the n- side are electrons.
The p-n junction diode allows the flow of current only in one direction and also does not allow the current flow in reverse direction.
We can also say that a p-n junction diode allows only forward bias and restricts reverse bias.
During the forward bias condition, the holes in the p-side will move from p-side to the n-side and the electrons in the n-side will move from n-side to p-side.
At the junction boundaries, concentration of minority charge carriers increases, i.e. at the p-junction the concentration of electrons increases and at the n-junction concentration of holes increases.
Hence this minority charge carrier combines with the majority charge carriers and produces photons and thus emits light.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that LED or light emitting diodes is a light source that is based on semiconductors.
We also know that LED is a simple p-n junction diode.
In the case of a p-n junction diode, we know that it only allows the flow of current in the forward direction and also restricts the flow of current in the reverse direction.
Therefore a p-n junction diode works under the forward bias condition.
Since LED or light emitting diode is a p-n junction diode, we can say that LED operates under forward bias.
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note:

The above figure shows us a p-n junction diode.
The p-n junction diode is a combination of p-type semiconductor and a n-type semiconductor.
Hence it has a p- side, a n-side and a depletion region.
Majority charge carriers on the p-side are holes and on the n- side are electrons.
The p-n junction diode allows the flow of current only in one direction and also does not allow the current flow in reverse direction.
We can also say that a p-n junction diode allows only forward bias and restricts reverse bias.
During the forward bias condition, the holes in the p-side will move from p-side to the n-side and the electrons in the n-side will move from n-side to p-side.
At the junction boundaries, concentration of minority charge carriers increases, i.e. at the p-junction the concentration of electrons increases and at the n-junction concentration of holes increases.
Hence this minority charge carrier combines with the majority charge carriers and produces photons and thus emits light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




