
An $L$ shaped thin metal rod is moving with velocity $\vec v = (2\hat i + 4\hat j)m{s^{ - 1}}$ in transverse uniform magnetic field of ${\vec B_0} = - 4\hat kT$ the potential difference between point $A$ and $B$ $({V_A} - {V_B})$ will be ?
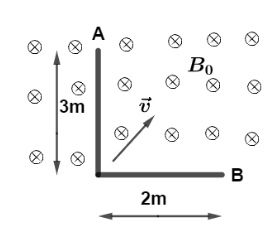
A. $56V$
B. $24V$
C. $32V$
D. $8V$

Answer
509.7k+ views
Hint:In order to solve this question we need to understand Faraday's law of magnetic induction which states that due to change in magnetic flux an emf would be induced in loop and current flows according to Lenz’s law. Magnetic flux could be changed by changing magnetic field or by changing either the area under loop or orientation of loop.
Complete step by step answer:
Considering the loop or rod in a magnetic field. Then we analyze the two parts of the rod individually. Now when this loop moves in a constant magnetic field the area under loop keeps changing and hence the flux changes. So an emf induced in a loop known as motional emf. Also when we find the magnetic force on loop due to velocity using relation,
$\vec F = q(\vec v \times \vec B)$
It points towards point $A$ and hence it is concluded that due to magnetic force electrons move toward point $B$ and positive charges move towards $A$ so potential difference is created. Also only the perpendicular component of $v$ is considered.
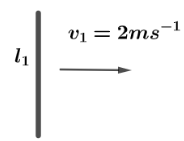
The first perpendicular part of rod OA velocity perpendicular is ${v_1} = 2\,m{s^{ - 2}}$ and $B = 4T$. So the motional emf induced between point $O$ and $A$ is ${e_1} = Bl{v_1}$, where $B$ is magnetic field, $l$ is length of rod and $v$ is speed of rod.
${e_1} = 4 \times 3 \times 2 = 24V$
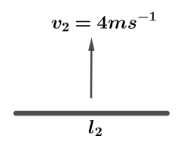
Similarly for part OB of rod speed considered is ${v_2} = 4m{s^{ - 2}}$ and $B = 4T$.
So emf induced is ${e_2} = Bl{v_2}$.
Putting values we get ${e_2} = 4 \times 2 \times 4 = 32V$.
So net emf induced in loop is $e = {e_1} + {e_2}$.
Putting values we get $e = 24 + 32 = 56V$.
So the correct answer is option A.
Note: It should be remembered that motional emf is only induced when the rod is moving with velocity perpendicular to constant magnetic field. Also here only velocity perpendicular to the length of part of rod is chosen so to make emf non-zero otherwise emf would be zero. Also both emf are added because both emf induces in the same direction.
Complete step by step answer:
Considering the loop or rod in a magnetic field. Then we analyze the two parts of the rod individually. Now when this loop moves in a constant magnetic field the area under loop keeps changing and hence the flux changes. So an emf induced in a loop known as motional emf. Also when we find the magnetic force on loop due to velocity using relation,
$\vec F = q(\vec v \times \vec B)$
It points towards point $A$ and hence it is concluded that due to magnetic force electrons move toward point $B$ and positive charges move towards $A$ so potential difference is created. Also only the perpendicular component of $v$ is considered.
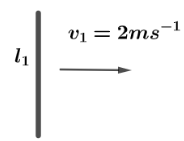
The first perpendicular part of rod OA velocity perpendicular is ${v_1} = 2\,m{s^{ - 2}}$ and $B = 4T$. So the motional emf induced between point $O$ and $A$ is ${e_1} = Bl{v_1}$, where $B$ is magnetic field, $l$ is length of rod and $v$ is speed of rod.
${e_1} = 4 \times 3 \times 2 = 24V$

Similarly for part OB of rod speed considered is ${v_2} = 4m{s^{ - 2}}$ and $B = 4T$.
So emf induced is ${e_2} = Bl{v_2}$.
Putting values we get ${e_2} = 4 \times 2 \times 4 = 32V$.
So net emf induced in loop is $e = {e_1} + {e_2}$.
Putting values we get $e = 24 + 32 = 56V$.
So the correct answer is option A.
Note: It should be remembered that motional emf is only induced when the rod is moving with velocity perpendicular to constant magnetic field. Also here only velocity perpendicular to the length of part of rod is chosen so to make emf non-zero otherwise emf would be zero. Also both emf are added because both emf induces in the same direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




