
An infinite wire is bent in the form of L and carries a current $I$ as shown in the figure below. Find the magnetic field at point O.
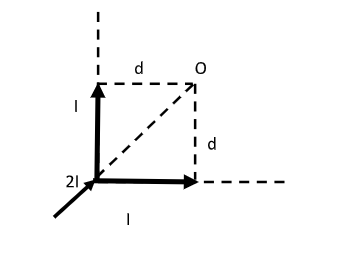
A) Zero
B) $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{I}{d}$
C) $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{I}{{2d}}$
D) $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} \times \dfrac{{2I}}{d}$

Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: The infinitely long wire bent in the shape of L constitutes two semi-infinite wires. The magnetic field at point O due to the two wires will be opposite in direction at the point of intersection as the current flow has different directions in the two wires.
Formula used:
The magnetic field at a point O for a finite wire carrying a current $I$ is given by, $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {\sin {\theta _1} + {\theta _2}} \right)$ where $d$ is the perpendicular distance from the point O to the wire, ${\mu _0}$ is the permeability of free space and ${\theta _1}$, ${\theta _2}$ are the angles formed at point O by line segments joining each end to O.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Sketch a figure representing the infinitely long wire bent in the form of L and list the parameters involved.
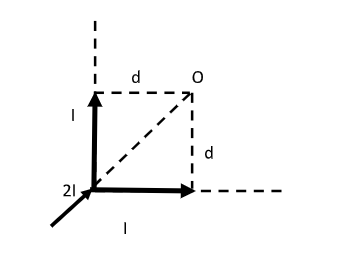
Here, the infinitely long wire is bent in the shape of L. We can now treat this infinitely long wire as two semi-infinite wires. For each wire, one end is finite and the other end is infinitely long.
A current $I$ flows through each wire, $2I$ represents the current at the junction of the two wires.
A point O is considered such that the perpendicular distance between point O and the wire is $d$.
The magnetic field at point O is unknown.
Step 2: Find the magnetic field at point O due to the current in the wire placed along the vertical direction.
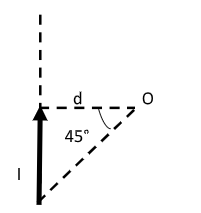
Let ${B_v}$ be the magnetic field at point O due to the current in the wire placed along the vertical direction.
We have the magnetic field at point O as ${B_v} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {\sin {\theta _1} + \sin {\theta _2}} \right)$ --------- (1)
Here, $d$ is the perpendicular distance from the point O to the wire, ${\mu _0}$ is the permeability of free space.
Also, ${\theta _1}$ and ${\theta _2}$ are the angles formed at point O by line segments joining the infinite end and finite end of the wire respectively to the point O.
For the infinite end, ${\theta _1} = 90^\circ $ and for the finite end, ${\theta _2} = 45^\circ $ .
Then equation (1) becomes, ${B_v} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {\sin 90^\circ + \sin 45^\circ } \right) = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$
Therefore, the magnetic field at O due to the current in the wire placed along the vertical direction is ${B_v} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$ -------- (A)
Step 3: Find the magnetic field at point O due to the current in the wire placed along the horizontal direction.
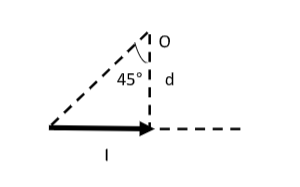
Let ${B_h}$ be the magnetic field at point O due to the current in the wire placed along the horizontal direction.
We have the magnetic field at point O as ${B_h} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {\sin {\theta _3} + \sin {\theta _4}} \right)$ --------- (2)
Here, $d$ is the perpendicular distance from the point O to the wire, ${\mu _0}$ is the permeability of free space.
Also, ${\theta _3}$ and ${\theta _4}$ are the angles formed at point O by line segments joining the infinite end and finite end of the wire respectively to O.
For the infinite end, ${\theta _3} = 90^\circ $ and for the finite end, ${\theta _4} = 45^\circ $.
Then equation (2) becomes, ${B_h} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {\sin 90^\circ + \sin 45^\circ } \right) = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$
Therefore, the magnetic field at O due to the current in the wire placed along the horizontal direction is ${B_h} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$ -------- (B)
Step 4: Find the net magnetic field at point O.
We thus have, the magnetic fields at point O due to the current in the two semi-infinite wires as given by equations (A) and (B) as ${B_v} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$ and ${B_h} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$
When the right-hand thumb rule is used at the point of intersection, the magnetic field lines will have two directions since the current flow along the two wires is different. The point O is essentially an imaginary point that actually exists at the point of intersection.
So, the net magnetic field at the point of intersection is ${B_{net}} = {B_v} - {B_h} = 0$.
Therefore, the magnetic field at point O is zero.
Note:
The right-hand thumb rule gives us the direction of the magnetic field at a point when the direction of the current is known. According to the right-hand thumb rule we consider a current-carrying wire in our right hand. Now the thumb points in the direction of the current and all the finger curling around the wire will give the direction of the magnetic field.
Formula used:
The magnetic field at a point O for a finite wire carrying a current $I$ is given by, $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {\sin {\theta _1} + {\theta _2}} \right)$ where $d$ is the perpendicular distance from the point O to the wire, ${\mu _0}$ is the permeability of free space and ${\theta _1}$, ${\theta _2}$ are the angles formed at point O by line segments joining each end to O.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Sketch a figure representing the infinitely long wire bent in the form of L and list the parameters involved.

Here, the infinitely long wire is bent in the shape of L. We can now treat this infinitely long wire as two semi-infinite wires. For each wire, one end is finite and the other end is infinitely long.
A current $I$ flows through each wire, $2I$ represents the current at the junction of the two wires.
A point O is considered such that the perpendicular distance between point O and the wire is $d$.
The magnetic field at point O is unknown.
Step 2: Find the magnetic field at point O due to the current in the wire placed along the vertical direction.

Let ${B_v}$ be the magnetic field at point O due to the current in the wire placed along the vertical direction.
We have the magnetic field at point O as ${B_v} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {\sin {\theta _1} + \sin {\theta _2}} \right)$ --------- (1)
Here, $d$ is the perpendicular distance from the point O to the wire, ${\mu _0}$ is the permeability of free space.
Also, ${\theta _1}$ and ${\theta _2}$ are the angles formed at point O by line segments joining the infinite end and finite end of the wire respectively to the point O.
For the infinite end, ${\theta _1} = 90^\circ $ and for the finite end, ${\theta _2} = 45^\circ $ .
Then equation (1) becomes, ${B_v} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {\sin 90^\circ + \sin 45^\circ } \right) = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$
Therefore, the magnetic field at O due to the current in the wire placed along the vertical direction is ${B_v} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$ -------- (A)
Step 3: Find the magnetic field at point O due to the current in the wire placed along the horizontal direction.

Let ${B_h}$ be the magnetic field at point O due to the current in the wire placed along the horizontal direction.
We have the magnetic field at point O as ${B_h} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {\sin {\theta _3} + \sin {\theta _4}} \right)$ --------- (2)
Here, $d$ is the perpendicular distance from the point O to the wire, ${\mu _0}$ is the permeability of free space.
Also, ${\theta _3}$ and ${\theta _4}$ are the angles formed at point O by line segments joining the infinite end and finite end of the wire respectively to O.
For the infinite end, ${\theta _3} = 90^\circ $ and for the finite end, ${\theta _4} = 45^\circ $.
Then equation (2) becomes, ${B_h} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {\sin 90^\circ + \sin 45^\circ } \right) = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$
Therefore, the magnetic field at O due to the current in the wire placed along the horizontal direction is ${B_h} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$ -------- (B)
Step 4: Find the net magnetic field at point O.
We thus have, the magnetic fields at point O due to the current in the two semi-infinite wires as given by equations (A) and (B) as ${B_v} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$ and ${B_h} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi d}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right)$
When the right-hand thumb rule is used at the point of intersection, the magnetic field lines will have two directions since the current flow along the two wires is different. The point O is essentially an imaginary point that actually exists at the point of intersection.
So, the net magnetic field at the point of intersection is ${B_{net}} = {B_v} - {B_h} = 0$.
Therefore, the magnetic field at point O is zero.
Note:
The right-hand thumb rule gives us the direction of the magnetic field at a point when the direction of the current is known. According to the right-hand thumb rule we consider a current-carrying wire in our right hand. Now the thumb points in the direction of the current and all the finger curling around the wire will give the direction of the magnetic field.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




