
An infinite non-conducting sheet of thickness $d$ and contains uniform charge distribution of charge density $\rho $. Which one of the following graphs represents the variation of Electric Field ${{E}_{x}}$ v/s $x$ (Here x is the distance from the central plane of non-conducting sheet) and $0(A).
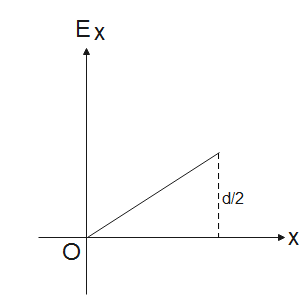
(B).
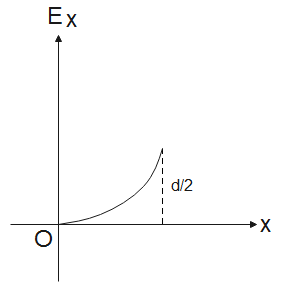
(C).
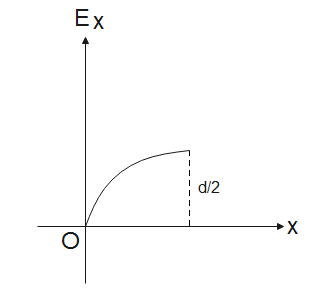
(D).
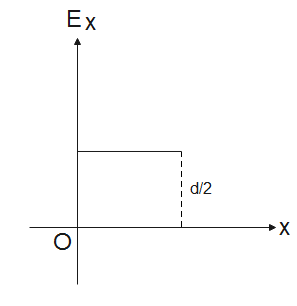

(B).

(C).

(D).

Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: Flux is the amount of electric field lines passing per unit area. Hence, the flux is the integration of electric field vectors and area vectors. By the gauss law, flux is charge divided by absolute permittivity. Using both equations, we can determine the electric sheet due to the charged sheet which will also give us the relation between electric field and distance from the sheet.
Formulas used:
$\phi =\oint{\vec{E}.d\vec{S}}$
$\phi =\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
Complete answer:
We know that the flux through a surface is given by-
$\phi =\oint{\vec{E}.d\vec{S}}$ - (1)
Here, $\phi $ is the flux passing through a surface
$\vec{E}$ is the electric field vector
$\vec{S}$ is the area vector
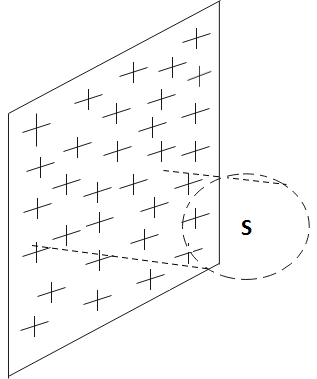
According to the gauss law, the flux passing through a surface will be-
$\phi =\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$ - (2)
Therefore, using eq (1) and eq (2), we have,
$\begin{align}
& \oint{EdS\cos 0=\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow E\oint{dS=}\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}} \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow ES=\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$ - (3)
We know that charge density is the charge per unit volume. Therefore,
$\rho =area\times thickness$
$\Rightarrow \rho =S\times d$ - (4)
From eq (3),
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow ES=\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}} \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{q}{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}} \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{qd}{Sd{{\varepsilon }_{0}}} \\
\end{align}$
Substituting from eq (4) in the above equation,
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{qd}{\rho {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
The electric field due to the infinite non-conducting sheet of thickness $d$ is $\dfrac{qd}{\rho {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$. It is independent of x or the distance from the centre of the sheet; this means the field remains uniform throughout.
Therefore, the electric field due to a charged sheet is $\dfrac{qd}{\rho {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$, it is independent of x.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note:
The electric field is a vector quantity and its direction is the direction in which positive charge flows. The dot product of two vectors gives a scalar quantity. The charge distribution can also be represented by surface charge density, it is the charge per unit area. The electric field due to a charged sheet will be the same at any distance from the centre of the sheet.
Formulas used:
$\phi =\oint{\vec{E}.d\vec{S}}$
$\phi =\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
Complete answer:
We know that the flux through a surface is given by-
$\phi =\oint{\vec{E}.d\vec{S}}$ - (1)
Here, $\phi $ is the flux passing through a surface
$\vec{E}$ is the electric field vector
$\vec{S}$ is the area vector

According to the gauss law, the flux passing through a surface will be-
$\phi =\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$ - (2)
Therefore, using eq (1) and eq (2), we have,
$\begin{align}
& \oint{EdS\cos 0=\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow E\oint{dS=}\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}} \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow ES=\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$ - (3)
We know that charge density is the charge per unit volume. Therefore,
$\rho =area\times thickness$
$\Rightarrow \rho =S\times d$ - (4)
From eq (3),
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow ES=\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}} \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{q}{S{{\varepsilon }_{0}}} \\
& \Rightarrow E=\dfrac{qd}{Sd{{\varepsilon }_{0}}} \\
\end{align}$
Substituting from eq (4) in the above equation,
$\Rightarrow E=\dfrac{qd}{\rho {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$
The electric field due to the infinite non-conducting sheet of thickness $d$ is $\dfrac{qd}{\rho {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$. It is independent of x or the distance from the centre of the sheet; this means the field remains uniform throughout.
Therefore, the electric field due to a charged sheet is $\dfrac{qd}{\rho {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}$, it is independent of x.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note:
The electric field is a vector quantity and its direction is the direction in which positive charge flows. The dot product of two vectors gives a scalar quantity. The charge distribution can also be represented by surface charge density, it is the charge per unit area. The electric field due to a charged sheet will be the same at any distance from the centre of the sheet.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




