
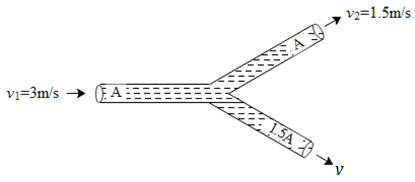
An incompressible liquid flows through a horizontal tube as shown in the following figure. Then velocity v of the fluid is

Answer
521k+ views
Hint: Assume that the liquid is non viscous and flows steadily. In the above diagram we can see that the liquid flows from one tube and splits into two. Since the mass of the liquid flowing from the initial tube to the other two tubes in unit time remains the same, we can use the equation of continuity to determine the velocity of the liquid across the cross sectional area i.e. 1.5A.
Formula used:
$A{{v}_{1}}=A{{v}_{2}}+(1.5)Av$
Complete step-by-step answer:
If we see the above diagram, we can see that the liquid flows from one tube and then divides into two different tubes. Whatever mass flows across the single tube in unit time the same will get divided into the two other tubes. Hence we will use the equation of continuity to determine the velocity ‘v’ across the cross section 1.5A. Let us say that a liquid flows from a cross section ‘A’ with velocity ‘v’ to another cross section ‘a’ with velocity V. Hence the equation of continuity is given by,
$Av=aV$
If the same liquid splits into n tubes having the different cross sectional areas than the above equation becomes,
$\begin{align}
& Av={{a}_{1}}{{V}_{1}}+{{a}_{2}}{{V}_{2}}....{{a}_{n}}{{V}_{n}} \\
& \Rightarrow Av=\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n}{{{a}_{i}}{{V}_{i}}} \\
\end{align}$
Applying the above equation to the Y shaped tube in the above diagram we get,
$\begin{align}
& A{{v}_{1}}=A{{v}_{2}}+1.5Av \\
& \Rightarrow A{{v}_{1}}=A({{v}_{2}}+1.5v) \\
& \Rightarrow 3m{{s}^{-1}}=1.5m{{s}^{-1}}+1.5v \\
& \Rightarrow 1.5=1.5v \\
& \Rightarrow v=1m{{s}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the velocity of the liquid flowing across the tube of cross sectional area 1.5A is equal to 1m/s.
Note: The equation of continuity is the special case of law of conservation of mass. The equation shows that velocity of the liquid is inversely proportional to the cross sectional area of the tube or the pipe. If the liquid is viscous and does not flow steadily than the above equation is no longer valid.
Formula used:
$A{{v}_{1}}=A{{v}_{2}}+(1.5)Av$
Complete step-by-step answer:
If we see the above diagram, we can see that the liquid flows from one tube and then divides into two different tubes. Whatever mass flows across the single tube in unit time the same will get divided into the two other tubes. Hence we will use the equation of continuity to determine the velocity ‘v’ across the cross section 1.5A. Let us say that a liquid flows from a cross section ‘A’ with velocity ‘v’ to another cross section ‘a’ with velocity V. Hence the equation of continuity is given by,
$Av=aV$
If the same liquid splits into n tubes having the different cross sectional areas than the above equation becomes,
$\begin{align}
& Av={{a}_{1}}{{V}_{1}}+{{a}_{2}}{{V}_{2}}....{{a}_{n}}{{V}_{n}} \\
& \Rightarrow Av=\sum\limits_{i=1}^{n}{{{a}_{i}}{{V}_{i}}} \\
\end{align}$
Applying the above equation to the Y shaped tube in the above diagram we get,
$\begin{align}
& A{{v}_{1}}=A{{v}_{2}}+1.5Av \\
& \Rightarrow A{{v}_{1}}=A({{v}_{2}}+1.5v) \\
& \Rightarrow 3m{{s}^{-1}}=1.5m{{s}^{-1}}+1.5v \\
& \Rightarrow 1.5=1.5v \\
& \Rightarrow v=1m{{s}^{-1}} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the velocity of the liquid flowing across the tube of cross sectional area 1.5A is equal to 1m/s.
Note: The equation of continuity is the special case of law of conservation of mass. The equation shows that velocity of the liquid is inversely proportional to the cross sectional area of the tube or the pipe. If the liquid is viscous and does not flow steadily than the above equation is no longer valid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




