
An ideal gas is initially at temperature $T $ and volume $V$. Its volume is increased by $\Delta V $ due to an increase in temperature$\Delta T$, pressure remaining constant. The quantity $\delta =\dfrac{\Delta V}{V\Delta T}$ varies with temperature as:
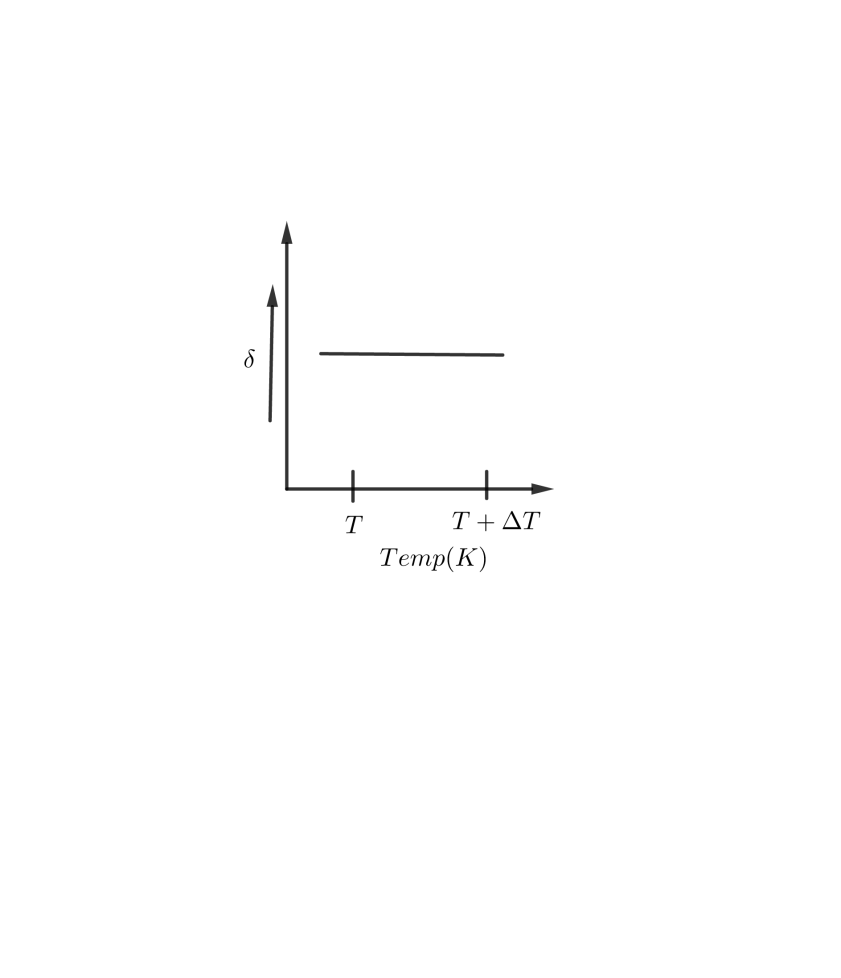
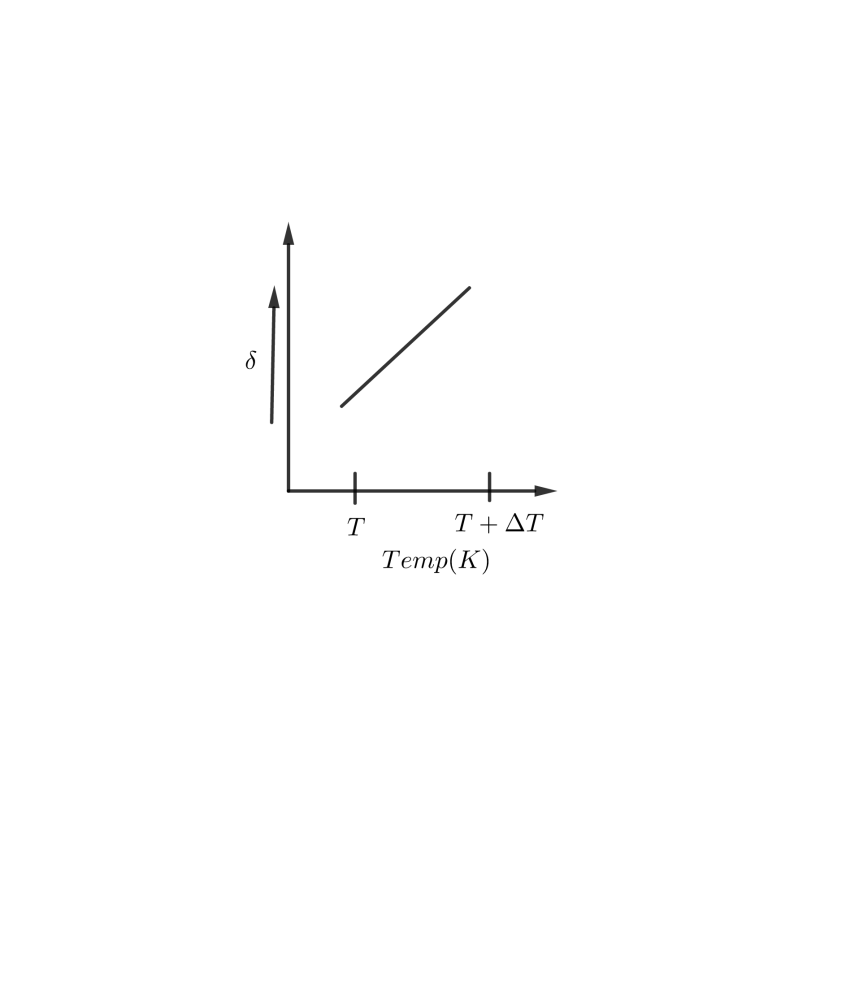
A B
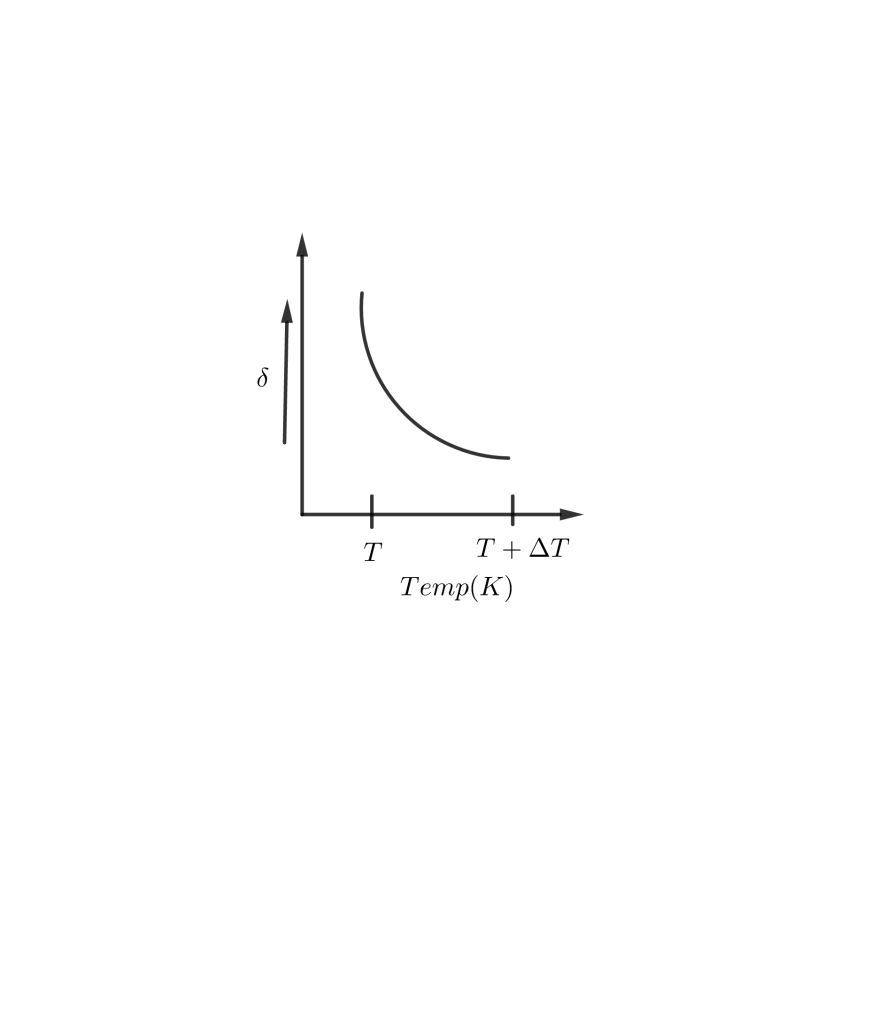
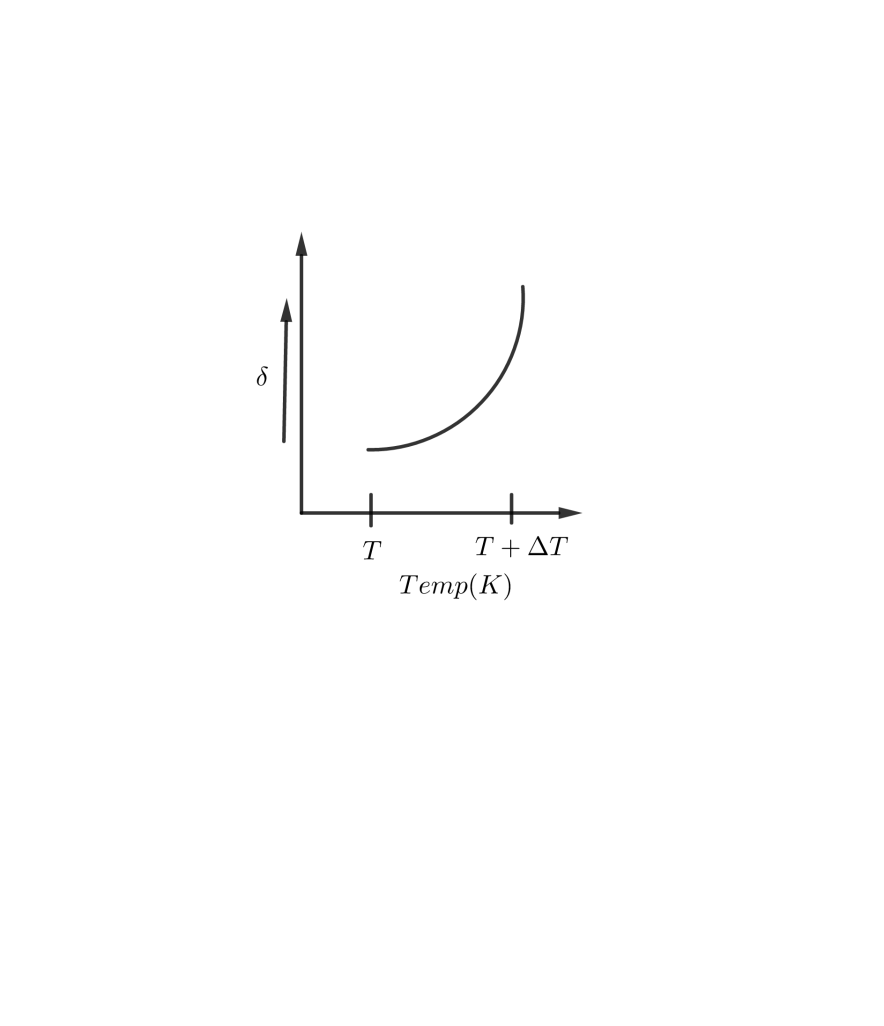
C D




Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: Use ideal gas law to find the relation between volume and temperature. Differentiate it to find the relation between the error in volume and the error in temperature.
$PV=nRT$
Here,
$\begin{align}
& P\text{ is pressure } \\
& V\text{ is volume} \\
& n\text{ is number of moles} \\
& R\text{ is ideal gas constant} \\
& T\text{ is temperature} \\
\end{align}$
Complete step by step answer:
From the ideal gas law,
$\dfrac{V}{T}=\dfrac{nR}{P}$
As $n$ and $R$ are constants,
$\dfrac{V}{T}=\text{constant at constant pressure}$
Differentiate with respect to $T$ keeping $V$ constant, and then differentiate with respect to $V$ keeping $T$ constant,
$\dfrac{\Delta V}{T}+\dfrac{V\Delta T}{-{{T}^{2}}}=0 \\ $
$\implies \dfrac{\Delta V}{V\Delta T}=\dfrac{1}{T} \\ $
$\implies \delta =\dfrac{1}{T} \\ $
Thus, when $T$ increases, $\delta$ decreases and vice-versa.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Additional Information:
$\delta$ is known as the volumetric thermal expansion coefficient.
A process in which the pressure remains constant is known as an isobaric process. The heat which is transferred to the system does the work and changes the internal energy of the system
Note:
$\dfrac{V}{T}=\text{constant}$, can be stated as: volume of an ideal gas at constant pressure is directly proportional to its temperature. This is known as Charles’s law. This law combined with Boyle’s law, Avogadro’s hypothesis and Gay-Lussac’s law gives the equation of state for an ideal gas, the ideal gas law.
As $T$ tends to low values, $\delta$ increases rapidly. At large values of $T$, $\delta$ tends to low values and becomes almost constant.
$PV=nRT$
Here,
$\begin{align}
& P\text{ is pressure } \\
& V\text{ is volume} \\
& n\text{ is number of moles} \\
& R\text{ is ideal gas constant} \\
& T\text{ is temperature} \\
\end{align}$
Complete step by step answer:
From the ideal gas law,
$\dfrac{V}{T}=\dfrac{nR}{P}$
As $n$ and $R$ are constants,
$\dfrac{V}{T}=\text{constant at constant pressure}$
Differentiate with respect to $T$ keeping $V$ constant, and then differentiate with respect to $V$ keeping $T$ constant,
$\dfrac{\Delta V}{T}+\dfrac{V\Delta T}{-{{T}^{2}}}=0 \\ $
$\implies \dfrac{\Delta V}{V\Delta T}=\dfrac{1}{T} \\ $
$\implies \delta =\dfrac{1}{T} \\ $
Thus, when $T$ increases, $\delta$ decreases and vice-versa.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Additional Information:
$\delta$ is known as the volumetric thermal expansion coefficient.
A process in which the pressure remains constant is known as an isobaric process. The heat which is transferred to the system does the work and changes the internal energy of the system
Note:
$\dfrac{V}{T}=\text{constant}$, can be stated as: volume of an ideal gas at constant pressure is directly proportional to its temperature. This is known as Charles’s law. This law combined with Boyle’s law, Avogadro’s hypothesis and Gay-Lussac’s law gives the equation of state for an ideal gas, the ideal gas law.
As $T$ tends to low values, $\delta$ increases rapidly. At large values of $T$, $\delta$ tends to low values and becomes almost constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




