
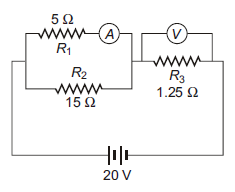
An ideal ammeter (zero resistance) and an ideal voltmeter (infinite resistance) are connected as shown in fig. The ammeter and the voltmeter readings are:
A.)$6.25A,3.75V$
B.)$0.00A,20V$
C.)$3.00A,5V$
D.)$6.00A,6.25V$

Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: An ideal voltmeter will have infinite resistance, and so is connected in parallel in a circuit. An ideal ammeter will have zero resistance and so is connected in series in a circuit.
Complete step by step answer:
The equivalent resistance is where the aggregate resistance connected either in parallel or series is calculated. Resistor circuits that combine series and parallel resistors networks together are generally known as Resistor Combination or mixed resistor circuits. The method of calculating the circuit’s equivalent resistance is the same as that for any individual series or parallel circuit.
From the given figure the equivalent resistance R of the combination is
$R=\dfrac{{{R}_{1}}\times {{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}+{{R}_{3}}$
$R=\dfrac{5\times 15}{5+15}+1.25$
$R=\dfrac{75}{20}+1.25$
\[\therefore R=5\Omega \]
Hence the current I through the circuit is
$I=\dfrac{V}{R}$
$I=\dfrac{20}{5}A=4A$
Now, current through $5\Omega $ resistance is
$I=\dfrac{V}{{{R}_{1}}}$
$\dfrac{15}{20}\times 4=3A$
Also, reading of voltmeter ${{V}_{r}}$ is equal to the potential drop across \[1.25\Omega \] resistance
${{V}_{r}}=I\times {{R}_{{{3}_{{}}}}}$
${{V}_{r}}=4\times 1.25$
${{V}_{r}}=5V$
Hence,
Reading of ammeter is $3A$
Reading of voltmeter is ${{V}_{r}}=5V$\[\]
Additional information:
The Voltmeter is a device used to measure the potential difference between two points. If we connect voltmeter in series, nothing magnificent would happen. The Voltmeter is a device of significantly high resistance, and it would impede the flow of current. Open circuit, and nothing spectacular achieved.
The Ammeter is a device of a marginally lower resistance value, since it is designed to measure the value of current in a circuit. So, it allows the current to pass through it, so as to obtain a reading. Now, if we connect an Ammeter in the parallel configuration, a large value of current would flow in the branch with the Ammeter, as current always chooses the path of least resistance. With a large amount of current flowing through the branch having the ammeter, even though alternate routes are available, the circuit would be short-circuited, and our Ammeter's wire would burn out. Essentially, it'll be damaged, and would display inaccurate readings
Therefore, Voltmeter is always connected in parallel and Ammeter is always connected in series in a circuit.
Note: During calculating the equivalent resistance, take the values of resistances in series and parallel combination appropriately.
Complete step by step answer:
The equivalent resistance is where the aggregate resistance connected either in parallel or series is calculated. Resistor circuits that combine series and parallel resistors networks together are generally known as Resistor Combination or mixed resistor circuits. The method of calculating the circuit’s equivalent resistance is the same as that for any individual series or parallel circuit.
From the given figure the equivalent resistance R of the combination is
$R=\dfrac{{{R}_{1}}\times {{R}_{2}}}{{{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}}+{{R}_{3}}$
$R=\dfrac{5\times 15}{5+15}+1.25$
$R=\dfrac{75}{20}+1.25$
\[\therefore R=5\Omega \]
Hence the current I through the circuit is
$I=\dfrac{V}{R}$
$I=\dfrac{20}{5}A=4A$
Now, current through $5\Omega $ resistance is
$I=\dfrac{V}{{{R}_{1}}}$
$\dfrac{15}{20}\times 4=3A$
Also, reading of voltmeter ${{V}_{r}}$ is equal to the potential drop across \[1.25\Omega \] resistance
${{V}_{r}}=I\times {{R}_{{{3}_{{}}}}}$
${{V}_{r}}=4\times 1.25$
${{V}_{r}}=5V$
Hence,
Reading of ammeter is $3A$
Reading of voltmeter is ${{V}_{r}}=5V$\[\]
Additional information:
The Voltmeter is a device used to measure the potential difference between two points. If we connect voltmeter in series, nothing magnificent would happen. The Voltmeter is a device of significantly high resistance, and it would impede the flow of current. Open circuit, and nothing spectacular achieved.
The Ammeter is a device of a marginally lower resistance value, since it is designed to measure the value of current in a circuit. So, it allows the current to pass through it, so as to obtain a reading. Now, if we connect an Ammeter in the parallel configuration, a large value of current would flow in the branch with the Ammeter, as current always chooses the path of least resistance. With a large amount of current flowing through the branch having the ammeter, even though alternate routes are available, the circuit would be short-circuited, and our Ammeter's wire would burn out. Essentially, it'll be damaged, and would display inaccurate readings
Therefore, Voltmeter is always connected in parallel and Ammeter is always connected in series in a circuit.
Note: During calculating the equivalent resistance, take the values of resistances in series and parallel combination appropriately.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




