
An example of disaccharide made up of two units of the same monosaccharide, is:
(A) Maltose
(B) Sucrose
(C) Lactose
(D) None
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: The disaccharide that has two same monosaccharide units from the options is a reducing sugar. The glycosidic bond in this disaccharide is of $\alpha $-type. If it is $\beta $-type, then the disaccharide is called cellulose.
Complete step by step solution:
Carbohydrates are the hydrates of carbon which have free aldehyde or ketone groups alongside hydroxyl groups. However, they also exist in pyranose and furanose forms.
- Depending upon the number of monosaccharide units obtained upon hydrolysis, carbohydrates are classified into categories like monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
- Disaccharide is a carbohydrate which upon its hydrolysis gives two molecules of monosaccharides. We need to find a disaccharide from the given options that give two monosaccharide units. Let’s see all of them one by one to get the answer.
A) Maltose:
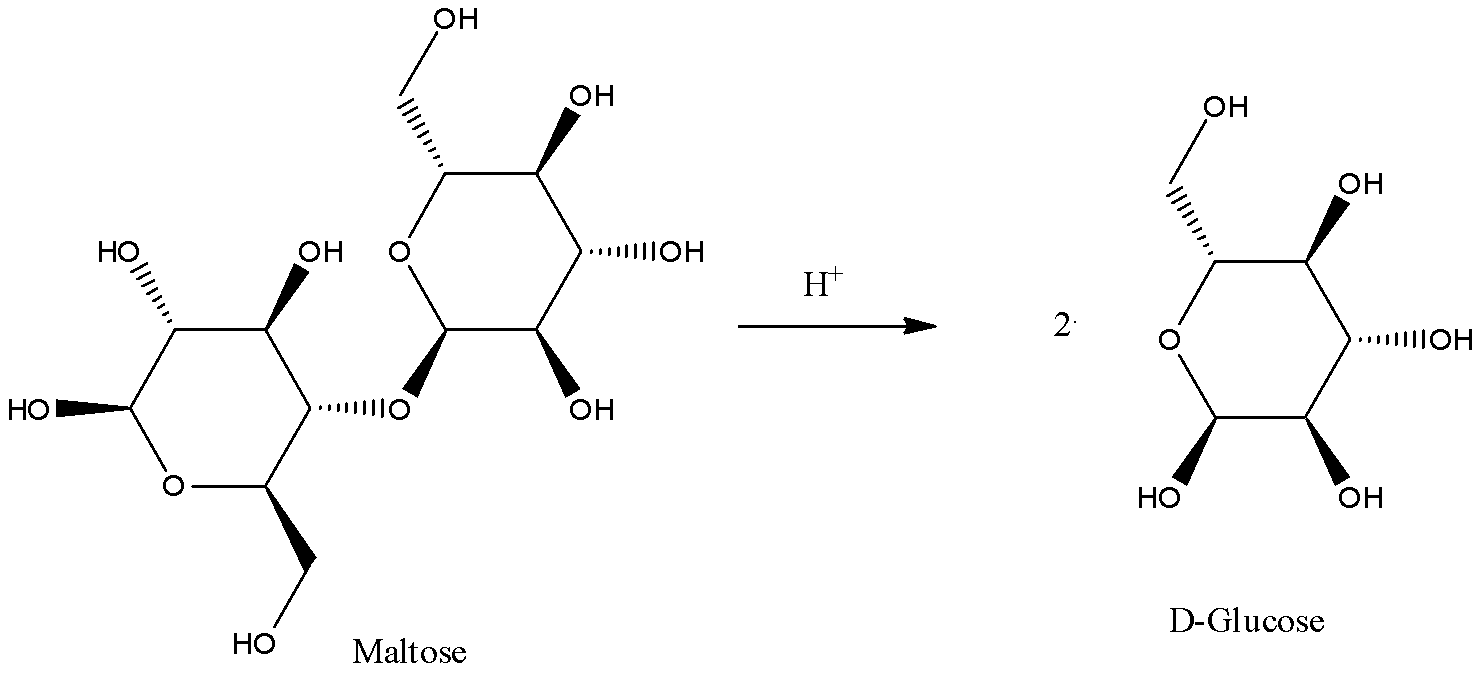
Thus, we can see that Maltose gives two molecules of D-Glucose upon hydrolysis. Thus, we can say that maltose is made up of two glucose molecules.
B) Sucrose:
When we hydrolyze sucrose, we get D-Glucose and D-Fructose. Thus, we can see that it is made up of two different monosaccharide molecules.
C) Lactose:
When we hydrolyze lactose, we get two monosaccharide units; galactose and glucose. Thus, it is also made up of two monosaccharide units.
So, from the above discussion, we can say that Maltose is a disaccharide which is made up of the same monosaccharide units.
Therefore the correct answer is (A).
Note: The disaccharides can be divided into broadly two categories; reducing and non-reducing sugars. In reducing sugars, the carbonyl group is free and in non-reducing sugars, there is no reducible centre present.
Complete step by step solution:
Carbohydrates are the hydrates of carbon which have free aldehyde or ketone groups alongside hydroxyl groups. However, they also exist in pyranose and furanose forms.
- Depending upon the number of monosaccharide units obtained upon hydrolysis, carbohydrates are classified into categories like monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
- Disaccharide is a carbohydrate which upon its hydrolysis gives two molecules of monosaccharides. We need to find a disaccharide from the given options that give two monosaccharide units. Let’s see all of them one by one to get the answer.
A) Maltose:

Thus, we can see that Maltose gives two molecules of D-Glucose upon hydrolysis. Thus, we can say that maltose is made up of two glucose molecules.
B) Sucrose:
When we hydrolyze sucrose, we get D-Glucose and D-Fructose. Thus, we can see that it is made up of two different monosaccharide molecules.
C) Lactose:
When we hydrolyze lactose, we get two monosaccharide units; galactose and glucose. Thus, it is also made up of two monosaccharide units.
So, from the above discussion, we can say that Maltose is a disaccharide which is made up of the same monosaccharide units.
Therefore the correct answer is (A).
Note: The disaccharides can be divided into broadly two categories; reducing and non-reducing sugars. In reducing sugars, the carbonyl group is free and in non-reducing sugars, there is no reducible centre present.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




