
An example of a secondary alcohol is:
A)1-propanol
B)2-propanol
C)1,2-propanol
D)1,2,3-propanol
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: To answer this answer, first we need to know what secondary alcohol is. A secondary alcohol is where the alcohol is placed which is bonded to two other carbon atoms.
Complete step-by-step answer:
-In chemistry, alcohol groups are those that in a compound there is at least one hydroxyl group attached. This hydroxyl group is the functional group of the compound.
-The alcohol groups are divided into three types on the basis of the total number of alkyl groups connected to the carbon connected to the hydroxyl group.
-Now, let us discuss the nomenclature of these compounds according to IUPAC.
-The primary alcohols have general formulas $\mathrm{RCH}_{2} \mathrm{OH}$. The simplest primary alcohol is methanol $\left(\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{OH}\right),$ for which $\mathrm{R}=\mathrm{H},$ and the next is ethanol, for which $\mathrm{R}=\mathrm{CH}_{3},$ the methyl group. Secondary alcohols are those of the form $\mathrm{RR}^{\prime} \mathrm{CHOH},$ the simplest of which is 2 -propanol $\left(\mathrm{R}=\mathrm{R}^{\prime}=\mathrm{CH}_{3}\right) .$ For the tertiary alcohols the general form is $\mathrm{RR}^{\prime} \mathrm{R}^{\prime \prime} \mathrm{COH} .$ The simplest example is tert-butanol ( 2-methylpropan-2-ol), for which each of R, R', and R" is CH $_{3}$. In these shorthands, $\mathrm{R}, \mathrm{R}^{\prime},$ and $\mathrm{R}^{\prime \prime}$ represent substituents, alkyl or other attached, generally organic groups.
-Discussing option A, we have 1 propanol. So, according to the IUPAC the number of carbon will start from the right one. But, as we can see that there is only one carbon attached to the hydroxyl group. Hence, it is primary alcohol.
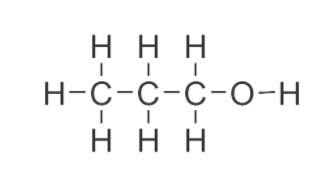
-Discussing option B, we have 2 propanol.The hydroxyl group is attached to a secondary C atom (C atom bearing only one H atom). Thus, it is clear that it is a secondary alcohol.
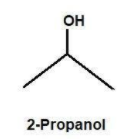
Clearly the answer is B.
Note: Always look out for the secondary carbon atom in the compound which bears the hydroxyl group. That is how, it is a secondary alcohol. A chemical test called Lucas test is also done to distinguish between the primary,secondary and tertiary alcohol. Primary alcohol does not respond to the test. Secondary takes a bit of time and gives the result, while the tertiary alcohols are the fastest in this test.
Complete step-by-step answer:
-In chemistry, alcohol groups are those that in a compound there is at least one hydroxyl group attached. This hydroxyl group is the functional group of the compound.
-The alcohol groups are divided into three types on the basis of the total number of alkyl groups connected to the carbon connected to the hydroxyl group.
-Now, let us discuss the nomenclature of these compounds according to IUPAC.
-The primary alcohols have general formulas $\mathrm{RCH}_{2} \mathrm{OH}$. The simplest primary alcohol is methanol $\left(\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{OH}\right),$ for which $\mathrm{R}=\mathrm{H},$ and the next is ethanol, for which $\mathrm{R}=\mathrm{CH}_{3},$ the methyl group. Secondary alcohols are those of the form $\mathrm{RR}^{\prime} \mathrm{CHOH},$ the simplest of which is 2 -propanol $\left(\mathrm{R}=\mathrm{R}^{\prime}=\mathrm{CH}_{3}\right) .$ For the tertiary alcohols the general form is $\mathrm{RR}^{\prime} \mathrm{R}^{\prime \prime} \mathrm{COH} .$ The simplest example is tert-butanol ( 2-methylpropan-2-ol), for which each of R, R', and R" is CH $_{3}$. In these shorthands, $\mathrm{R}, \mathrm{R}^{\prime},$ and $\mathrm{R}^{\prime \prime}$ represent substituents, alkyl or other attached, generally organic groups.
-Discussing option A, we have 1 propanol. So, according to the IUPAC the number of carbon will start from the right one. But, as we can see that there is only one carbon attached to the hydroxyl group. Hence, it is primary alcohol.

-Discussing option B, we have 2 propanol.The hydroxyl group is attached to a secondary C atom (C atom bearing only one H atom). Thus, it is clear that it is a secondary alcohol.

Clearly the answer is B.
Note: Always look out for the secondary carbon atom in the compound which bears the hydroxyl group. That is how, it is a secondary alcohol. A chemical test called Lucas test is also done to distinguish between the primary,secondary and tertiary alcohol. Primary alcohol does not respond to the test. Secondary takes a bit of time and gives the result, while the tertiary alcohols are the fastest in this test.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE

Explain sex determination in humans with line diag class 12 biology CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE

What is myopia and hypermetropia How are they corrected class 12 physics CBSE




