
An ethereal solution of 4 - nitrochlorobenzene is treated with metallic sodium. The product formed is:
(A) Aminobenzene
(B) $ 4,4 - Dinitrobiphenyl $
(C) $ p - Chloroaniline $
(D) Benzene Diazonium Chloride
Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint :In order to answer this question, you must recall the Fittig Reaction in which two moles of reactant is taken and 1 mole of product is formed, write the complete reaction and then conclude the product formed. Perform the mechanism carefully and correctly. Then you will be able to answer this question.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Step 1. Wurtz-Fittig reaction : The Wurtz-Fittig reaction is the chemical reaction of aryl halides with alkyl halides and sodium metal in the presence of dry ether to give substituted aromatic compounds. There are two approaches to describing the mechanism of the Wurtz–Fittig reaction. The first involves the sodium-mediated formation of both alkyl and aryl radicals. The alkyl and aryl radicals then combine to form a substituted aromatic compound.
Step 2. In this step we will write the Fittig Reaction for $ 4 - nitrochlorobenzene $ :
Treat 2 moles of $ 4 - nitrochlorobenzene $ with two moles of metallic Sodium. And this is the Fittig reaction.
In the intermediate process $ 2\,\,moles $ of $ NaCl $ is removed and leaving behind the product i.e. $ 4,4 - Dinitrobiphenyl $ .
The reaction is as follows:
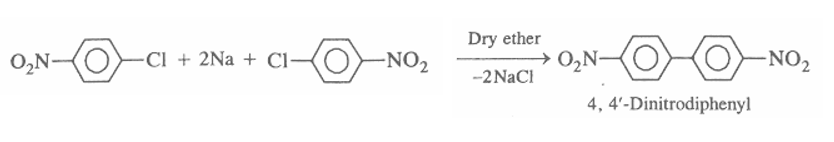
Hence we got the product of the following above Fittig Reaction as $ 4,4 - Dinitrobiphenyl $ .
And therefore, Option B is the correct answer.
Note :
4-Nitrochlorobenzene is the organic compound with the formula $ Cl{C_6}H{ _4}N{O_2} $ . It is a pale yellow solid. 4-Nitrochlorobenzene is a common intermediate in the production of a number of industrially useful compounds, including common antioxidants found in rubber. Another major use of 4-nitrochlorobenzene is its condensation with aniline to produce 4-nitrodiphenylamine. Reductive alkylation of the nitro group affords secondary aryl amines, which are useful antioxidants for rubber.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Step 1. Wurtz-Fittig reaction : The Wurtz-Fittig reaction is the chemical reaction of aryl halides with alkyl halides and sodium metal in the presence of dry ether to give substituted aromatic compounds. There are two approaches to describing the mechanism of the Wurtz–Fittig reaction. The first involves the sodium-mediated formation of both alkyl and aryl radicals. The alkyl and aryl radicals then combine to form a substituted aromatic compound.
Step 2. In this step we will write the Fittig Reaction for $ 4 - nitrochlorobenzene $ :
Treat 2 moles of $ 4 - nitrochlorobenzene $ with two moles of metallic Sodium. And this is the Fittig reaction.
In the intermediate process $ 2\,\,moles $ of $ NaCl $ is removed and leaving behind the product i.e. $ 4,4 - Dinitrobiphenyl $ .
The reaction is as follows:

Hence we got the product of the following above Fittig Reaction as $ 4,4 - Dinitrobiphenyl $ .
And therefore, Option B is the correct answer.
Note :
4-Nitrochlorobenzene is the organic compound with the formula $ Cl{C_6}H{ _4}N{O_2} $ . It is a pale yellow solid. 4-Nitrochlorobenzene is a common intermediate in the production of a number of industrially useful compounds, including common antioxidants found in rubber. Another major use of 4-nitrochlorobenzene is its condensation with aniline to produce 4-nitrodiphenylamine. Reductive alkylation of the nitro group affords secondary aryl amines, which are useful antioxidants for rubber.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




