
An ellipse with foci (-1, 1) and (1, 1) passes through (0, 0), then its equation is ?
A. ${{x}^{2}}+2{{y}^{2}}-8y=0$
B. ${{x}^{2}}+2{{y}^{2}}+4y=0$
C. ${{x}^{2}}+2{{y}^{2}}+8y=0$
D. ${{x}^{2}}+2{{y}^{2}}-4y=0$
Answer
598.5k+ views
Hint: We know that the general equation of ellipse is given as, $\dfrac{x}{{{\left( a \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y}{{{\left( b \right)}^{2}}}=1$. We also know that the distance between foci of the same ellipse is equal to $2ae$. We will use this concept to find the centre of the ellipse and the point a and b respectively. And in the final step, we will put the value of a, b and the centre of ellipse coordinates in the general equation of the ellipse to get the equation of the required ellipse.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given in the question that (-1, 1) and (1, 1) are the foci of the ellipse and the ellipse passes through point (0, 0). We have been asked to find the equation of this ellipse.
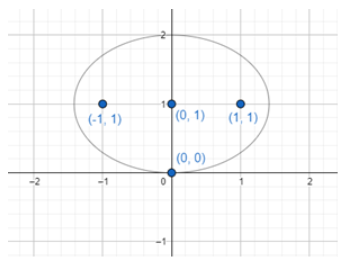
As we can see the centre of the ellipse = mid-point of the line having the coordinates (-1, 1) and (1, 1). So, form the mid-point distance formula, we will get,
Coordinates of the centre of ellipse = $\dfrac{-1+1}{2},\dfrac{1+1}{2}\Rightarrow \left( 0,1 \right)$.
Thus, we get the centre of the ellipse as (0, 1). Now it is given that the ellipse also passes through the point (0, 0) and we know that a and b gives the distance of the major axis and minor axis from the centre of the ellipse. Now if we look at the figure, we get to know that the distance between point (0, 0) and centre of the ellipse (0, 1) gives the length of the minor axis. We know that the distance between any two points, $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is given by $d=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$. Now, here, we have $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)=\left( 0,0 \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=\left( 0,1 \right)$. So, we will get,
$\begin{align}
& d=\sqrt{{{\left( 0-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 0-1 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow d=\sqrt{0+{{1}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow d=\sqrt{1} \\
& \Rightarrow d=1 \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the distance between point (0, 0) and the centre of the ellipse (0, 1) is 1 unit. So, we can say that the length of the minor axis (b) = 1. Now, we know that $ae=b$, where a is the length of the major axis and e is the eccentricity. We also know that $e=\sqrt{1-\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}$. So, putting the values of $e=\sqrt{1-\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}$ in $ae=b$, we get,
$\begin{align}
& a\sqrt{1-\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}=b \\
& \\
\end{align}$
Now, we have the value of b = 1, so we will substitute it in the above. So, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow a\sqrt{\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}-{{1}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{a\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{1}^{2}}}}{a}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-1}=1 \\
\end{align}$
We will now square both the sides and so get,
${{a}^{2}}-1=1$
We will now transpose 1 from the LHS to the RHS, so, we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{a}^{2}}=1+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}=2 \\
& \Rightarrow a=\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we have all the values to find the equation of the ellipse, but the new centre has shifted to the point (0, 1). And we know that the general equation of the ellipse is $\dfrac{x}{{{\left( a \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y}{{{\left( b \right)}^{2}}}=1$. So, the equation of the required ellipse is given by,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{\left( x-0 \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( \sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}+2\left( x \right)\left( 0 \right)}{2}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}+1-2\left( y \right)\left( 1 \right)}{1}=1 \\
\end{align}$
On taking the LCM as 2 in the LHS, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+2{{y}^{2}}+2-4y}{2}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+2{{y}^{2}}+2-4y=2 \\
\end{align}$
We will transpose 2 from the LHS to the RHS, so we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+2{{y}^{2}}-4y=2-2 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+2{{y}^{2}}-4y=0 \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the required equation of the ellipse will be ${{x}^{2}}+2{{y}^{2}}-4y=0$.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note: Many students first find the centre and then take the length of the major axis as twice the length of the distance between the centre of ellipse and foci. As a result, they may directly take the value of a = 2 and b = 2, which is incorrect. We cannot take the length of the major axis and minor axis as twice the length of the distance between the centre and foci of the ellipse.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given in the question that (-1, 1) and (1, 1) are the foci of the ellipse and the ellipse passes through point (0, 0). We have been asked to find the equation of this ellipse.

As we can see the centre of the ellipse = mid-point of the line having the coordinates (-1, 1) and (1, 1). So, form the mid-point distance formula, we will get,
Coordinates of the centre of ellipse = $\dfrac{-1+1}{2},\dfrac{1+1}{2}\Rightarrow \left( 0,1 \right)$.
Thus, we get the centre of the ellipse as (0, 1). Now it is given that the ellipse also passes through the point (0, 0) and we know that a and b gives the distance of the major axis and minor axis from the centre of the ellipse. Now if we look at the figure, we get to know that the distance between point (0, 0) and centre of the ellipse (0, 1) gives the length of the minor axis. We know that the distance between any two points, $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is given by $d=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$. Now, here, we have $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)=\left( 0,0 \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=\left( 0,1 \right)$. So, we will get,
$\begin{align}
& d=\sqrt{{{\left( 0-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 0-1 \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow d=\sqrt{0+{{1}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow d=\sqrt{1} \\
& \Rightarrow d=1 \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the distance between point (0, 0) and the centre of the ellipse (0, 1) is 1 unit. So, we can say that the length of the minor axis (b) = 1. Now, we know that $ae=b$, where a is the length of the major axis and e is the eccentricity. We also know that $e=\sqrt{1-\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}$. So, putting the values of $e=\sqrt{1-\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}$ in $ae=b$, we get,
$\begin{align}
& a\sqrt{1-\dfrac{{{b}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}=b \\
& \\
\end{align}$
Now, we have the value of b = 1, so we will substitute it in the above. So, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow a\sqrt{\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}-{{1}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}}}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{a\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-{{1}^{2}}}}{a}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-1}=1 \\
\end{align}$
We will now square both the sides and so get,
${{a}^{2}}-1=1$
We will now transpose 1 from the LHS to the RHS, so, we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{a}^{2}}=1+1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}=2 \\
& \Rightarrow a=\sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we have all the values to find the equation of the ellipse, but the new centre has shifted to the point (0, 1). And we know that the general equation of the ellipse is $\dfrac{x}{{{\left( a \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{y}{{{\left( b \right)}^{2}}}=1$. So, the equation of the required ellipse is given by,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{\left( x-0 \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( \sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}{{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}+2\left( x \right)\left( 0 \right)}{2}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}+1-2\left( y \right)\left( 1 \right)}{1}=1 \\
\end{align}$
On taking the LCM as 2 in the LHS, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}+2{{y}^{2}}+2-4y}{2}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+2{{y}^{2}}+2-4y=2 \\
\end{align}$
We will transpose 2 from the LHS to the RHS, so we get,
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+2{{y}^{2}}-4y=2-2 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+2{{y}^{2}}-4y=0 \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the required equation of the ellipse will be ${{x}^{2}}+2{{y}^{2}}-4y=0$.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D.
Note: Many students first find the centre and then take the length of the major axis as twice the length of the distance between the centre of ellipse and foci. As a result, they may directly take the value of a = 2 and b = 2, which is incorrect. We cannot take the length of the major axis and minor axis as twice the length of the distance between the centre and foci of the ellipse.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




