
An electron enters into a space between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor at an angle of $\alpha $ with the plates and leaves at an angle of $\beta $ to the plates. The ratio of its K.E. while leaving to enter the capacitor will be:
A) ${\left( {\dfrac{{\cos \alpha }}{{\cos \beta }}} \right)^2}$
B) ${\left( {\dfrac{{\cos \beta }}{{\cos \alpha }}} \right)^2}$
C) ${\left( {\dfrac{{\sin \alpha }}{{\sin \beta }}} \right)^2}$
D) ${\left( {\dfrac{{\sin \beta }}{{\sin \alpha }}} \right)^2}$
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: We know a charge particle enters in an electric field then an electrostatic force acts on it if the charge particle is electron means negative charge then the force acted on this is opposite to direction of electric field.
And in which direction a force acts on a particle in that direction velocity of particle has changed and other components of velocity in other direction will not be changed.
Complete step by step answer:
To understand the situation we draw a diagram which is given below In this diagram there are two plates of a capacitor one is positively charged and other is negatively charged. Electron enters with an angle $\alpha $ with a negative plate. When entering the inside capacitor a force acts on the electron in the opposite direction of the electric field which is positive plate to negative plate of capacitor.
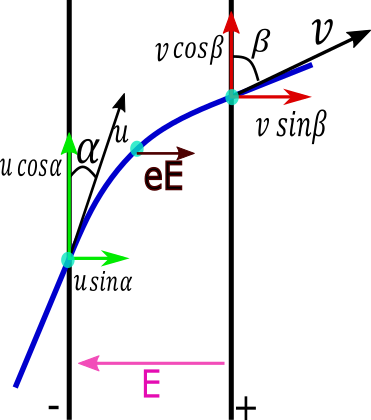
Force on the electron due to the electric field E is $eE$ to the positive plate.
Due to this force the horizontal component of initial velocity will change but the vertical component of velocity will not change.
So we can say that the vertical component of initial and final velocities should be the same.
We assume the initial velocity of electron is $u$ with angle $\alpha $ as shown in above figure
And the final velocity of the electron will be $v$ with angle $\beta $ as shown in figure.
horizontal component of initial velocity=horizontal component of final velocity
$ \Rightarrow u\cos \alpha = v\cos \beta $
Rearranging
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{u}{v} = \dfrac{{\cos \beta }}{{\cos \alpha }}$ .......... (1)
So we get the ratio of initial and final velocities
Now formula for K.E is $K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Initial K.E $K.{E_{in}} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2}$
Final K.E $K.{E_f} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Divide initial and final K.E
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{K.{E_{in}}}}{{K.{E_f}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2}}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{K.{E_{in}}}}{{K.{E_f}}} = \dfrac{{{u^2}}}{{{v^2}}}$
It can be written as
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{K.{E_f}}}{{K.{E_{in}}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{v}{u}} \right)^2}$
Now put the value from equation (1)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{K.{E_f}}}{{K.{E_{in}}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{\cos \alpha }}{{\cos \beta }}} \right)^2}$
$\therefore $ The ratio of its K.E. while leaving to enter the capacitor will be ${\left( {\dfrac{{\cos \alpha }}{{\cos \beta }}} \right)^2}$
Hence the option A is correct.
Note:
Inside a capacitor there is an electric field formed due to positive and negative charged plates and electrons feel an electrostatic force on it opposite to it.
Why do we take vertical component constant because the electrostatic force which acts on electrons in horizontal direction in this question so we know by Newton’s law acceleration produced in the same direction of force due to this only horizontal component increases and vertical component remains same.
And in which direction a force acts on a particle in that direction velocity of particle has changed and other components of velocity in other direction will not be changed.
Complete step by step answer:
To understand the situation we draw a diagram which is given below In this diagram there are two plates of a capacitor one is positively charged and other is negatively charged. Electron enters with an angle $\alpha $ with a negative plate. When entering the inside capacitor a force acts on the electron in the opposite direction of the electric field which is positive plate to negative plate of capacitor.

Force on the electron due to the electric field E is $eE$ to the positive plate.
Due to this force the horizontal component of initial velocity will change but the vertical component of velocity will not change.
So we can say that the vertical component of initial and final velocities should be the same.
We assume the initial velocity of electron is $u$ with angle $\alpha $ as shown in above figure
And the final velocity of the electron will be $v$ with angle $\beta $ as shown in figure.
horizontal component of initial velocity=horizontal component of final velocity
$ \Rightarrow u\cos \alpha = v\cos \beta $
Rearranging
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{u}{v} = \dfrac{{\cos \beta }}{{\cos \alpha }}$ .......... (1)
So we get the ratio of initial and final velocities
Now formula for K.E is $K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Initial K.E $K.{E_{in}} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2}$
Final K.E $K.{E_f} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Divide initial and final K.E
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{K.{E_{in}}}}{{K.{E_f}}} = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2}}}{{\dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{K.{E_{in}}}}{{K.{E_f}}} = \dfrac{{{u^2}}}{{{v^2}}}$
It can be written as
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{K.{E_f}}}{{K.{E_{in}}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{v}{u}} \right)^2}$
Now put the value from equation (1)
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{K.{E_f}}}{{K.{E_{in}}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{\cos \alpha }}{{\cos \beta }}} \right)^2}$
$\therefore $ The ratio of its K.E. while leaving to enter the capacitor will be ${\left( {\dfrac{{\cos \alpha }}{{\cos \beta }}} \right)^2}$
Hence the option A is correct.
Note:
Inside a capacitor there is an electric field formed due to positive and negative charged plates and electrons feel an electrostatic force on it opposite to it.
Why do we take vertical component constant because the electrostatic force which acts on electrons in horizontal direction in this question so we know by Newton’s law acceleration produced in the same direction of force due to this only horizontal component increases and vertical component remains same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




