
An astronomical telescope has an angular magnification of magnitude $ 5 $ for distant objects. The separation between the object and an eyepiece is $ 36cm $ and the final image is formed at infinity. The focal length $ f_O $ of the objective and $ f_e $ of the eyepiece are
$ \left( A \right)f_O = 45cm\,\,and\,f_e = - 9cm $
$ \left( B \right)f_O = 50cm\,\,and\,f_e = - 10cm $
$ \left( C \right)f_O = 7.2cm\,\,and\,f_e = - 5cm $
$ \left( D \right)f_O = 30cm\,\,and\,f_e = - 6cm $
Answer
493.8k+ views
Hint: First draw a ray diagram of an astronomical telescope so as to analyze the problem briefly and it will be easy to use the sign conversion while calculating the solution. We know the angular magnification now applying this angular magnification formula we can find the relation between the focal length of the objective and eyepiece lens. Now putting this relation in the separation formula of the astronomical telescope we can find the respective values.
Complete step by step solution:
As per the problem we know there is an astronomical telescope that has an angular magnification of magnitude $ 5 $ for distant objects. The separation between the object and an eyepiece is $ 36cm $ and the final image is formed at infinity.
We need to calculate the focal length $ f_O $ of the objective and $ f_e $ of the eyepiece lens.
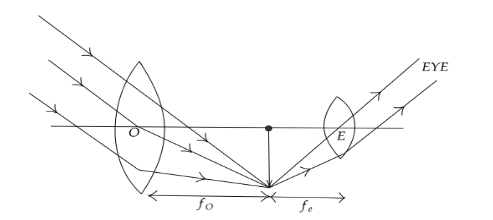
We have,
Angular magnification equals $ 5 $ .
We know the angular magnification of an astronomical telescope is represented as,
$ m = \dfrac{{f_O}}{{f_e}} $
Putting the given value we will get,
$ 5 = \dfrac{{f_O}}{{f_e}} $
Rearranging the above equation we will get,
$ 5f_e = f_O $
Now in the given problem,
The separation between the object and an eyepiece is $ 36cm $ and the final image is formed at infinity.
Hence,
$ L = f_O + f_e $
Where,
L is the separation.
Now putting the known vale we will get,
$ 36cm = 5f_e + f_e $
$ \Rightarrow 36cm = 6f_e \Rightarrow f_e = 6cm $
Now with relation between focal length of objective and eyepiece we will get,
$ 5f_e = f_O $
$ \Rightarrow 5 \times 6cm = f_O = 30cm $
Therefore the correction option is $ \left( D \right) $ .
Note:
Now here our eyepiece focal length is taken as negative as it lies on the left side of the eyepiece length. And by default we have taken the right side as positive. Remember that an astronomical telescope always forms virtual, inverted and magnified images and the focal length of this telescope is small.
Complete step by step solution:
As per the problem we know there is an astronomical telescope that has an angular magnification of magnitude $ 5 $ for distant objects. The separation between the object and an eyepiece is $ 36cm $ and the final image is formed at infinity.
We need to calculate the focal length $ f_O $ of the objective and $ f_e $ of the eyepiece lens.

We have,
Angular magnification equals $ 5 $ .
We know the angular magnification of an astronomical telescope is represented as,
$ m = \dfrac{{f_O}}{{f_e}} $
Putting the given value we will get,
$ 5 = \dfrac{{f_O}}{{f_e}} $
Rearranging the above equation we will get,
$ 5f_e = f_O $
Now in the given problem,
The separation between the object and an eyepiece is $ 36cm $ and the final image is formed at infinity.
Hence,
$ L = f_O + f_e $
Where,
L is the separation.
Now putting the known vale we will get,
$ 36cm = 5f_e + f_e $
$ \Rightarrow 36cm = 6f_e \Rightarrow f_e = 6cm $
Now with relation between focal length of objective and eyepiece we will get,
$ 5f_e = f_O $
$ \Rightarrow 5 \times 6cm = f_O = 30cm $
Therefore the correction option is $ \left( D \right) $ .
Note:
Now here our eyepiece focal length is taken as negative as it lies on the left side of the eyepiece length. And by default we have taken the right side as positive. Remember that an astronomical telescope always forms virtual, inverted and magnified images and the focal length of this telescope is small.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




