
An astronomical telescope arranged for normal adjustment has a magnification of $6$. If the length of the telescope is $35cm$, then the focal lengths of objective and eyepiece respectively are:
$A)\text{ }30cm,5cm$
$B)\text{ }5cm,30cm$
$C)\text{ 4}0cm,5cm$
$D)\text{ }30cm,6cm$
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: This problem can be solved by using the formula for the magnification of the telescope and its total length as a function of its objective and eyepiece focal length. This will give two equations which can be solved for the two variables, that is the focal lengths of the eyepiece and the objective.
Formula used:
$m=\dfrac{{{f}_{o}}}{{{f}_{e}}}$
$L={{f}_{o}}+{{f}_{e}}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
The magnification of a telescope is given by the ratio of the focal length of the objective to that of the eyepiece, while the total length of the telescope is considered to be the distance between the objective and the eyepiece. The telescope is designed in such a way that the foci of the objective and eyepiece overlap and hence, the total length is nothing but the sum of the focal lengths of the objective and the eyepiece.
A diagram will make it clearer.
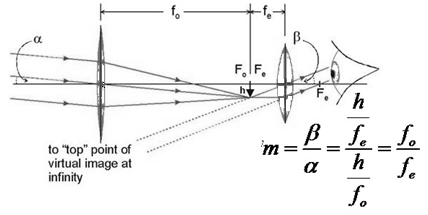
As is clear from the figure, the length between the objective and the eyepiece is the sum of their focal lengths.
Therefore,
The magnification $m$ of a telescope of objective focal length ${{f}_{o}}$ and eyepiece focal length ${{f}_{e}}$ is given by
$m=\dfrac{{{f}_{o}}}{{{f}_{e}}}$ -(1)
Also, the total length $L$ of the telescope of objective focal length ${{f}_{o}}$ and eyepiece focal length ${{f}_{e}}$ is given by
$L={{f}_{o}}+{{f}_{e}}$ -(2)
Therefore, let us analyze the question.
Let the objective and eyepiece focal lengths of the telescope be ${{f}_{o}}$ and ${{f}_{e}}$ respectively.
The magnification of the telescope is $m=6$.
The length of the telescope is $L=35cm$.
Therefore, using (1), we get,
$6=\dfrac{{{f}_{o}}}{{{f}_{e}}}$
$\therefore {{f}_{o}}=6{{f}_{e}}$ --(3)
Using (2), we get,
$35={{f}_{o}}+{{f}_{e}}$
Using (3) we get,
$35=6{{f}_{e}}+{{f}_{e}}=7{{f}_{e}}$
$\therefore {{f}_{e}}=\dfrac{35}{7}=5cm$ --(4)
Putting (4) in (3), we get,
${{f}_{o}}=6\times 5cm=30cm$
Therefore the objective and eyepiece focal lengths of the telescope are $30cm$ and $5cm$ respectively.
Therefore, the correct option is $A)\text{ }30cm,5cm$.
Note: This problem could also have been solved quickly by using the method of elimination of options. From the magnification given, it is clear that the focal length of the objective must be six times the focal length of the eyepiece. Upon analyzing the questions we find that only in option $A)\text{ }30cm,5cm$, the focal lengths satisfy this condition and hence, this must be the answer. However, one must follow these methods only in competitive examinations. If the question requires a written explanation and calculations to be shown, it is better to proceed as done in the complete step by step answer.
Formula used:
$m=\dfrac{{{f}_{o}}}{{{f}_{e}}}$
$L={{f}_{o}}+{{f}_{e}}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
The magnification of a telescope is given by the ratio of the focal length of the objective to that of the eyepiece, while the total length of the telescope is considered to be the distance between the objective and the eyepiece. The telescope is designed in such a way that the foci of the objective and eyepiece overlap and hence, the total length is nothing but the sum of the focal lengths of the objective and the eyepiece.
A diagram will make it clearer.

As is clear from the figure, the length between the objective and the eyepiece is the sum of their focal lengths.
Therefore,
The magnification $m$ of a telescope of objective focal length ${{f}_{o}}$ and eyepiece focal length ${{f}_{e}}$ is given by
$m=\dfrac{{{f}_{o}}}{{{f}_{e}}}$ -(1)
Also, the total length $L$ of the telescope of objective focal length ${{f}_{o}}$ and eyepiece focal length ${{f}_{e}}$ is given by
$L={{f}_{o}}+{{f}_{e}}$ -(2)
Therefore, let us analyze the question.
Let the objective and eyepiece focal lengths of the telescope be ${{f}_{o}}$ and ${{f}_{e}}$ respectively.
The magnification of the telescope is $m=6$.
The length of the telescope is $L=35cm$.
Therefore, using (1), we get,
$6=\dfrac{{{f}_{o}}}{{{f}_{e}}}$
$\therefore {{f}_{o}}=6{{f}_{e}}$ --(3)
Using (2), we get,
$35={{f}_{o}}+{{f}_{e}}$
Using (3) we get,
$35=6{{f}_{e}}+{{f}_{e}}=7{{f}_{e}}$
$\therefore {{f}_{e}}=\dfrac{35}{7}=5cm$ --(4)
Putting (4) in (3), we get,
${{f}_{o}}=6\times 5cm=30cm$
Therefore the objective and eyepiece focal lengths of the telescope are $30cm$ and $5cm$ respectively.
Therefore, the correct option is $A)\text{ }30cm,5cm$.
Note: This problem could also have been solved quickly by using the method of elimination of options. From the magnification given, it is clear that the focal length of the objective must be six times the focal length of the eyepiece. Upon analyzing the questions we find that only in option $A)\text{ }30cm,5cm$, the focal lengths satisfy this condition and hence, this must be the answer. However, one must follow these methods only in competitive examinations. If the question requires a written explanation and calculations to be shown, it is better to proceed as done in the complete step by step answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




